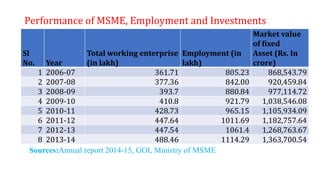
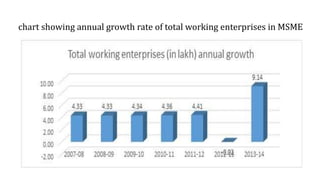
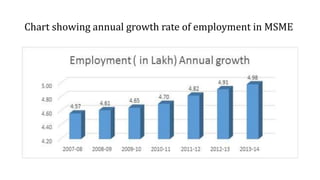
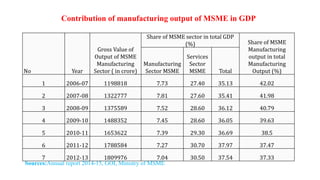
The document discusses India's small-scale sector, also known as the MSME sector. It defines micro, small, and medium enterprises based on their investment in plant and machinery. In 2007, the Ministry of Small Scale Industries and Ministry of Agro and Rural Industries merged to form the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. MSMEs play an important role in the Indian economy by generating employment, promoting equitable income distribution and effective capital mobilization. The document provides statistics on MSME growth and contribution to GDP. It also outlines various government policies and programs that support the development and growth of MSMEs.