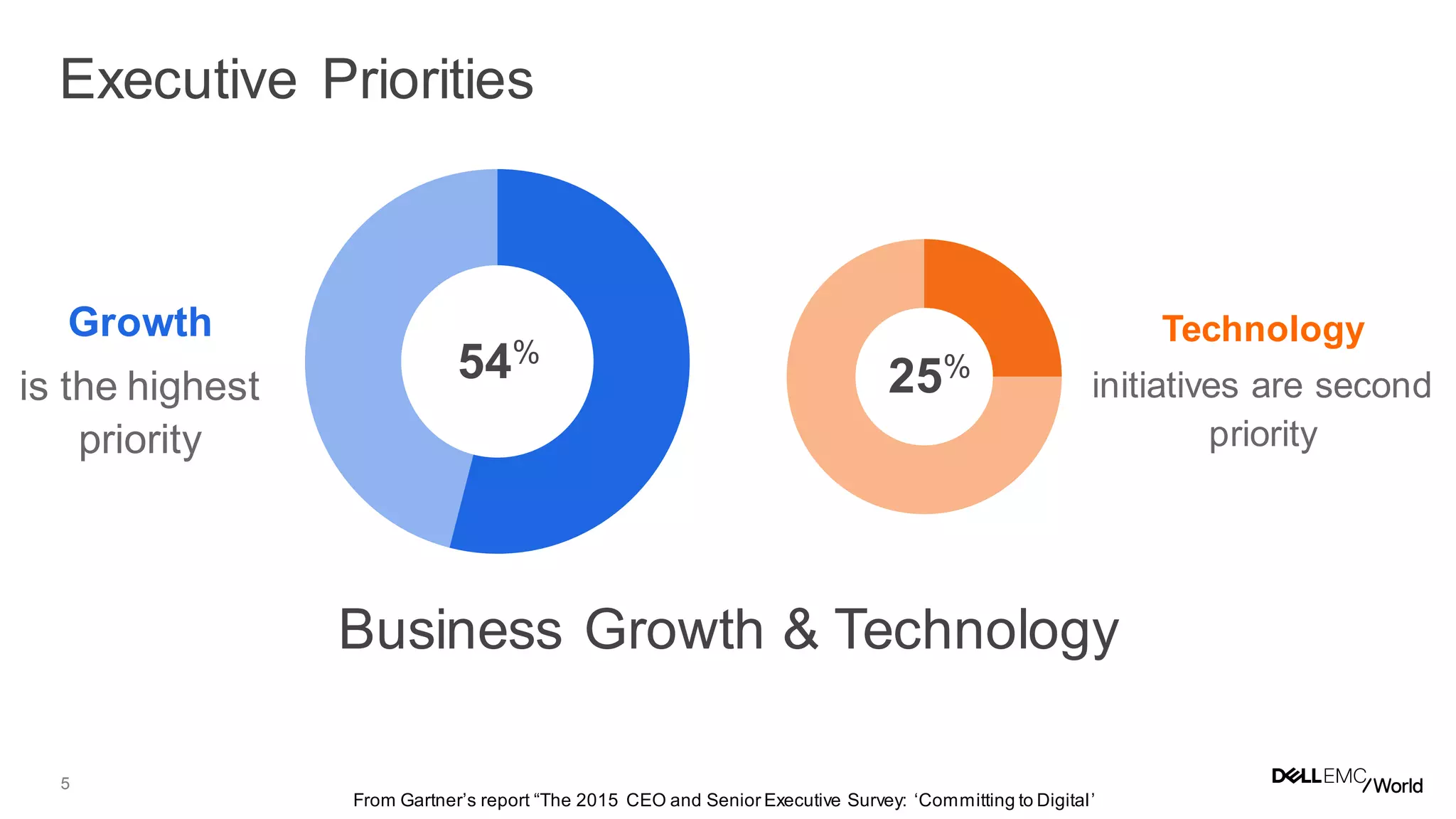
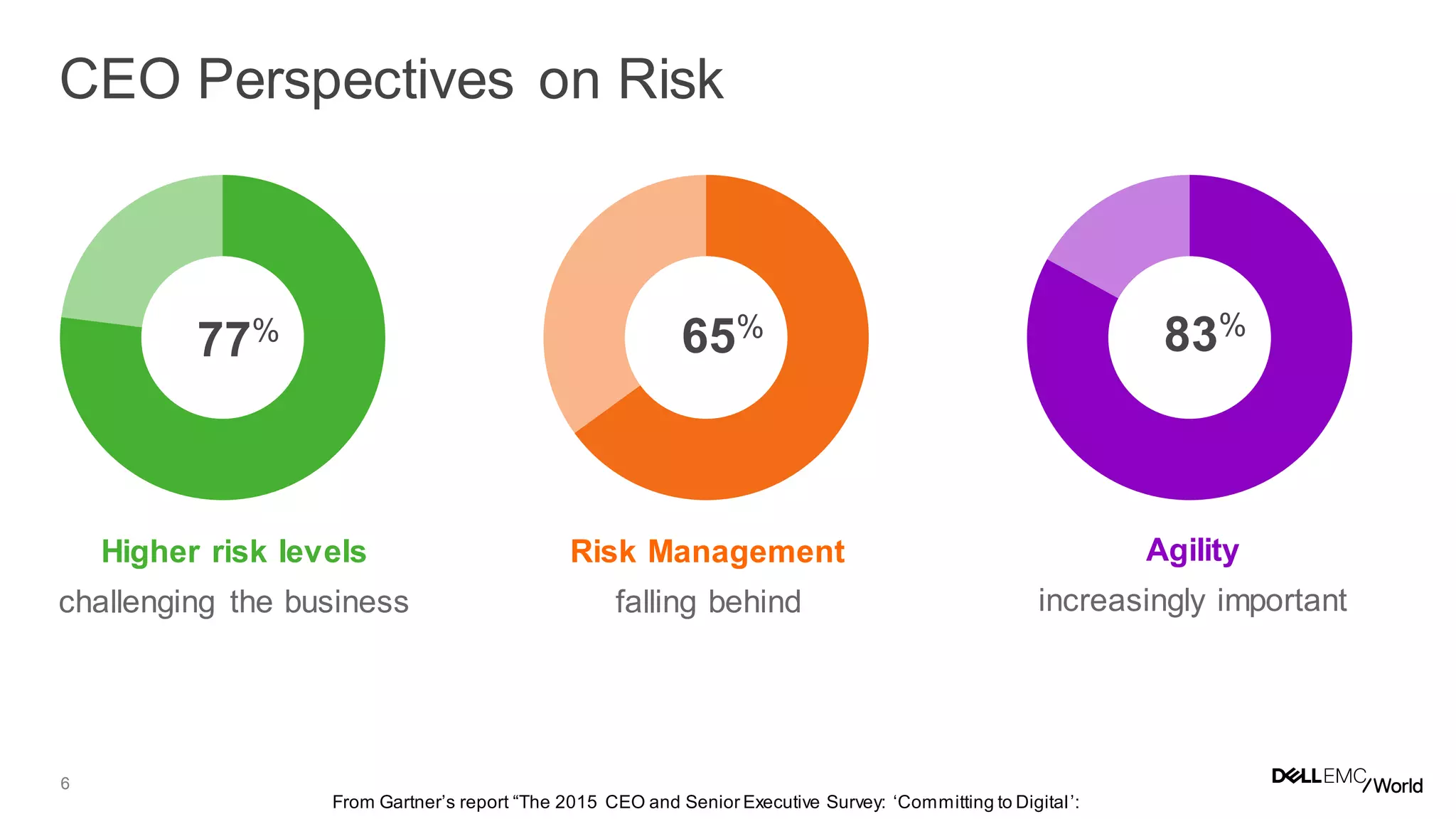
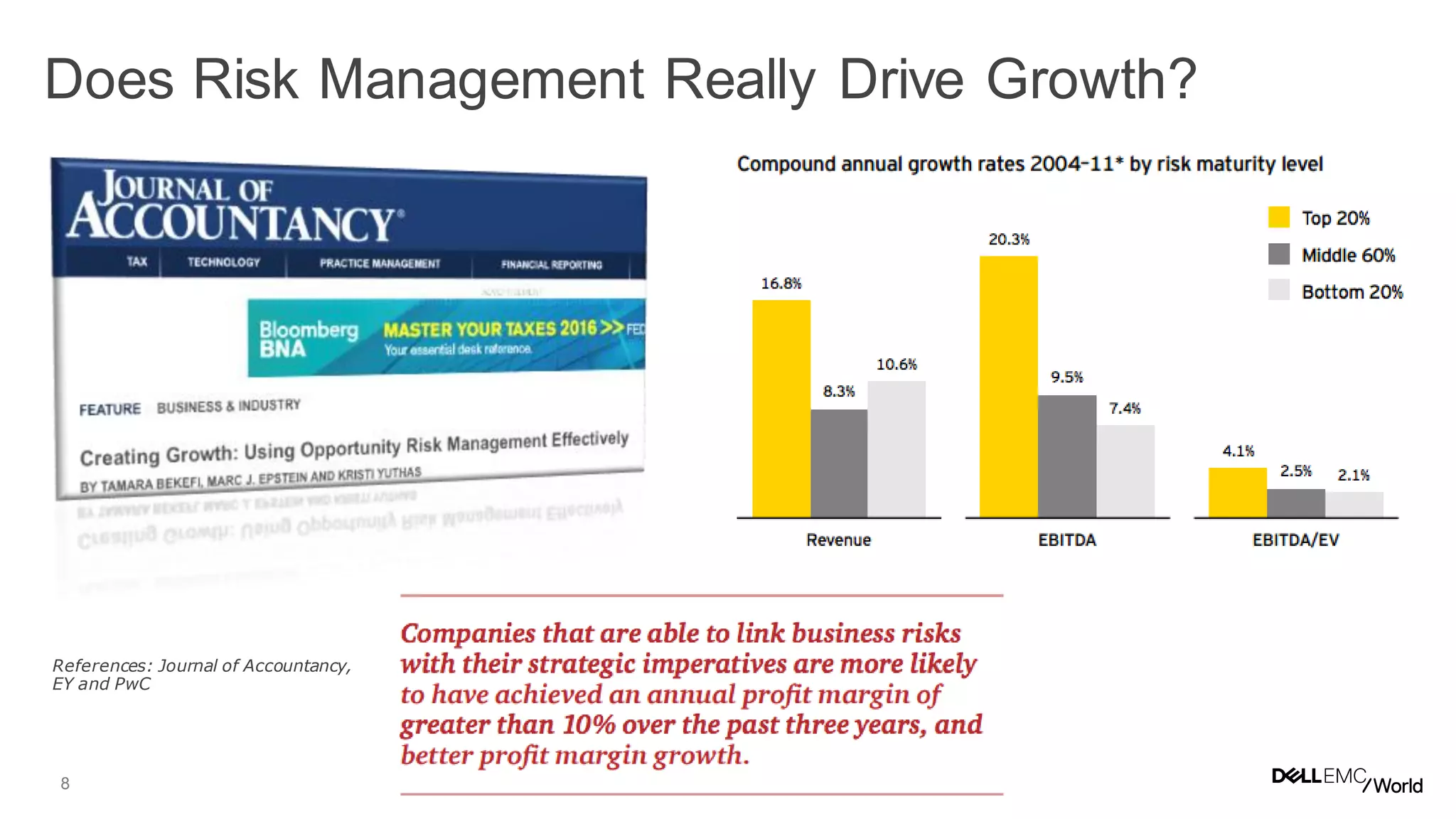
