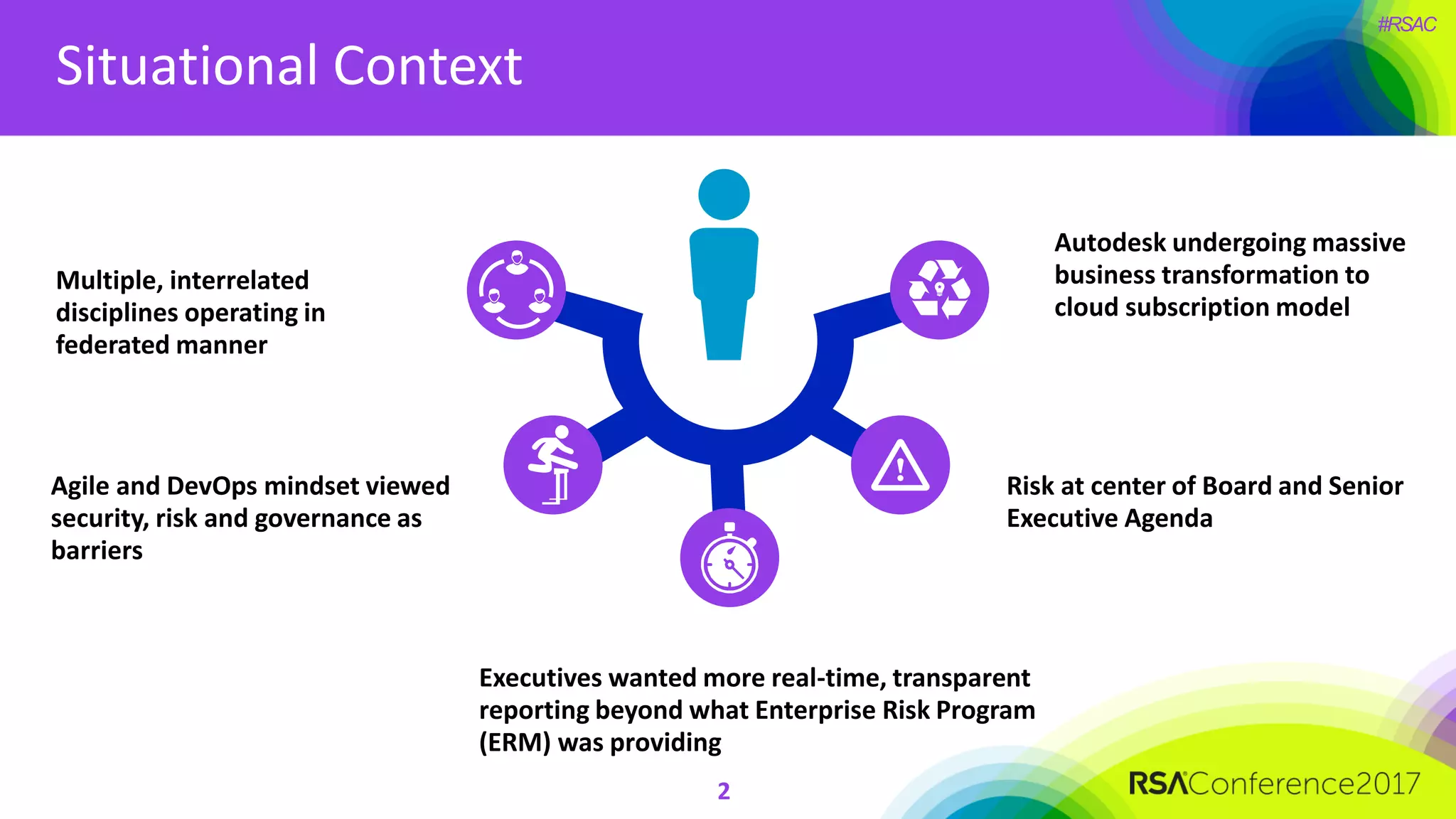
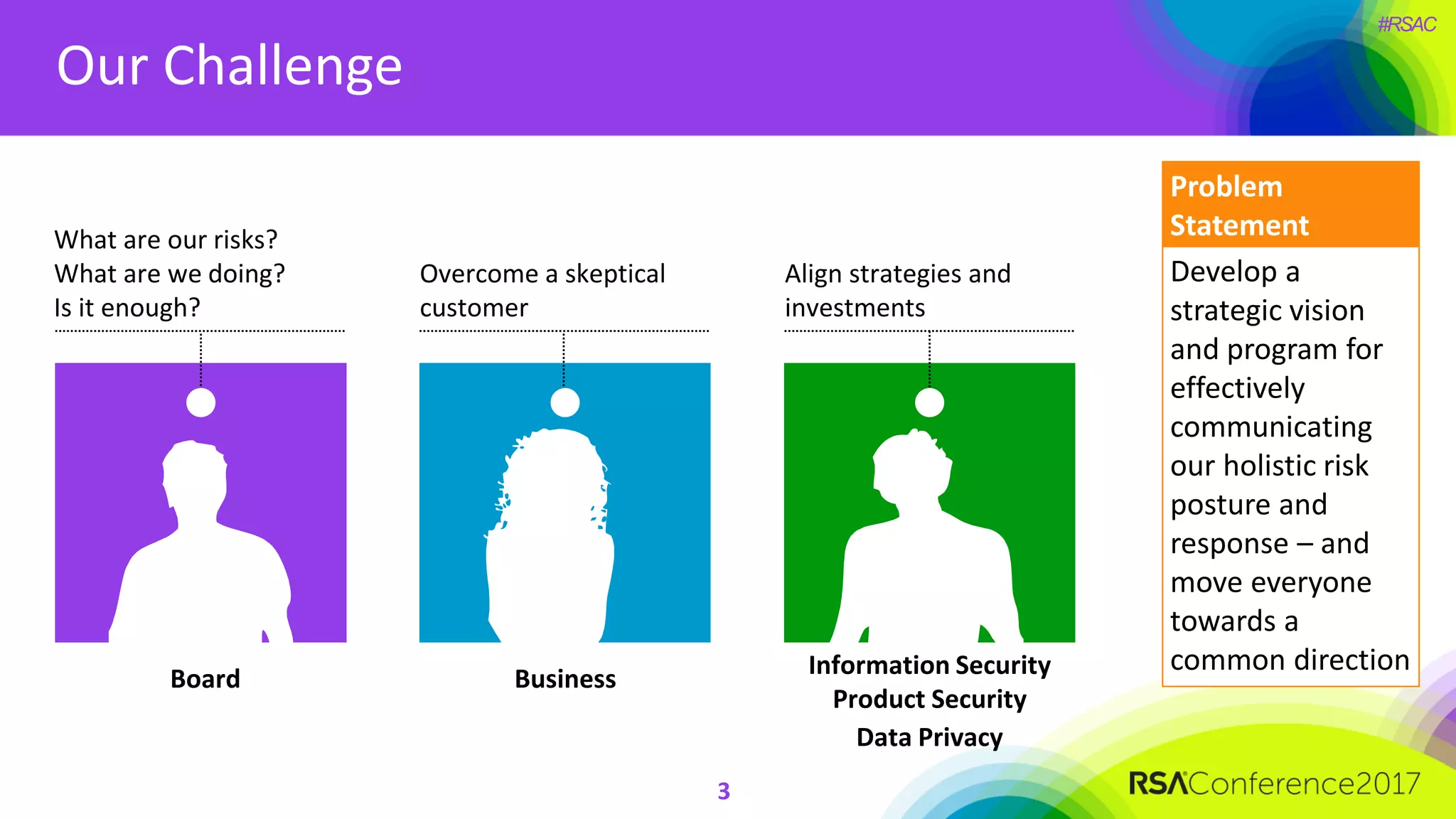
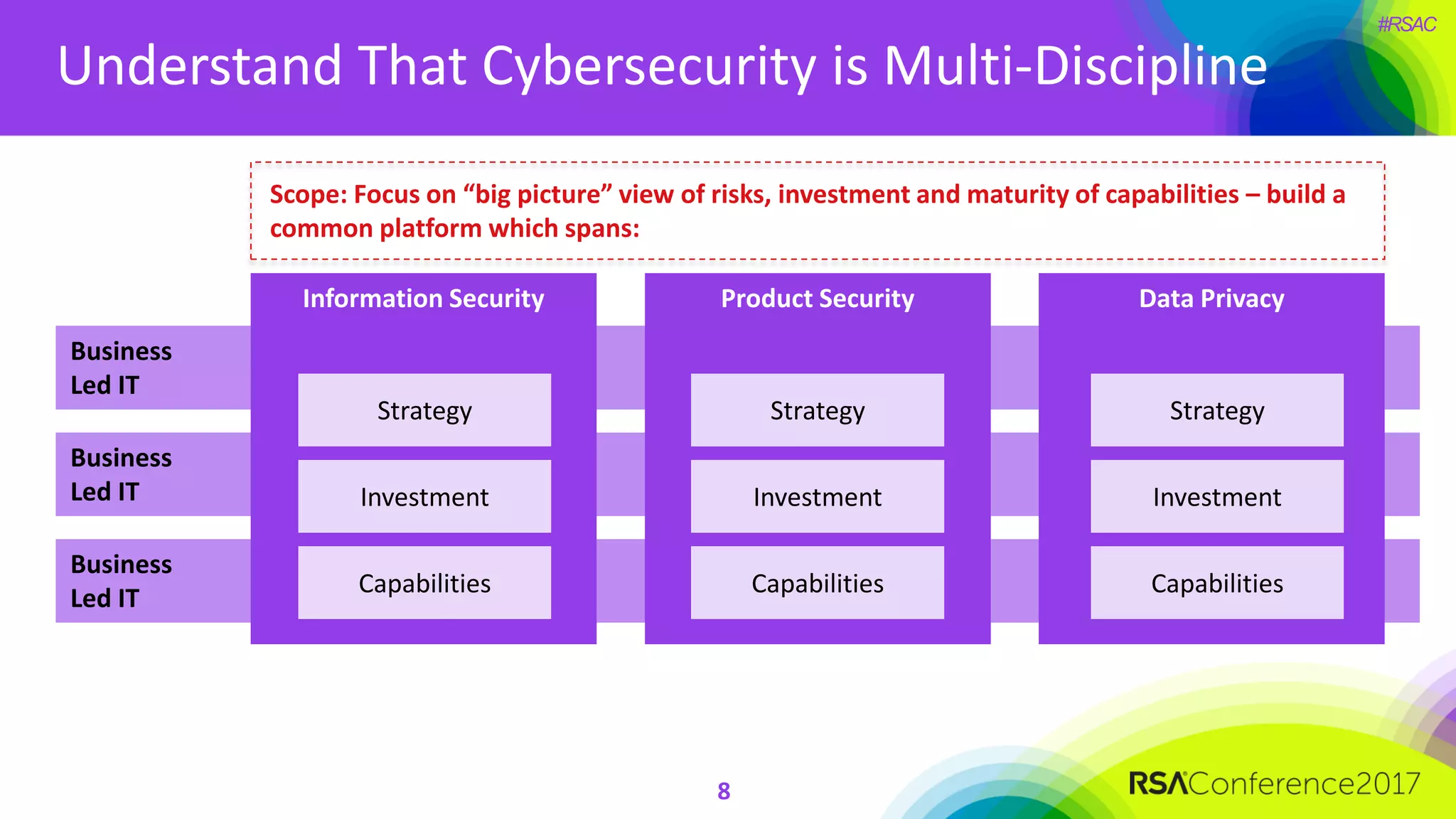
