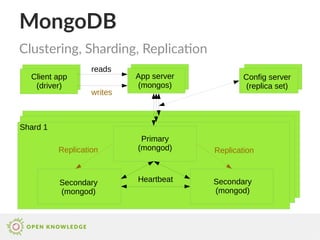
MongoDB is a document-oriented NoSQL database that stores data as binary JSON (BSON) and allows for ad-hoc queries and high performance. It features various schema design principles such as embedded documents and referencing, as well as aggregation and indexing capabilities for optimized query performance. It is suitable for handling large datasets, allowing for scalability and flexibility in data management.



![MongoDB
SELECT * FROM Person
WHERE id > 10
AND name <> “Mueller“;
SELECT p.name FROM Person p
JOIN Address a
ON p.address = a.id
WHERE a.city = “Leipzig“
ORDER BY p.name DESC;
SELECT * FROM
WHERE name IS NOT NULL;
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM PERSON
WHERE name = “Mueller“;
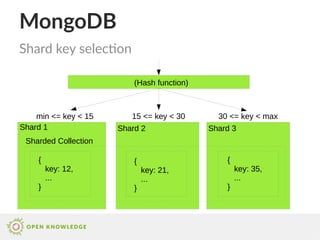
Relational vs. document based: syntax (2/3)
db.Person.find({ $and: [
{ _id: { $gt: ObjectId("...") }},
{ name: { $ne: "Mueller" }}]});
db.Person.find(
{ Address.city: “Leipzig“ },
{ name: 1, _id: 0 }
).sort({ name: -1 });
db.Person.find( { name: {
$not: { $type: 10 }, $exists: true }});
db.Person.count({ name: “Mueller“ });
db.Person.find(
{ name: “Mueller“ }).count();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbschemadesignpatterns-161110221927/85/Mongo-DB-schema-design-patterns-5-320.jpg)


![MongoDB
● applicable for 1:1 and 1:n when
n can‘t get to large
● Embedded document cannot get
too large
● Embedded document not very
likely to change
● arrays that grow without bound
should never be embedded
schema design: embedded document
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
City: “Leipzig“,
Street: “Burgstr. 1“,
Person: [
{
Name: “Mueller“,
},
{
Name: “Schneider“,
},
]
}
Address](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbschemadesignpatterns-161110221927/85/Mongo-DB-schema-design-patterns-8-320.jpg)
![MongoDB
● applicable for :n when n can‘t
get to large
● Referenced document likely to
change often in future
● there are many referenced
documents expected, so storing
only the reference is cheaper
● there are large referenced
documents expected, so storing
only the reference is cheaper
● arrays that grow without bound
should never be embedded
● Address should be accessible on
its own
schema design: referencing
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
City: “Leipzig“,
Street: “Burgstr. 1“,
Person: [
ObjectId(“...“), ObjectId(“...“),
]
}
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
Name: “Mueller“,
}
Address
Person](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbschemadesignpatterns-161110221927/85/Mongo-DB-schema-design-patterns-9-320.jpg)

![MongoDB
● applicable for m:n when n and m
can‘t get to large and application
requires to navigate both ends
● disadvantage: need to update
operations when changing
references
schema design: two way referencing
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
City: “Leipzig“,
Street: “Burgstr. 1“,
Person: [
ObjectId(“...“), ObjectId(“...“),
]
}
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
Name: “Mueller“,
Address: [
ObjectId(“...“), ObjectId(“...“),
]
}
Address
Person](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbschemadesignpatterns-161110221927/85/Mongo-DB-schema-design-patterns-11-320.jpg)
![MongoDB
● queries expected to filter by
certain fields of the referenced
document, so including this field
already in the hosts saves an
additional query at application
level
● disadvantage: two update
operations for duplicated field
● disadvantage: additional
memory consumption
schema design: denormalization
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
City: “Leipzig“,
Street: “Burgstr. 1“,
}
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
Name: “Mueller“,
Address: [
{
id: ObjectId(“...“),
city: “Leipzig“,
}, ...
]
}
Address
Person](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbschemadesignpatterns-161110221927/85/Mongo-DB-schema-design-patterns-12-320.jpg)
![MongoDB
● applicable for :n relations when
n can get very large and it‘s
expected that application will
use pagination anyway
● DB schema will already create
the chunks, the application will
later query for
schema design: bucketing
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
City: “Leipzig“,
Street: “Burgstr. 1“,
}
{
_id: ObjectId(“...“),
Address: ObjectId(“...“),
Page: 13,
Count: 50,
Persons: [
{ Name: “Mueller“ }, ...
]
}
Address
Person](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbschemadesignpatterns-161110221927/85/Mongo-DB-schema-design-patterns-13-320.jpg)

![MongoDB
Aggregation Framework
db.Person.aggregate( [
{ $match: { name: { $ne: "Fischer" } } },
{ $group: {
_id: "$name",
city_occurs: { $addToSet: "$Address.city" }
} },
{ $project: {
_id: "$_id",
city_count: { $size: "$city_occurs" }
}},
{ $sort: { name: 1 } }
{ $match: { city_count: { $gt: 1 } }},
{ $out: "PersonCityCount"}
] );
PersonCityCount
{
_id: Mueller,
city_count: 2,
},
{
_id: Schmidt,
city_count: 3,
}, ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbschemadesignpatterns-161110221927/85/Mongo-DB-schema-design-patterns-15-320.jpg)
![MongoDB
Map-Reduce
● More control than aggregation framework, but slower
var map = function() {
if(this.name != "Fischer") emit(this.name, this.Address.city);
}
var reduce = function(key, values) {
var distinct = [];
for(value in values) {
if(distinct.indexOf(value) == -1) distinct.push(value);
}
return distinct.length;
}
db.Person.mapReduce(map, reduce,
{
out: "PersonCityCount2"
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbschemadesignpatterns-161110221927/85/Mongo-DB-schema-design-patterns-16-320.jpg)