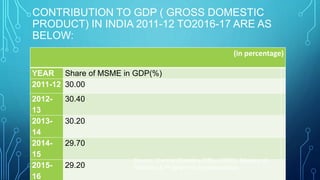
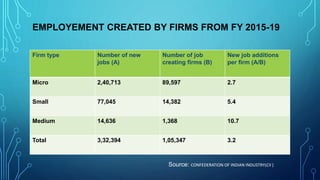
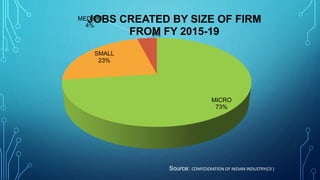
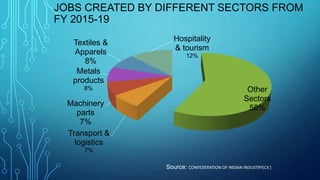
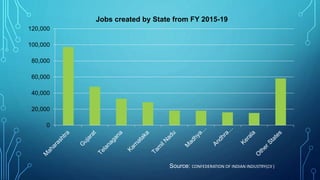
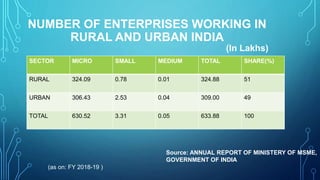
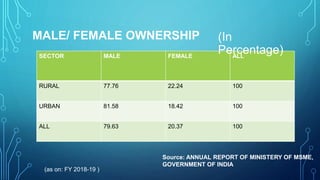
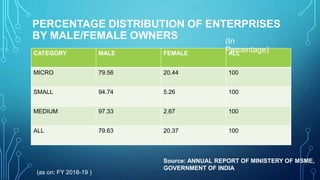
Micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) are vital to economic growth globally, providing significant employment and contributing to GDP. In India, reforms such as the MSME Amendment Bill of 2018 have shifted classification criteria to annual turnover, enhancing the support for these enterprises. Despite their importance, MSMEs face challenges like credit access, infrastructure deficits, and competition, necessitating comprehensive government measures to support their growth.