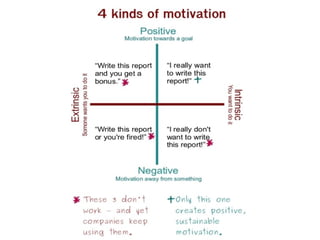
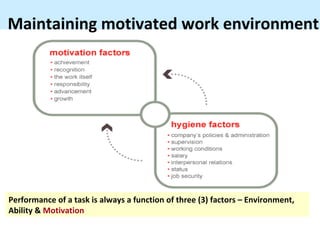
This document discusses employee motivation in the workplace. It defines motivation as what causes people to act and behave in certain goal-oriented ways. Motivation comes from biological, emotional, and social factors. The document outlines different types of motivation like basic needs, personal needs, and social needs. It also discusses intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation and different personality types in the workplace. Finally, it provides tips for managers to maintain a motivated work environment like removing barriers to motivation and using leadership skills to increase job satisfaction.