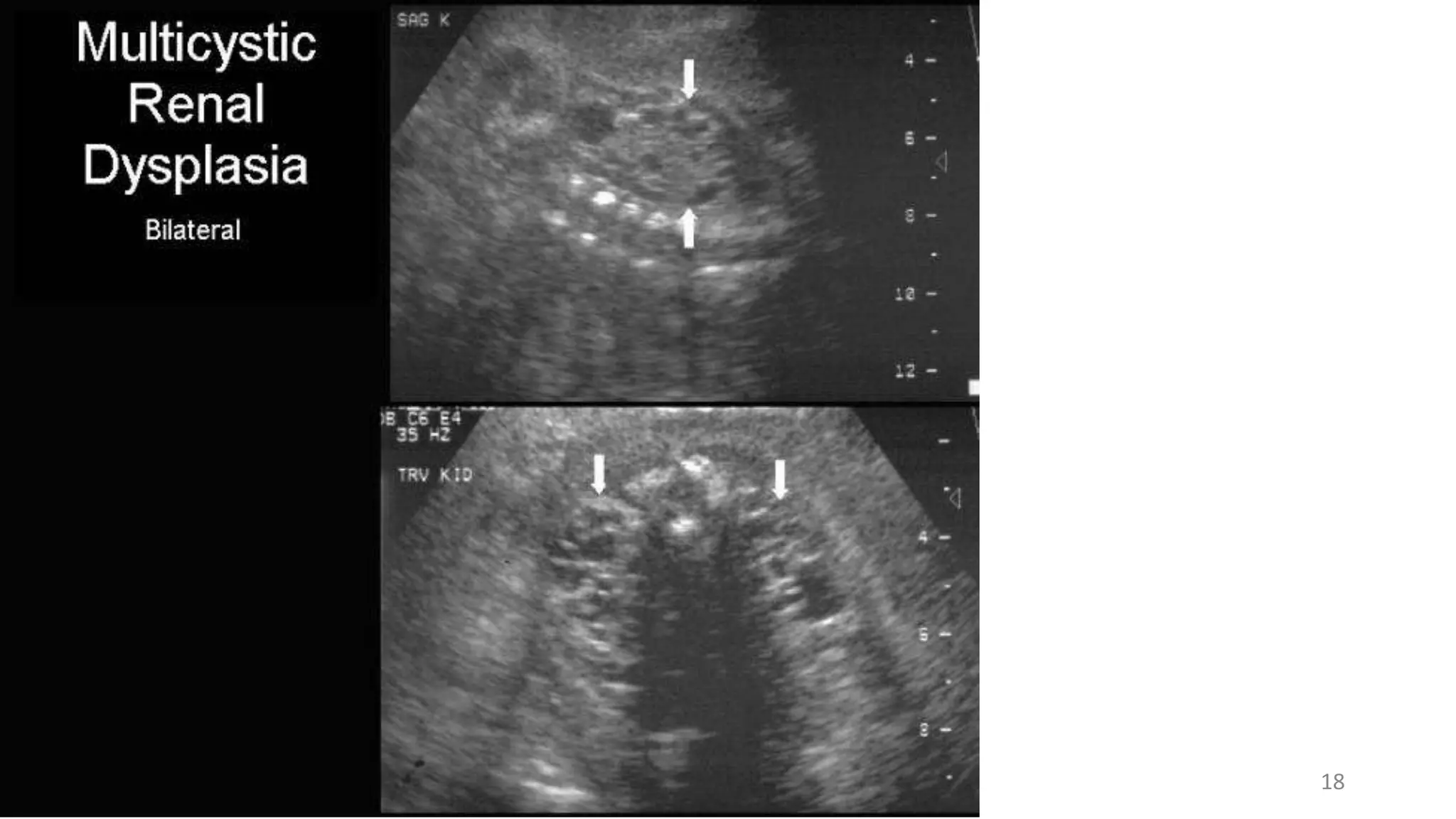
Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney (MDCK) is a non-heritable developmental disorder where the kidney is replaced by non-functioning cysts. It is usually unilateral and asymptomatic, though it can present as an abdominal mass. Imaging such as ultrasound is used for diagnosis and shows cysts of varying sizes replacing normal renal architecture with no communication between cysts. Treatment involves follow up monitoring, with nephrectomy in some cases of hypertension or massive enlargement. Differential diagnosis includes other cystic kidney diseases and tumors.