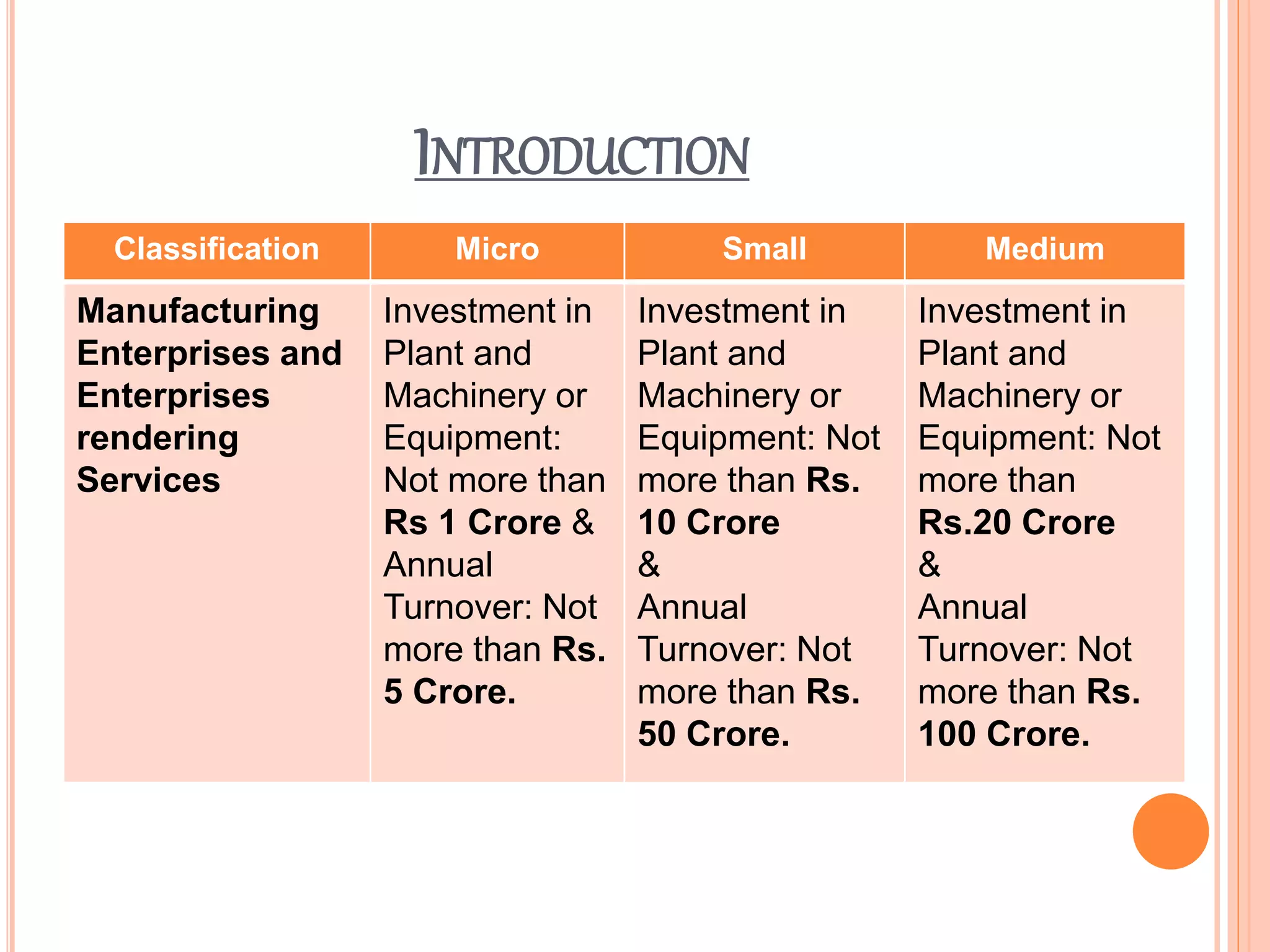
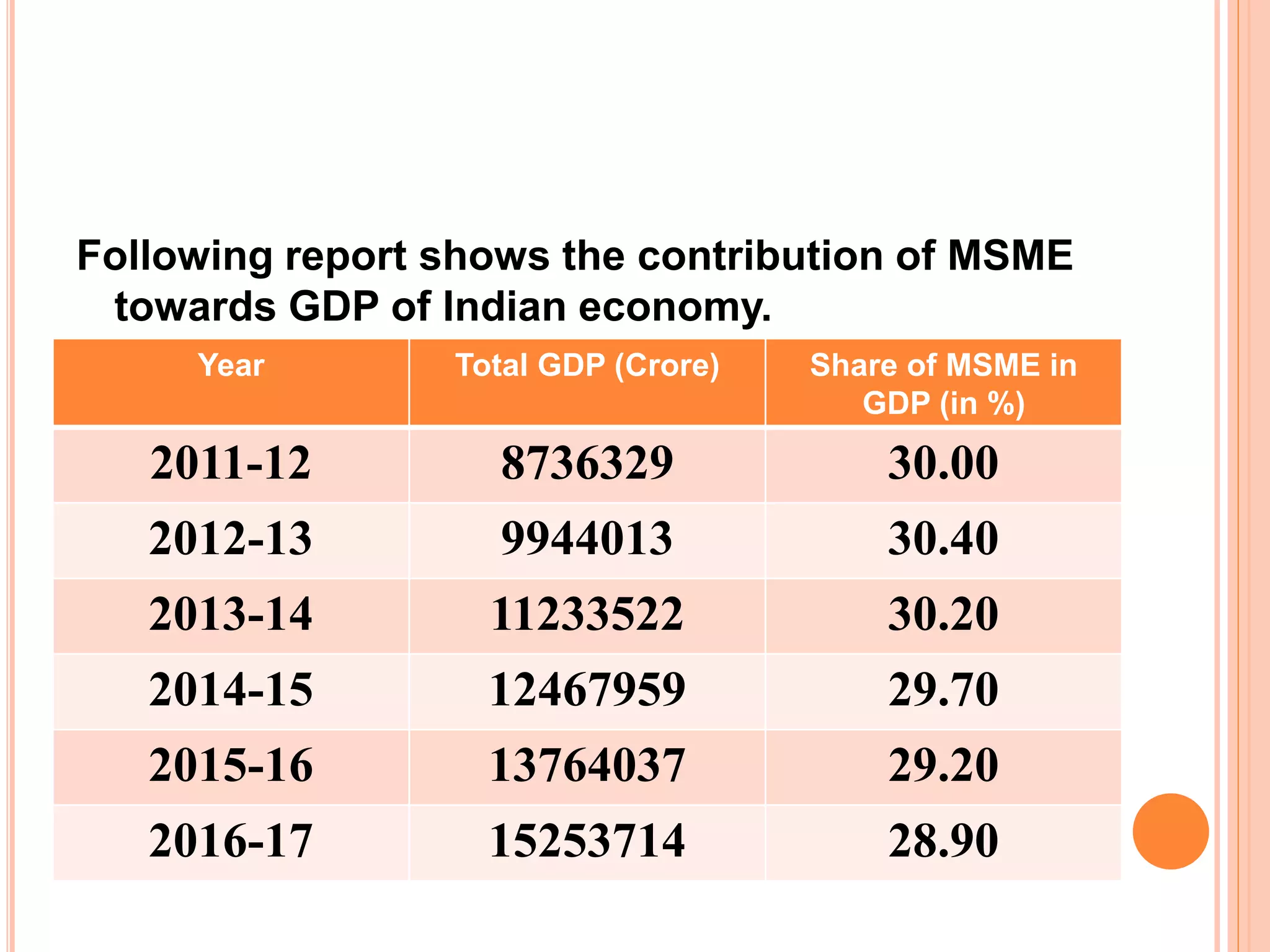
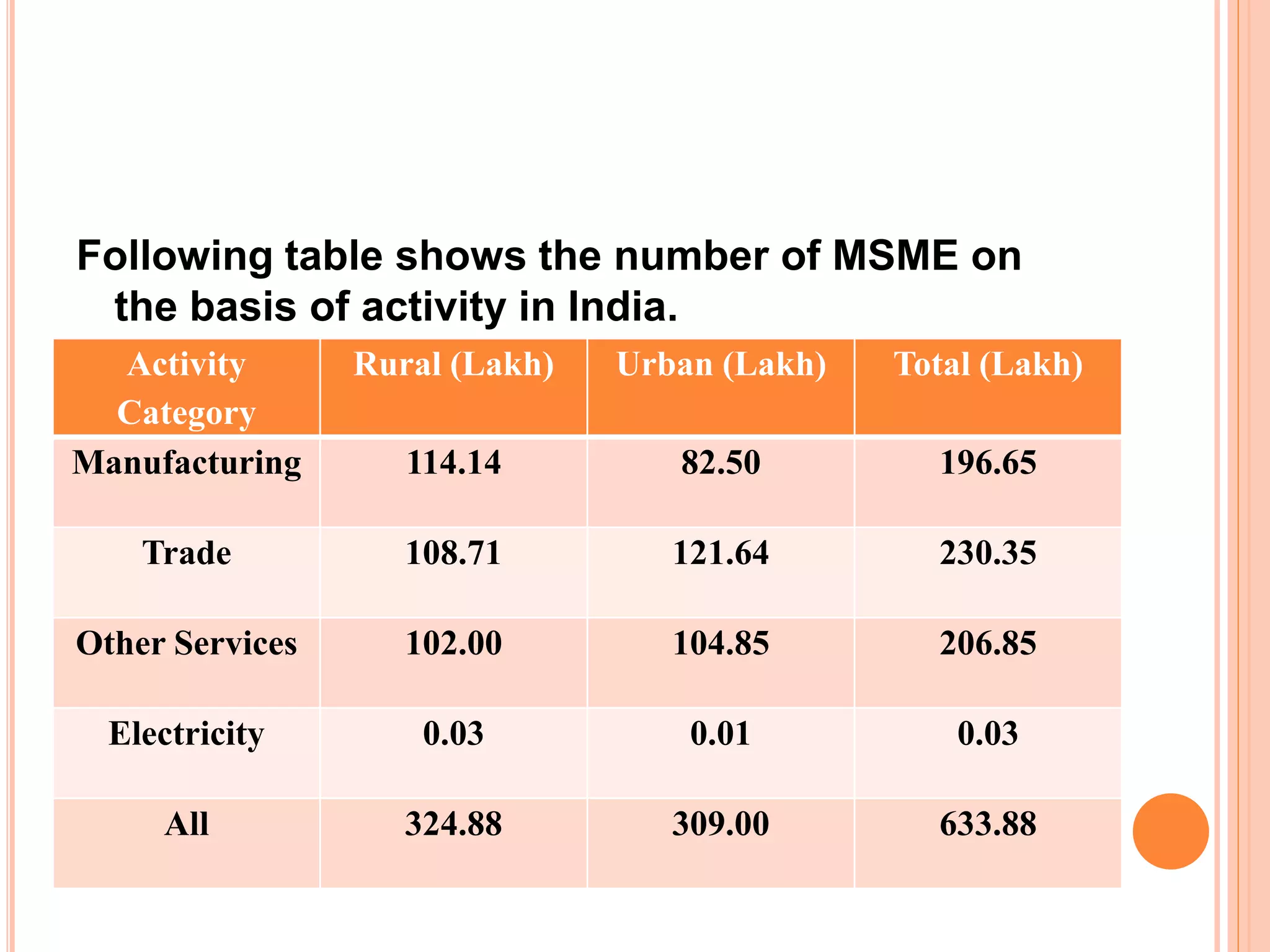
This document analyzes the role of MSMEs in the Indian economy before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. It finds that MSMEs contribute 30-40% of India's GDP and provide the highest rates of employment. However, the pandemic severely impacted MSMEs. The government launched several measures like credit guarantees and delayed loan repayments to support MSMEs. There is an expectation that MSMEs will help revitalize the economy by boosting demand, employment, and reducing imports. Suggestions include efficiently allocating relief funds, promoting local production and exports, and developing rural enterprises.