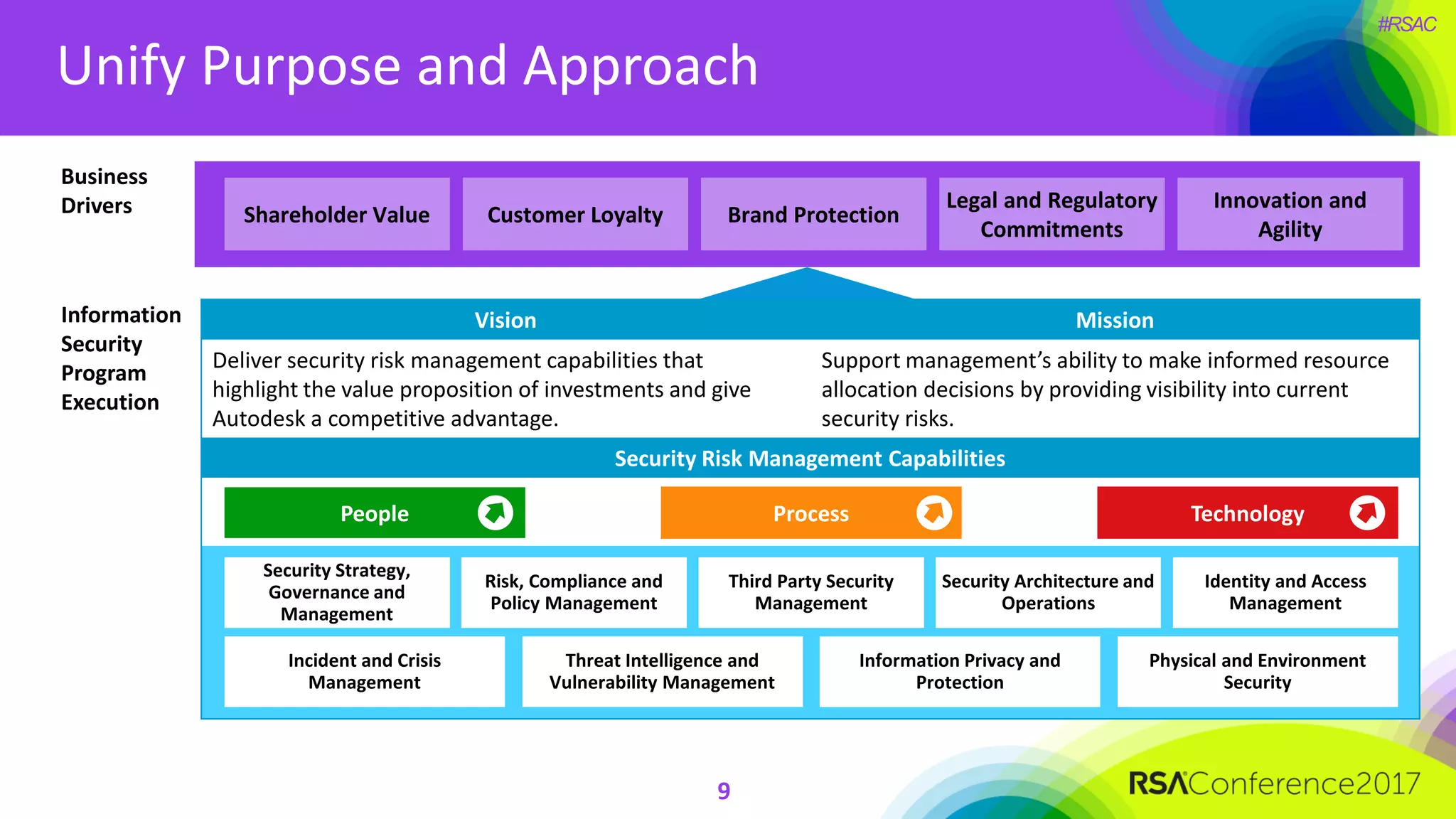
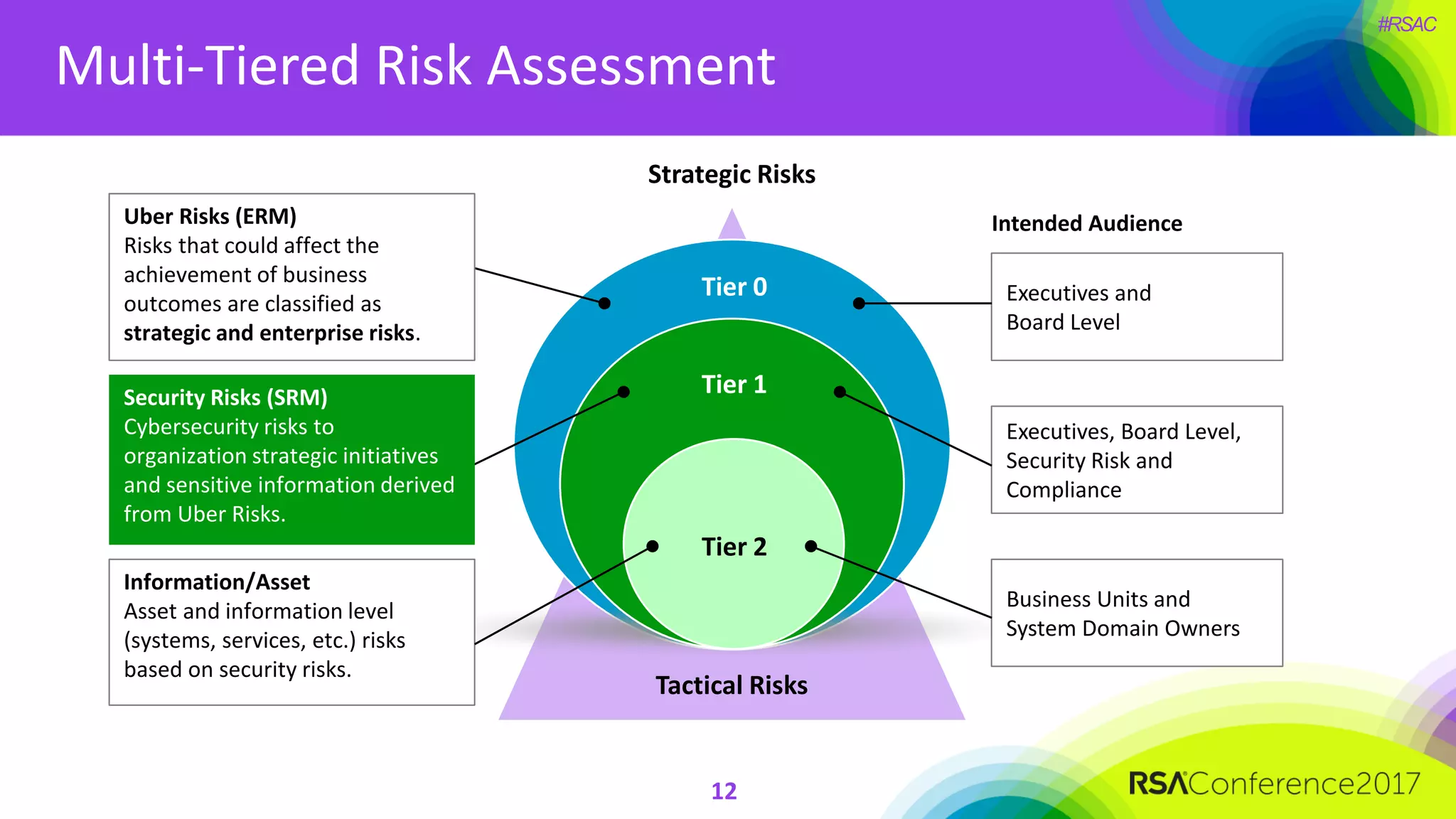
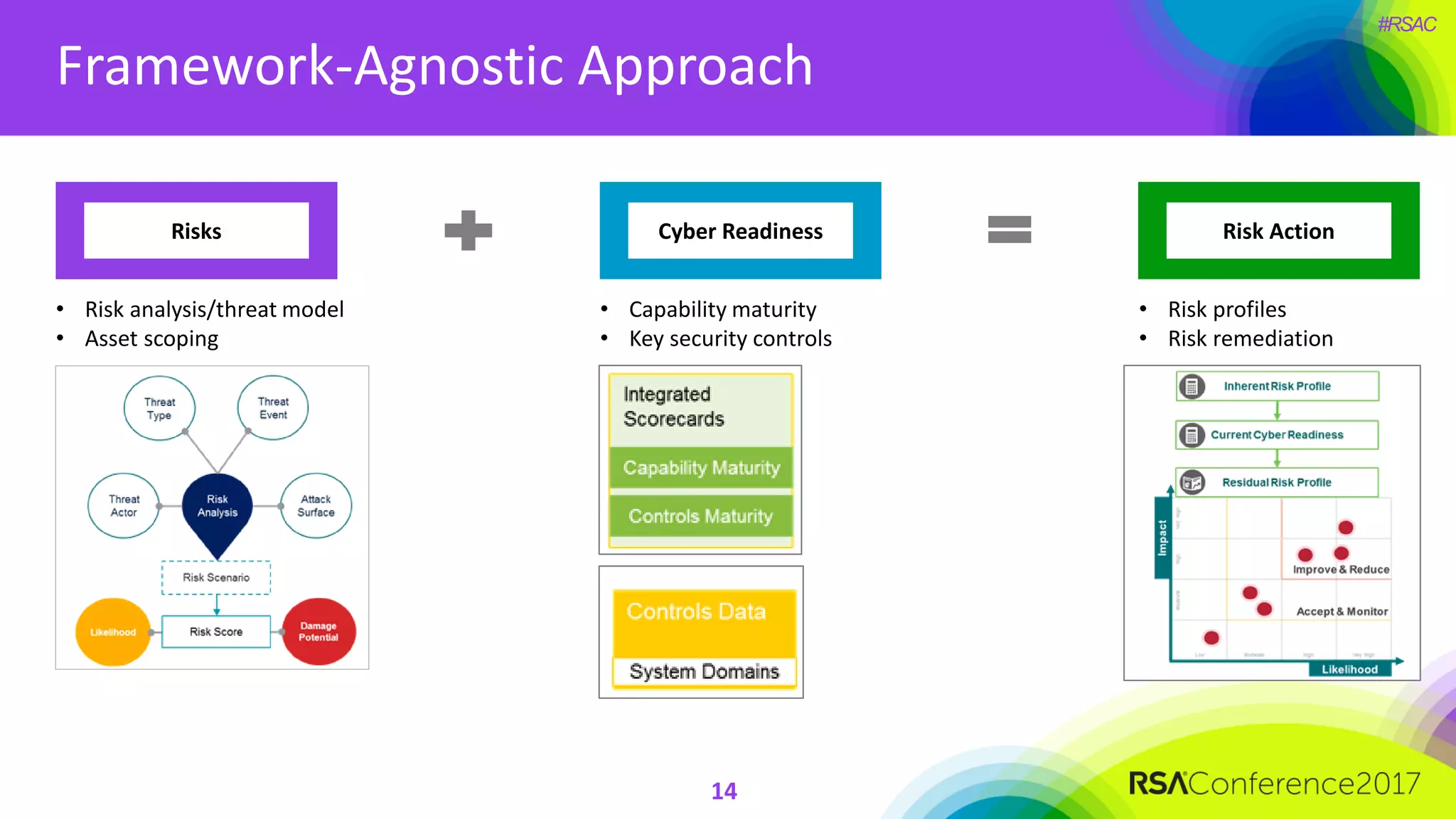