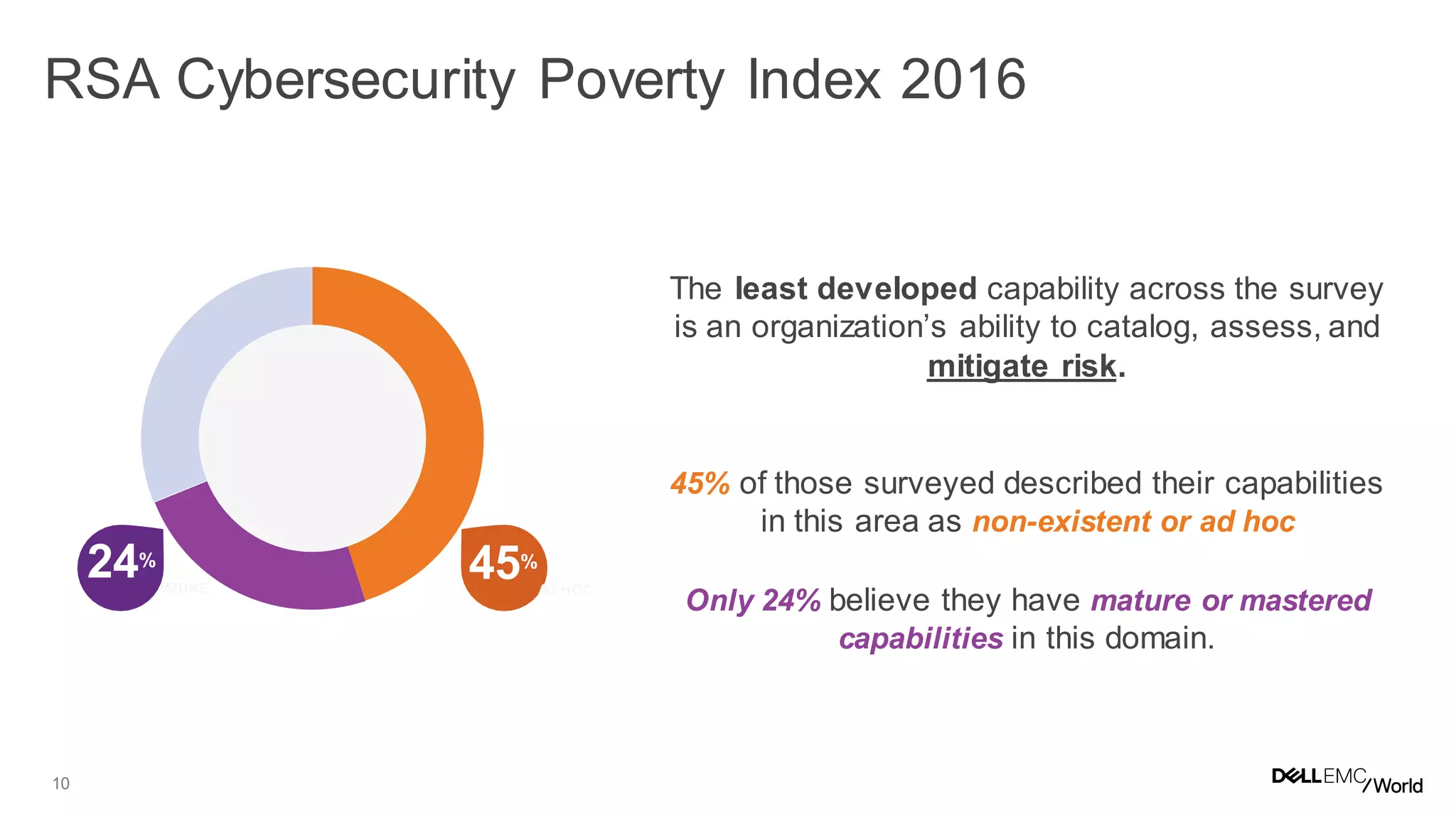
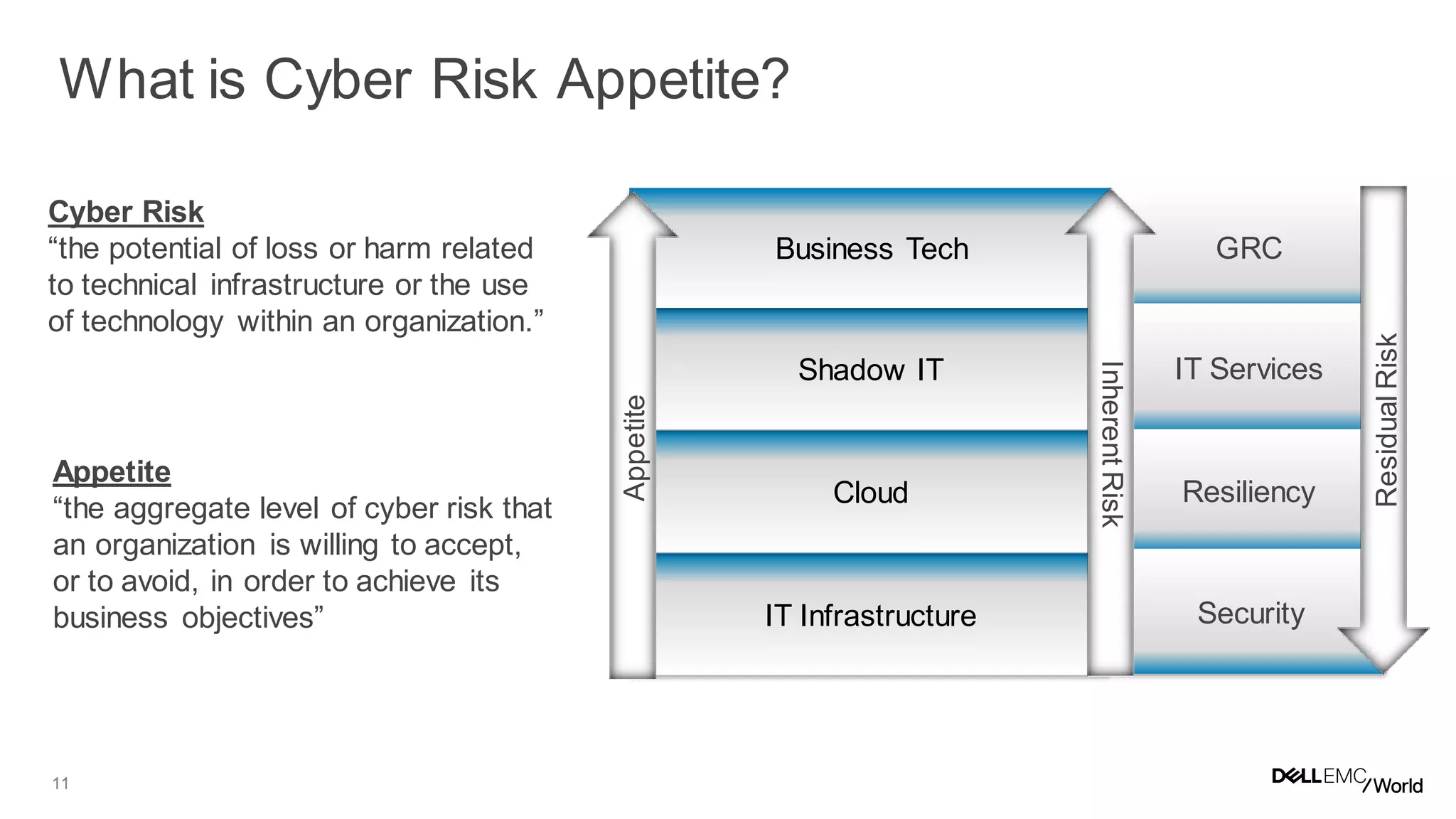
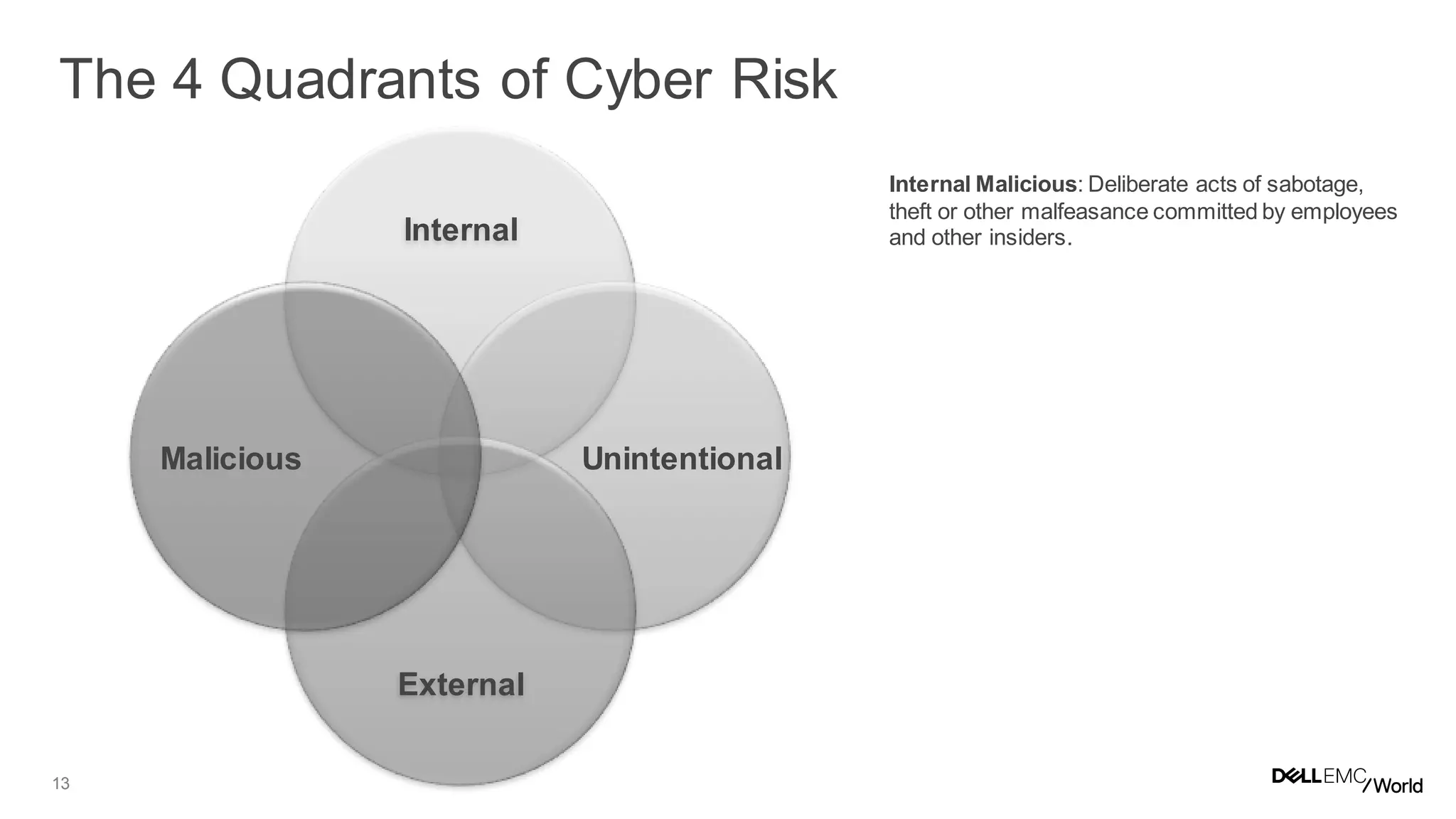
