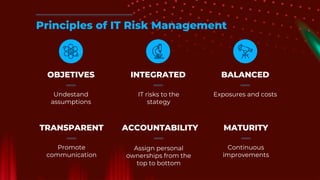
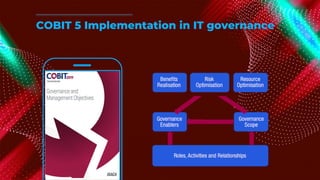
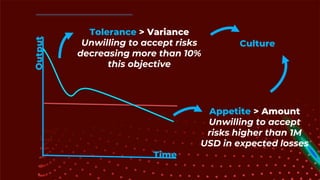
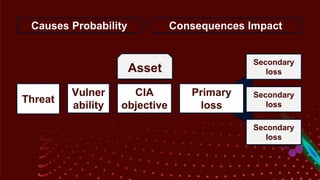
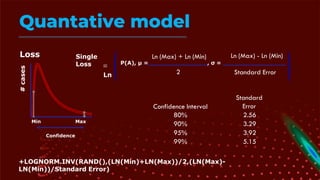
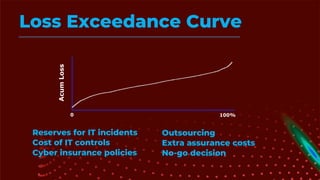
The document outlines the principles and processes of information risk management, emphasizing the importance of cultivating an organizational culture that is aware of and tolerates risk. It details the frameworks and methodologies, such as ISACA and COBIT, used to govern IT risks and make informed business decisions, while balancing costs and exposures. Additionally, it covers the steps for creating risk scenarios, responding to risks, and monitoring key risk indicators to ensure effective risk management and communication within the organization.