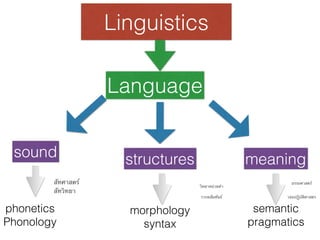
The document discusses linguistics and the different levels of language analysis including phonetics, phonology, morphology, syntax, semantics, and pragmatics. It then focuses on morphology, explaining the different types of morphemes including roots, stems, bases, affixes. It provides examples of different kinds of words according to their morpheme structure such as simple words, complex words, and compound words. Finally, it discusses the different types of prefixes and suffixes, providing examples for each.