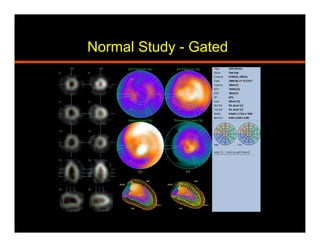
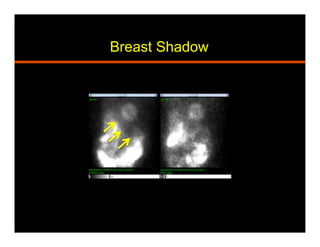
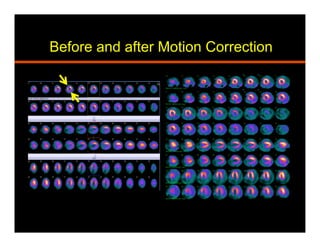
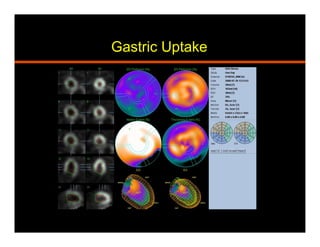
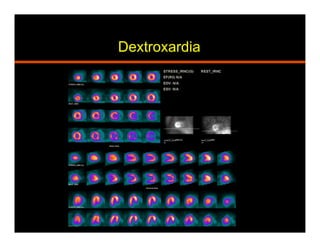
The document discusses common artifacts seen on SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) scans, their causes, and how to recognize and address them. It outlines artifacts related to soft tissue attenuation, patient motion, non-cardiac uptake, diseases that can mimic perfusion defects, image normalization issues, and technical problems related to acquisition, processing, and camera quality. The goal is to help physicians accurately interpret MPI scans by recognizing artifact patterns and ensuring high quality imaging.