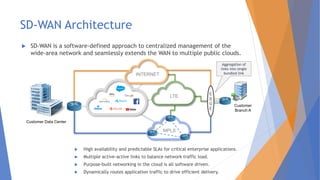
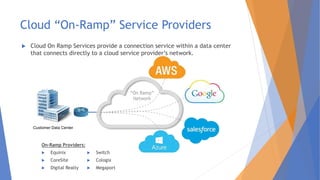
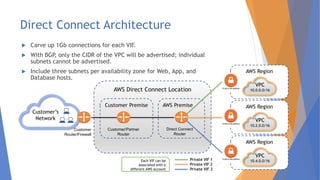
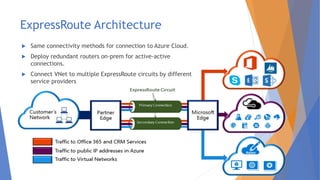
This document discusses the networking complexities that arise in hybrid and multi-cloud environments. It notes that routing traffic securely between disparate cloud platforms is challenging, and that managing multiple providers each with their own management and security methods complicates operations. The document then explores specific complexities around modernization, monitoring, suppliers and connectivity. It proposes several potential methods for simplifying this complexity, such as SD-WAN, cloud on-ramp service providers, carrier-neutral colocation, AWS Direct Connect and Azure ExpressRoute.