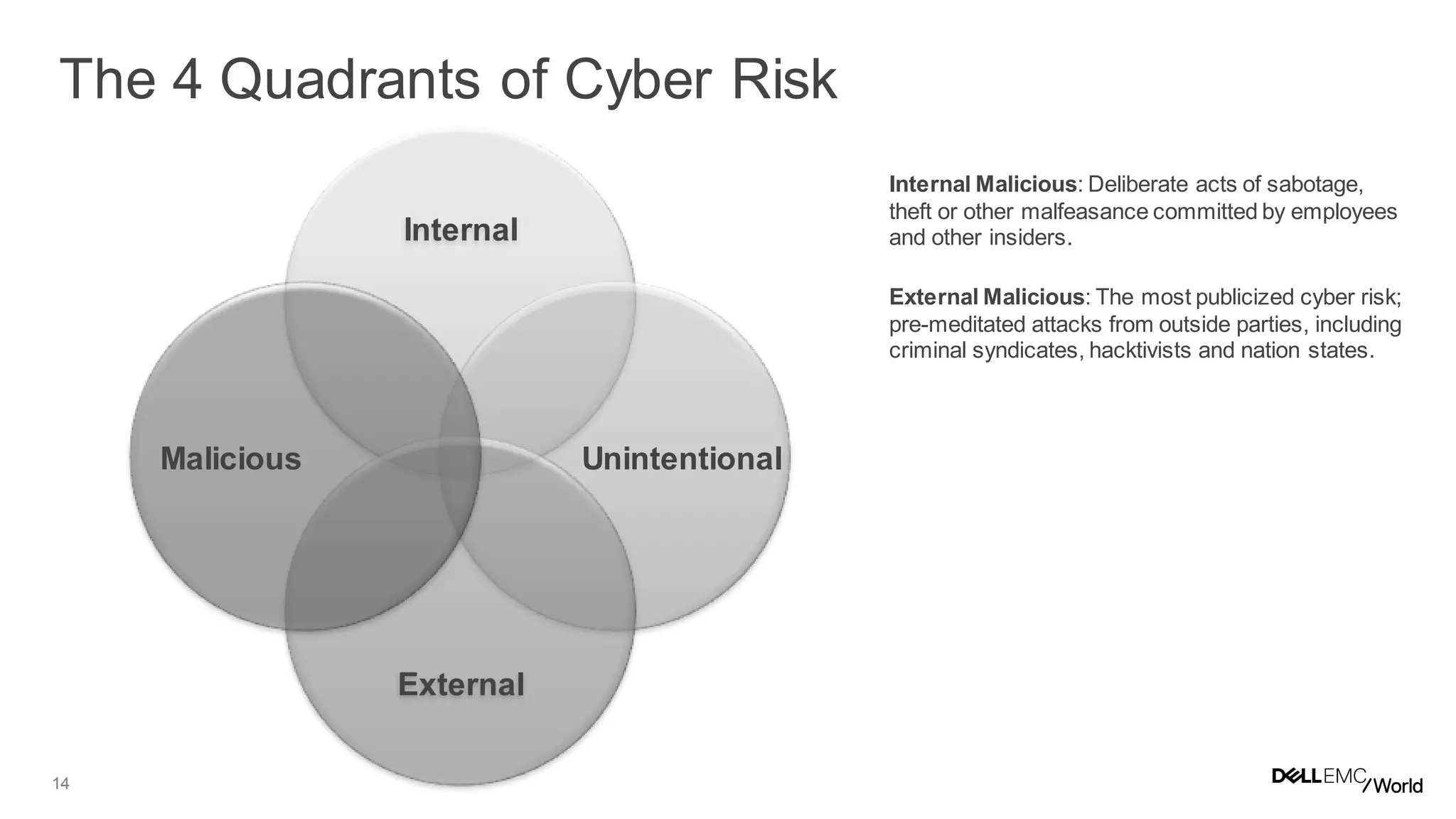
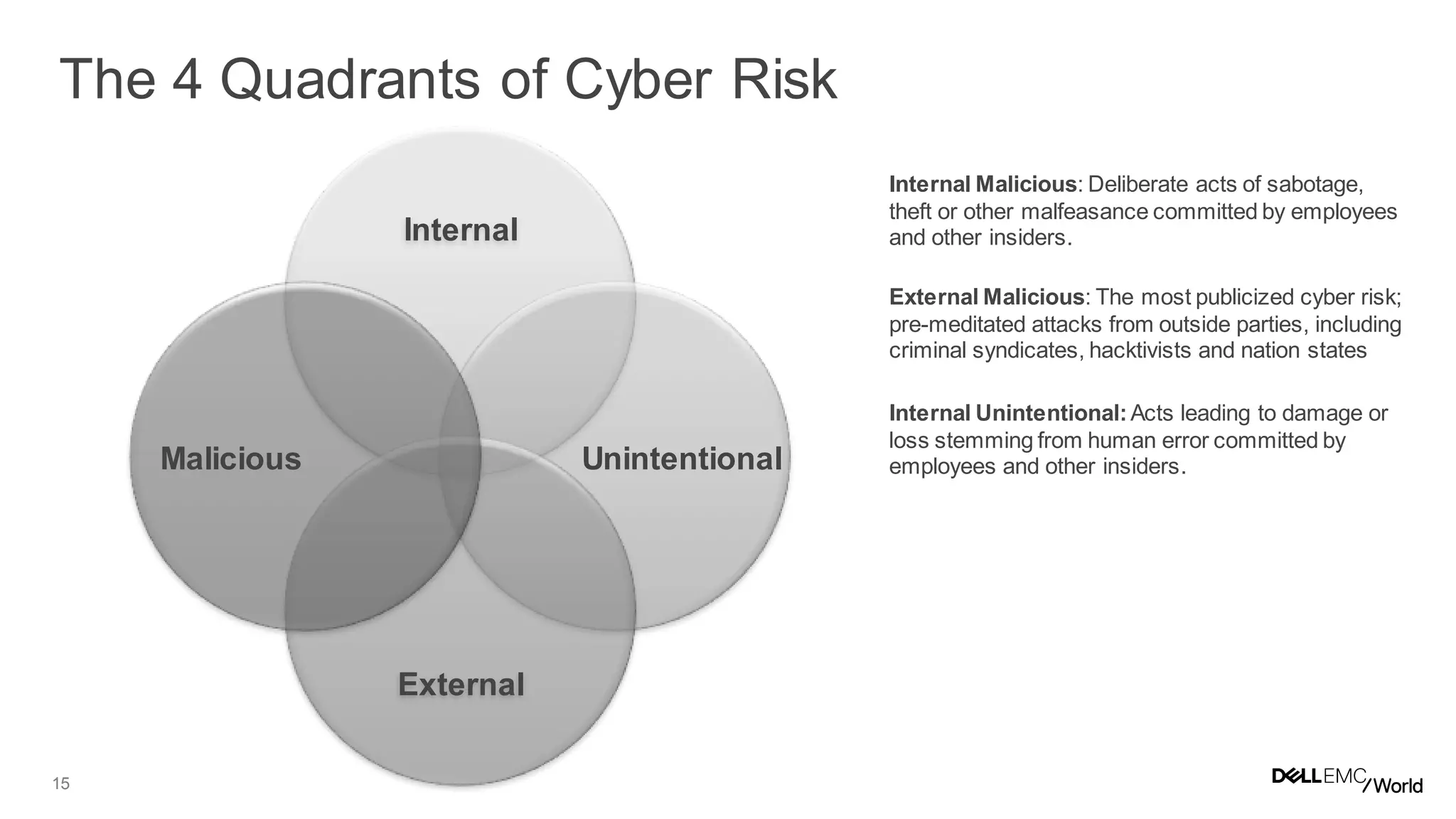
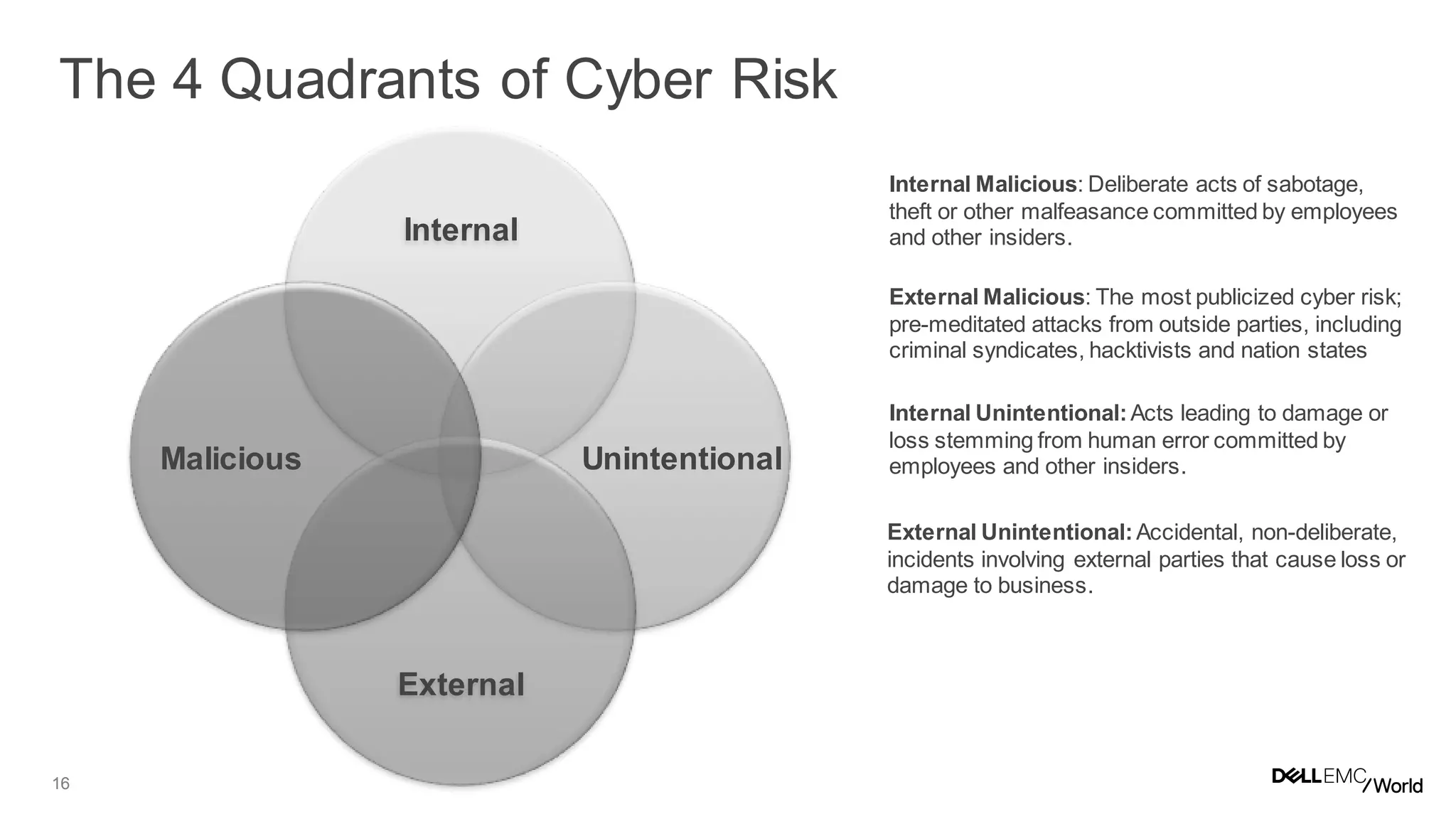
