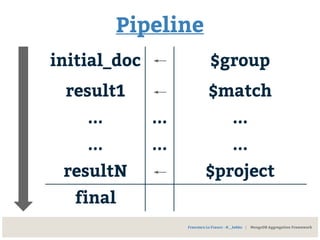
The document discusses MongoDB's data modeling, highlighting its document-oriented approach and BSON representation. It covers key concepts like collections, references, embedding, and denormalization, emphasizing trade-offs between ease of access and update complexity. Additionally, it outlines the aggregation framework, including CRUD operations, single-purpose aggregation, and pipeline processing for data analysis.







![MongoDB Data Model example (BLOG POST):
{
"_id": ObjectId("508d27069cc1ae293b36928d"),
"title": "This is the title",
"tags": [
"chocolate",
"milk"
],
"created_date": ISODate("2012-10-28T12:41:39.110Z"),
"author_id": ObjectId("508d280e9cc1ae293b36928e"),
"comments": [
{
"content": "This is the body of comment",
"author_id": ObjectId("508d34"),
"tag": "coffee"},
{
"content": "This is the body of comment",
"author_id": ObjectId("508d35")}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-8-320.jpg)
![MongoDB Data Model example (BLOG POST):
{
"_id": ObjectId("508d27069cc1ae293b36928d"),
"title": "This is the title",
"tags": [
"chocolate",
"milk"
],
"created_date": ISODate("2012-10-28T12:41:39.110Z"),
"author_id": ObjectId("508d280e9cc1ae293b36928e"),
"comments": [
{
"content": "This is the body of comment",
"author_id": ObjectId("508d34"),
"tag": "coffee"},
{
"content": "This is the body of comment",
"author_id": ObjectId("508d35")}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-9-320.jpg)
![MongoDB Data Model example (BLOG POST):
{
"_id": ObjectId("508d27069cc1ae293b36928d"),
"title": "This is the title",
"tags": [
"chocolate",
"milk"
],
"created_date": ISODate("2012-10-28T12:41:39.110Z"),
"author_id": ObjectId("508d280e9cc1ae293b36928e"),
"comments": [
{
"content": "This is the body of comment",
"author_id": ObjectId("508d34"),
"tag": "coffee"},
{
"content": "This is the body of comment",
"author_id": ObjectId("508d35")}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-10-320.jpg)

![One to few
> db.employee.findOne()
{
name: 'Kate Monster',
ssn: '123-456-7890',
addresses:
[{ street: 'Lombard Street, 26',
zip_code: '22545'
},
{ street: 'Abbey Road, 99',
zip_code: '33568'
}]
}
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-12-320.jpg)



![One to many
> db.products.findOne()
{
name: 'smoke shifter',
manufacturer: 'Acme Corp',
catalog_number: 1234,
parts: [
ObjectID('AAAAF17CD2AAAAAAF17CD2AA'),
ObjectID('F17CD2AAAAAAF17CD2AAAAAA'),
ObjectID('D2AAAAAAF17CD2AAAAAAF17C'),
// etc
]
}
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-16-320.jpg)

![Advantages:
- Easy to search and update an individual
referenced document (a single part)
- free N-to-N schema without join table
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework
parts: [
ObjectID('AAAAF17CD2AAAAAAF17CD2AA'),
ObjectID('F17CD2AAAAAAF17CD2AAAAAA'),
ObjectID('D2AAAAAAF17CD2AAAAAAF17C')
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-18-320.jpg)



![To be denormalized
> db.products.findOne()
{
name: 'smoke shifter',
manufacturer: 'Acme Corp',
catalog_number: 1234,
parts: [
ObjectID('AAAA'),
ObjectID('F17C'),
ObjectID('D2AA'),
// etc
]
}
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-23-320.jpg)
![Denormalized (partial + one side)
> db.products.findOne()
{
name: 'smoke shifter',
manufacturer: 'Acme Corp',
catalog_number: 1234,
parts: [
{ id: ObjectID('AAAA'), name: 'part1'},
{ id: ObjectID('F17C'), name: 'part2'},
{ id: ObjectID('D2AA'), name: 'part3'},
// etc
]
}
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-24-320.jpg)







![Two Phase Commit Example
TODO: transfer 100$ from A to B
Account A:
total: 1000,
on_going_transactions: [];
Account B:
total: 500,
on_going_transactions: [];
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-32-320.jpg)
















![distinct
{ name: "jim", age: 0 }
{ name: "kim", age: 1 }
{ name: "dim", age: 4 }
{ name: "sim", age: 2 }
db.foe.distinct("age")=[0, 1, 4, 2]
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-50-320.jpg)


![group
[
{ age: 12, count: 6 },
{ age: 14, count: 7 }
]
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-53-320.jpg)












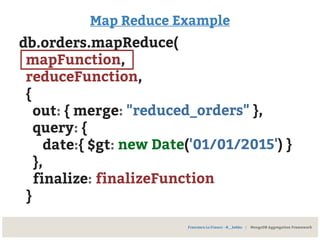
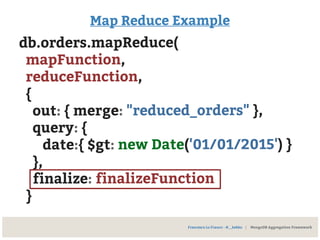
![Map Reduce Example
var mapFunction =
function() {
var key = this.sku;
var value = {
tot: this.total
qty: this.qty
};
emit(key, value);
}
Result:
{ 01A: [{tot: 88, qty: 8}, {tot: 79, qty: 7}] },
{ 02B: {tot: 27, qty: 9} },
{ 03C: [{tot: 24, qty: 8}, {tot: 12, qty: 3}] }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-70-320.jpg)
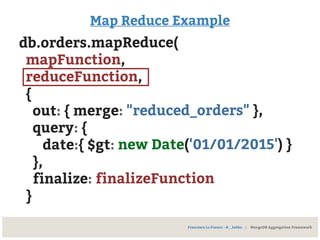
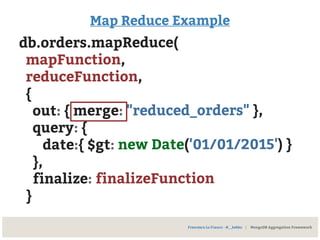
![Map Reduce Example
var reduceFunction =
reducedVal = { qty: 0, tot: 0}
function(key, values) {
for(var i, i < values.length, i++) {
reducedVal.qty += values[i].qty
reducedVal.tot += values[i].tot
};
return reducedVal;
Francesco Lo Franco - @__kekko | MongoDB Aggregation Framework](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbhowtomodelandextractyourdata-150228175033-conversion-gate02/85/MongoDB-How-to-model-and-extract-your-data-72-320.jpg)