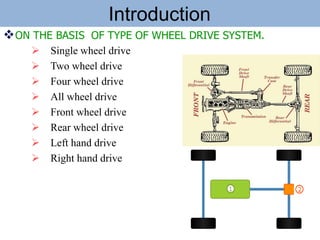
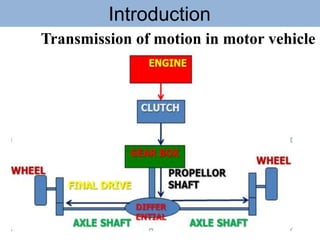
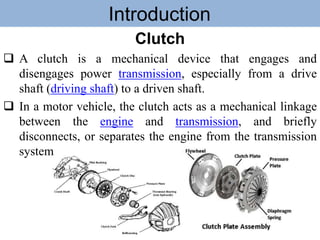
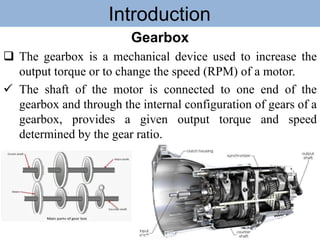
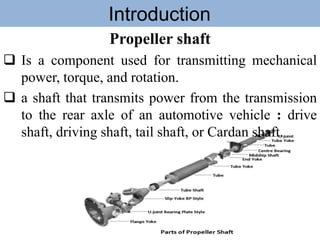
The document outlines the definition and classification of motor vehicles, explaining types based on wheels, prime movers, weight, purpose served, fuel used, and wheel drive systems. It also discusses key components involved in the transmission of motion within motor vehicles, including the engine, clutch, gearbox, propeller shaft, differential gearbox, axle shaft, and wheels. Additionally, it offers historical context with reference to the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic's definition of a motor vehicle.