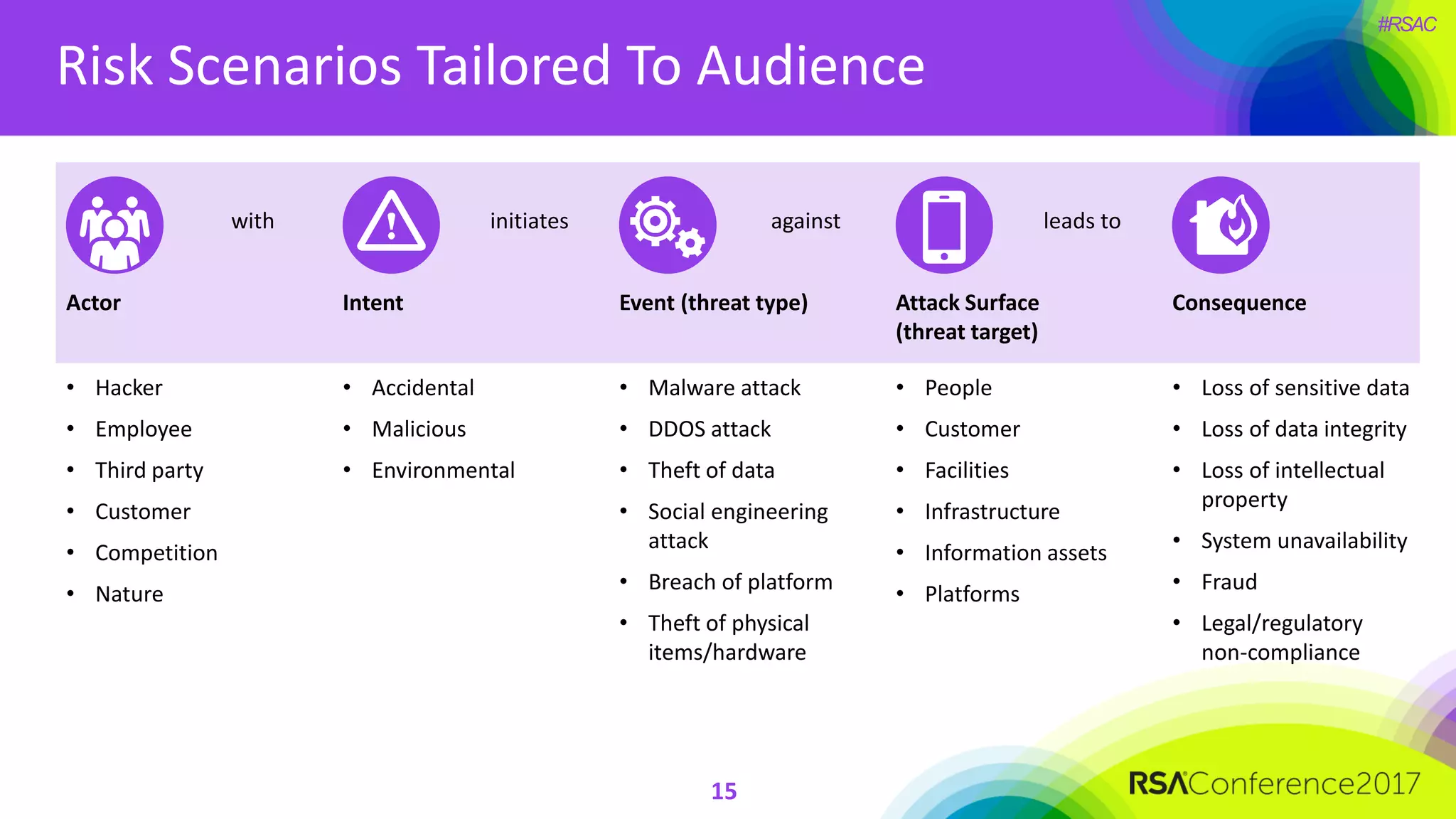
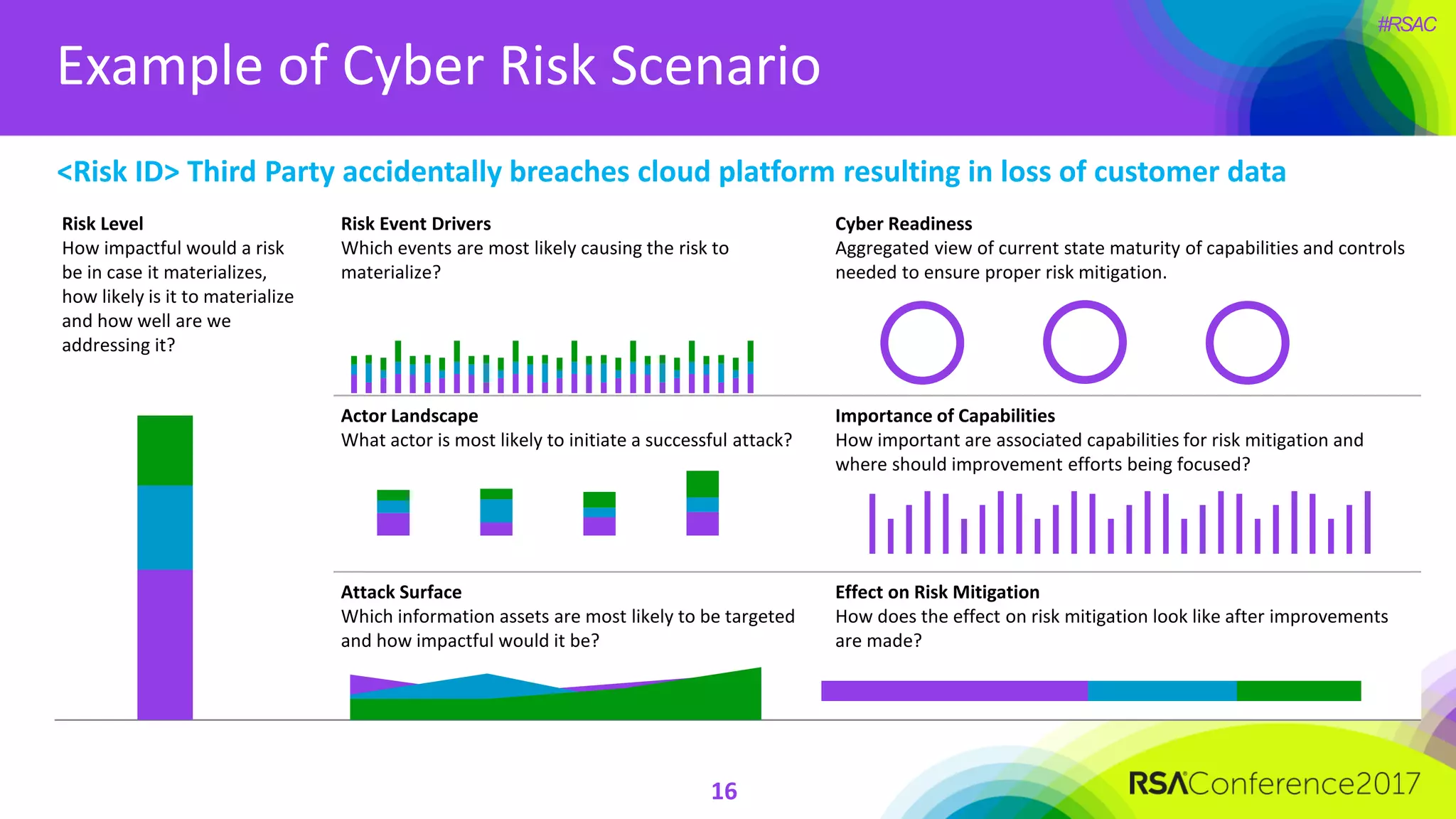
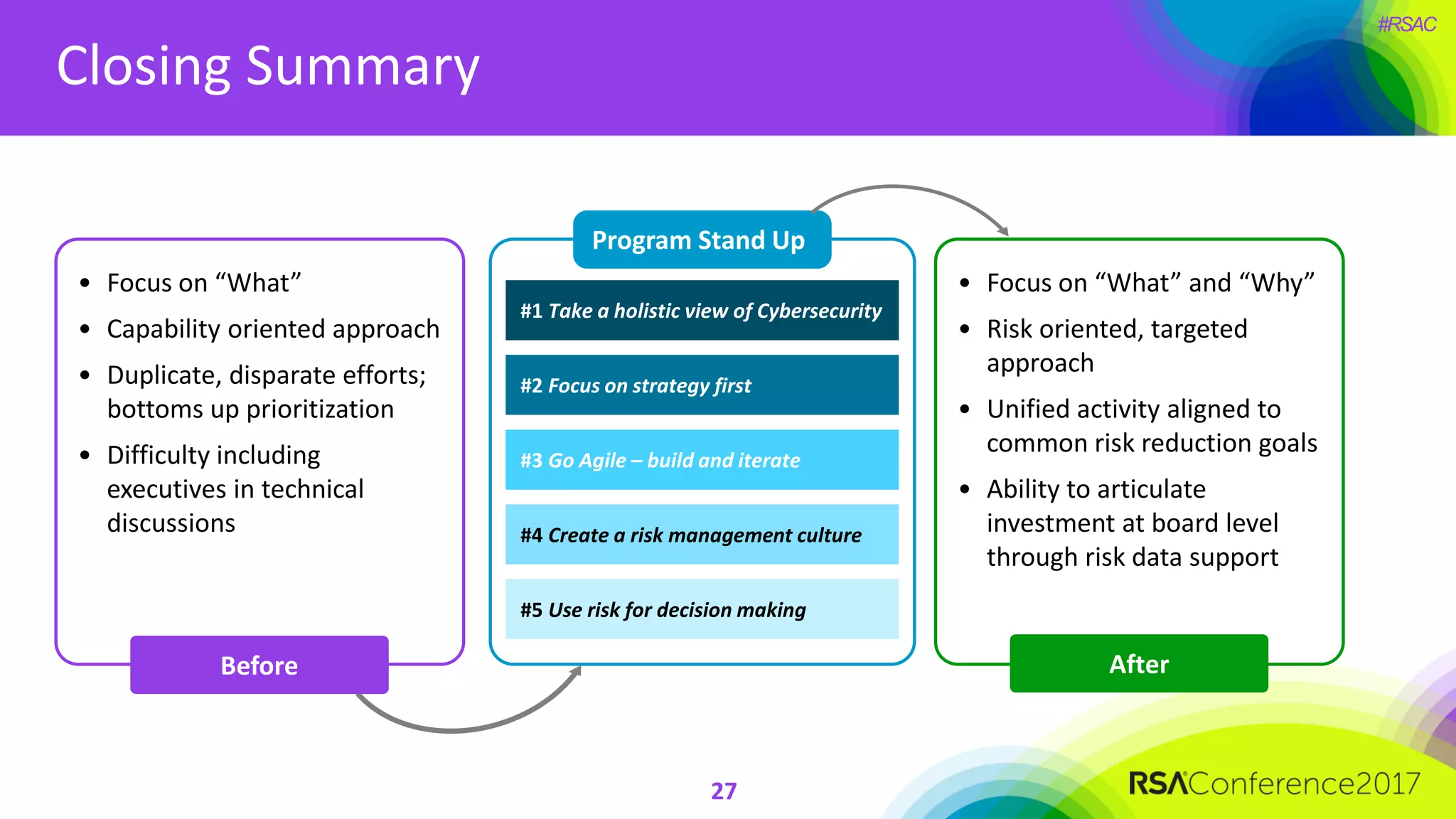
