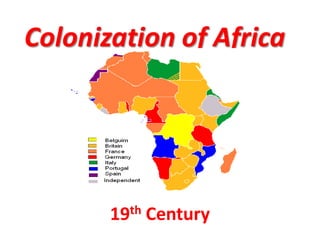
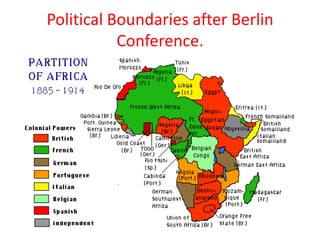
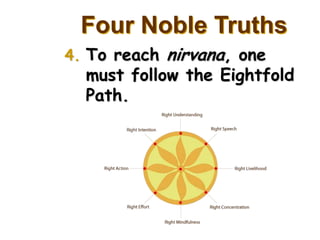
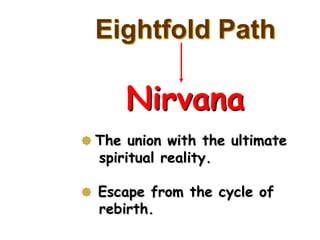
The document provides information about the colonization of Africa by European powers in the 19th century. It discusses how Europeans established colonies in Africa beginning in the early 19th century during a period of rapid European expansion globally. Some of the reasons cited for increased European colonialism in Africa include the abolition of slavery, a newfound economic interest in exploiting Africa's vast natural wealth, and the Berlin Conference which divided political control of African territory among European nations. The major European colonial powers that controlled African land and peoples mentioned were Belgium, Britain, France, Germany, Italy, Portugal, and Spain.