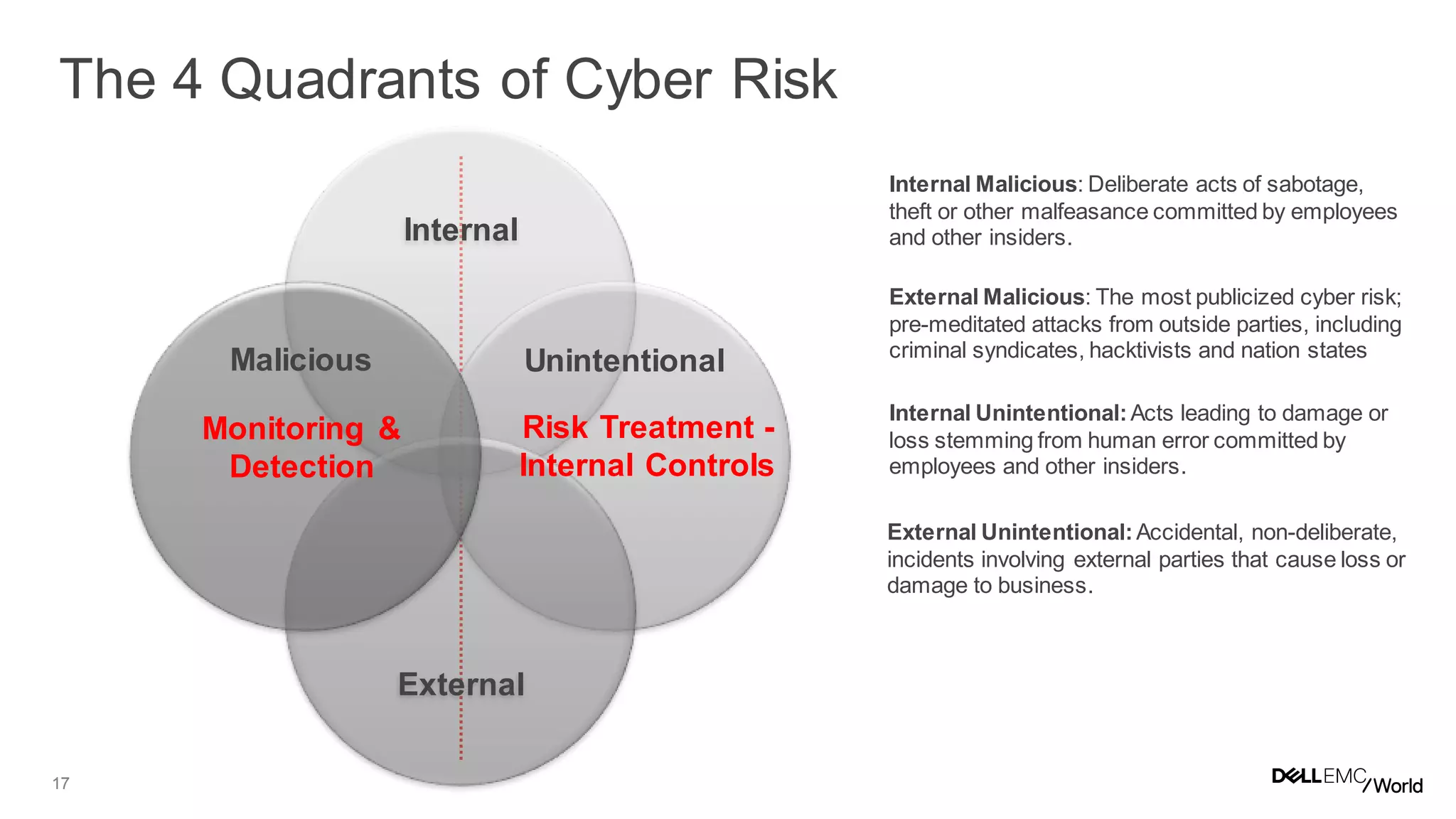
The document discusses the challenges organizations face in managing increasing complexity and volume of cyber risks within the context of integrated business and digital strategies. It highlights the inadequacies of current risk management techniques in addressing new risks created by digital business models and emphasizes the need for organizations to adopt a holistic approach to risk management. Additionally, it outlines the importance of aligning technology and business strategies to improve risk oversight and resilience.