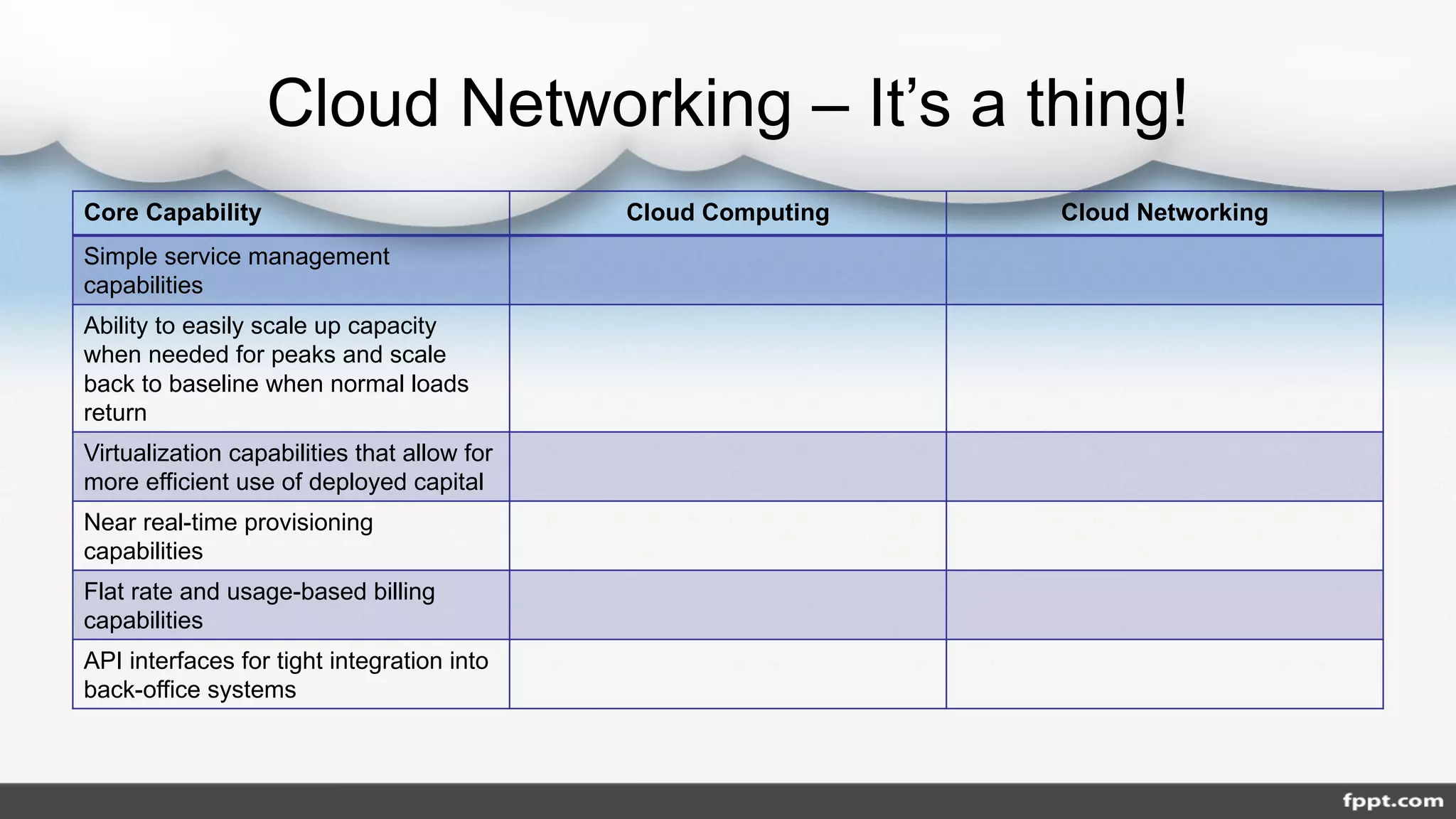
Will Charnock discussed the evolution of cloud networking from traditional infrastructure services. Cloud computing changed customer expectations by offering on-demand computing through simple interfaces. This new model requires networking services to also provide on-demand, virtualized capacity and near real-time provisioning through APIs and portals. Cloud networking services allow customers to dynamically scale bandwidth and interconnectivity based on usage and only pay for resources consumed.