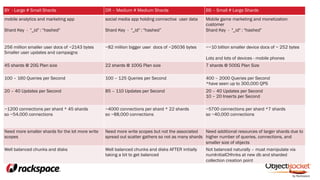
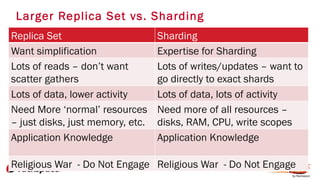
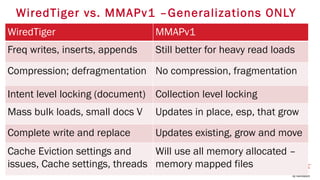
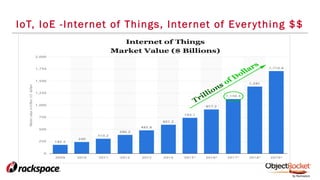
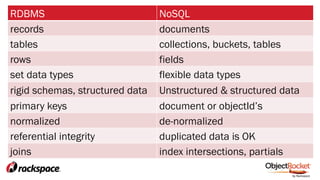
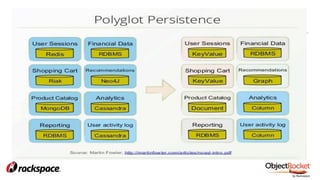
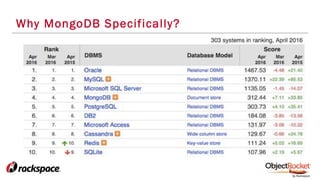
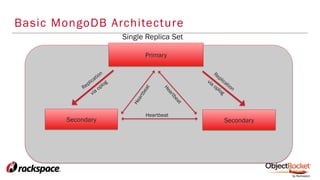
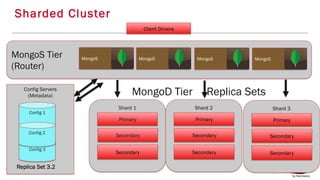
The document provides an in-depth overview of sharding in MongoDB 3.x, detailing its necessity for scalability, performance, and high availability. It discusses the importance of selecting appropriate shard keys, the general sharding process, and considerations for managing shards. Additionally, it covers practical examples, commands, and potential pitfalls related to sharding and storage engine choices.














![Sample Shard Key Evaluation Queries/Aggs
• **Run Queries and Aggregations against unused Secondaries**
SECONDARY> db.events.new.aggregate([{$project:{”BoxId":1}},{ $group: { _id: "$BoxId"} },{ $group: { _id:
1, count: { $sum: 1 } } }],{allowDiskUse:true})
{ "_id" : 1, "count" : 3303464 ** Note good cardinality here**
• SECONDARY> db.events.new.aggregate([{$project:{”BoxId":1}},{$group: { _id:"$BoxId",number : {$sum:
1}}},{$sort:{number:-1}},{$limit:20}],{allowDiskUse:true})
• { "_id" : "pnx-xxxxxxxx.003", "number" : 46889 }
• { "_id" : "jhx-xxxxxxxx.002, "number" : 23644 }
• { "_id" : "3tq9-xxxxxxxx.001", "number" : 17769 }
-Look for NULLS and for DISTINCT
-Look at sample values of documents and fields near FRONT and BACK of the collection](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kimberlywilkinsmongodbrevisedshardingperc2016scpublicapril2016-160420001346/85/MongoDB-Revised-Sharding-Guidelines-MongoDB-3-x_Kimberly_Wilkins-25-320.jpg)
![Another Shard Key Aggregation example
• Run aggregation query to find the most common reference id (rid) values
and sort to give you the top 5.
• Run against the PROFILE collection and can run on SECONDARIES of busy
systems to prevent impact to your application that works via primaries.
SECONDARY> db.items.aggregate([{$project:{rid:1}},
{$group:{_id:"$rid",count:{$sum:1}}},{$sort:
{count:-1}},{$limit:5}])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kimberlywilkinsmongodbrevisedshardingperc2016scpublicapril2016-160420001346/85/MongoDB-Revised-Sharding-Guidelines-MongoDB-3-x_Kimberly_Wilkins-26-320.jpg)



![Snippet - javascript to create javascript
[host1] > mongo –nodb
>
count=16;
while (count<17){
print("db.runCommand( { enablesharding : ’hits-2016-"+count+"' } ) ;");
print("db.adminCommand({shardCollection:’hits-2016-"+count+".hits-2016-"+count
+"', key:{'_id' : 'hashed'}, numInitialChunks : 2000});")
count++
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/kimberlywilkinsmongodbrevisedshardingperc2016scpublicapril2016-160420001346/85/MongoDB-Revised-Sharding-Guidelines-MongoDB-3-x_Kimberly_Wilkins-30-320.jpg)