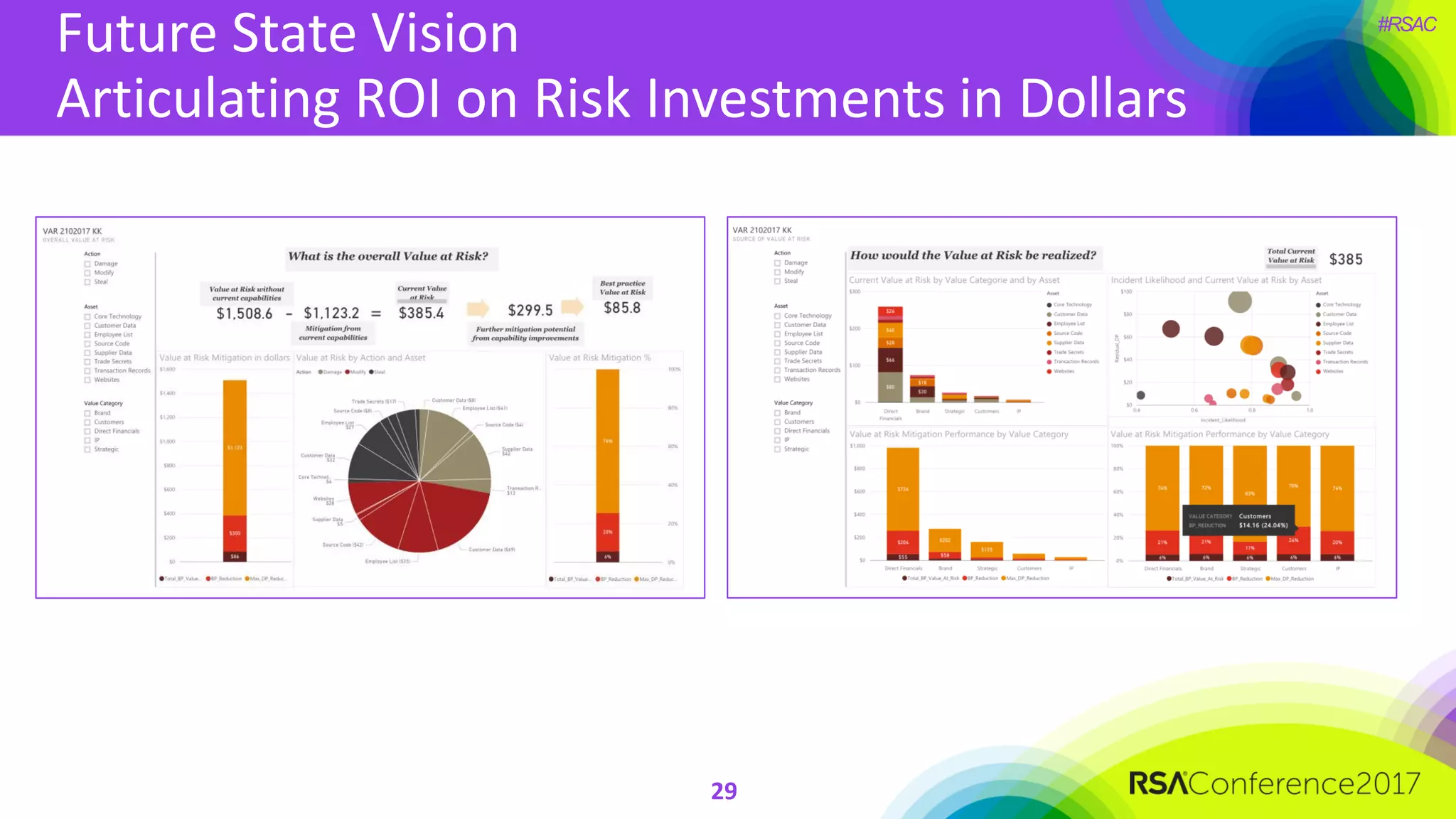
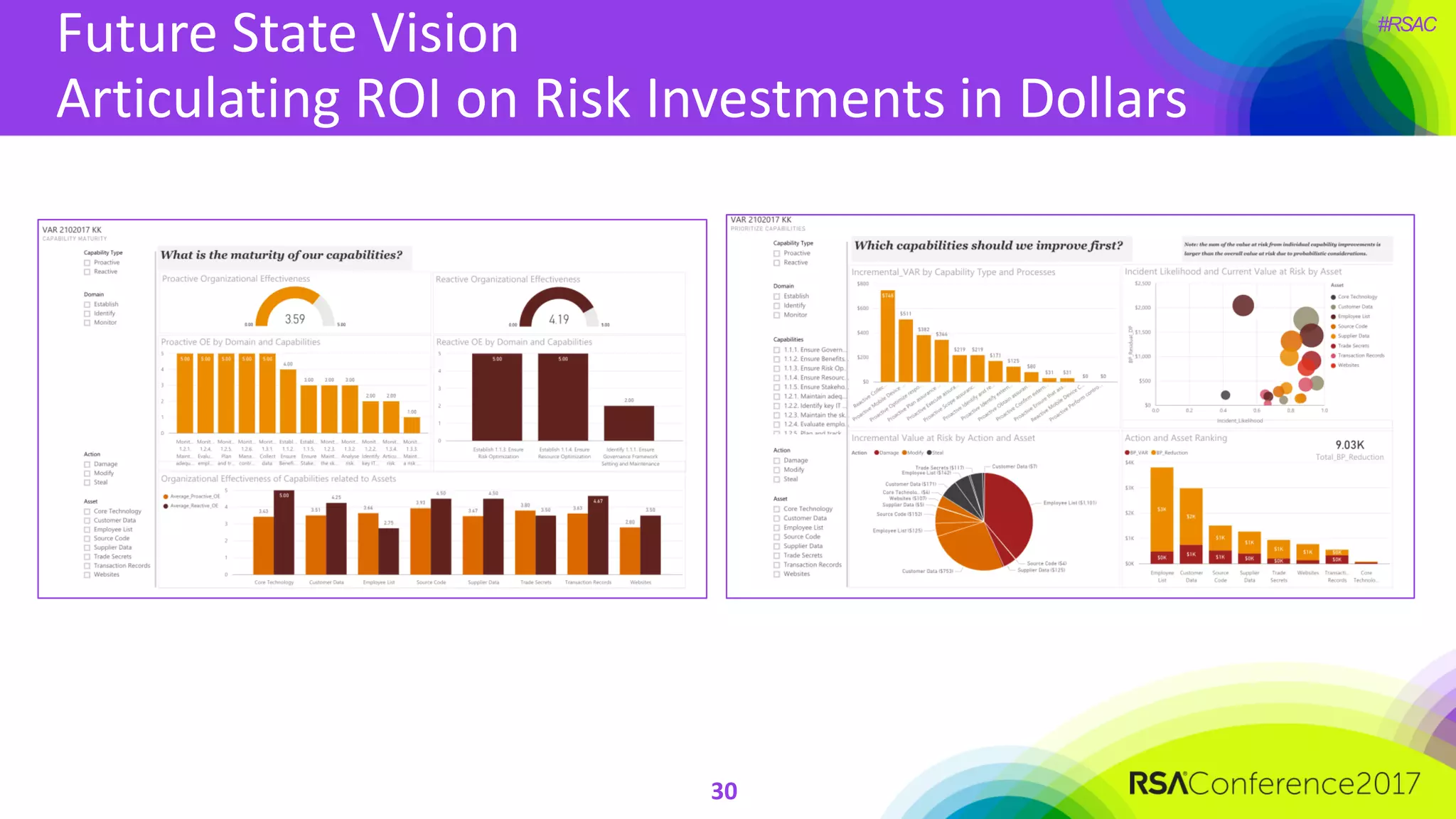
The document outlines the strategies and lessons learned by Autodesk in jumpstarting their cyber-risk program amidst a business transformation to a cloud-based model. It emphasizes a holistic approach to cybersecurity through five key secrets: taking a comprehensive view, prioritizing strategy, adopting an agile mindset, fostering a risk management culture, and using risk for decision-making. The approach aims to enhance communication of the organization's risk posture and align all stakeholders towards common objectives in an efficient manner.