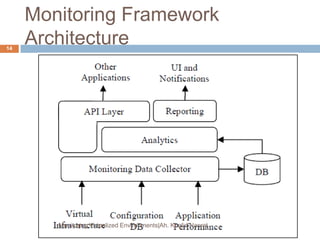
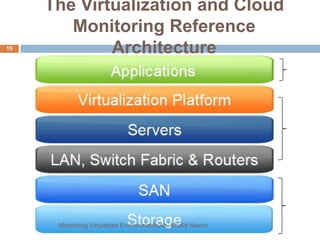
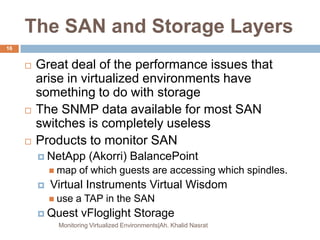
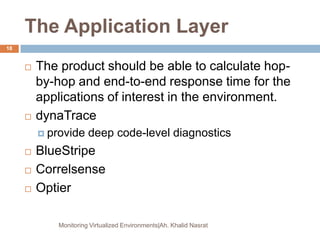
This document discusses monitoring virtualized environments. It begins by explaining virtualization and its benefits, then discusses metrics that should be monitored, including performance, capacity, security, and billing. It presents a monitoring framework architecture and examines tools like eG VM Monitor that can provide comprehensive visibility. While eG VM Monitor effectively monitors all aspects of the virtual infrastructure, it has drawbacks of complexity and cost. Overall, the document emphasizes the importance of monitoring virtualized environments and provides guidance on selecting tools and approaches.