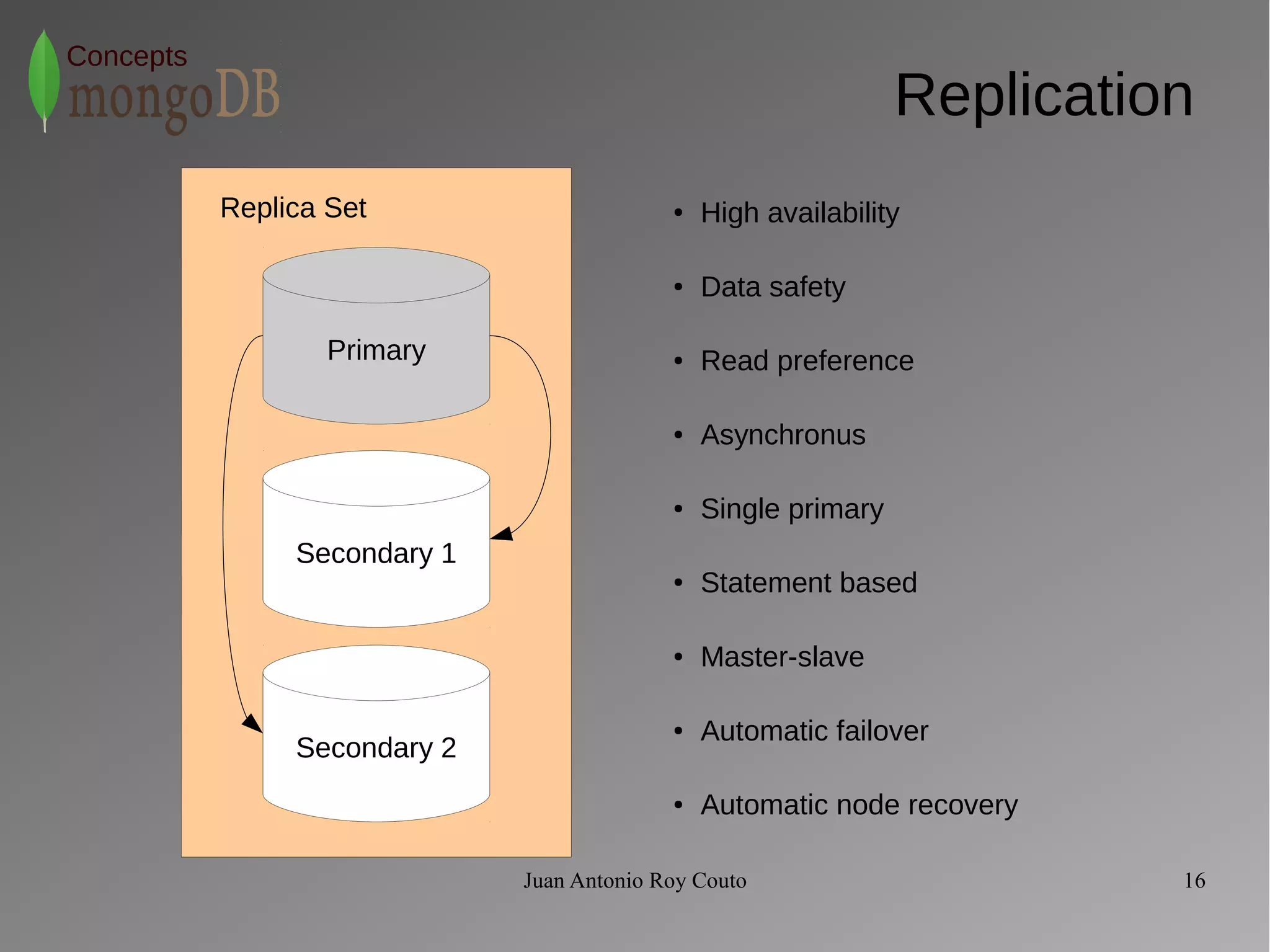
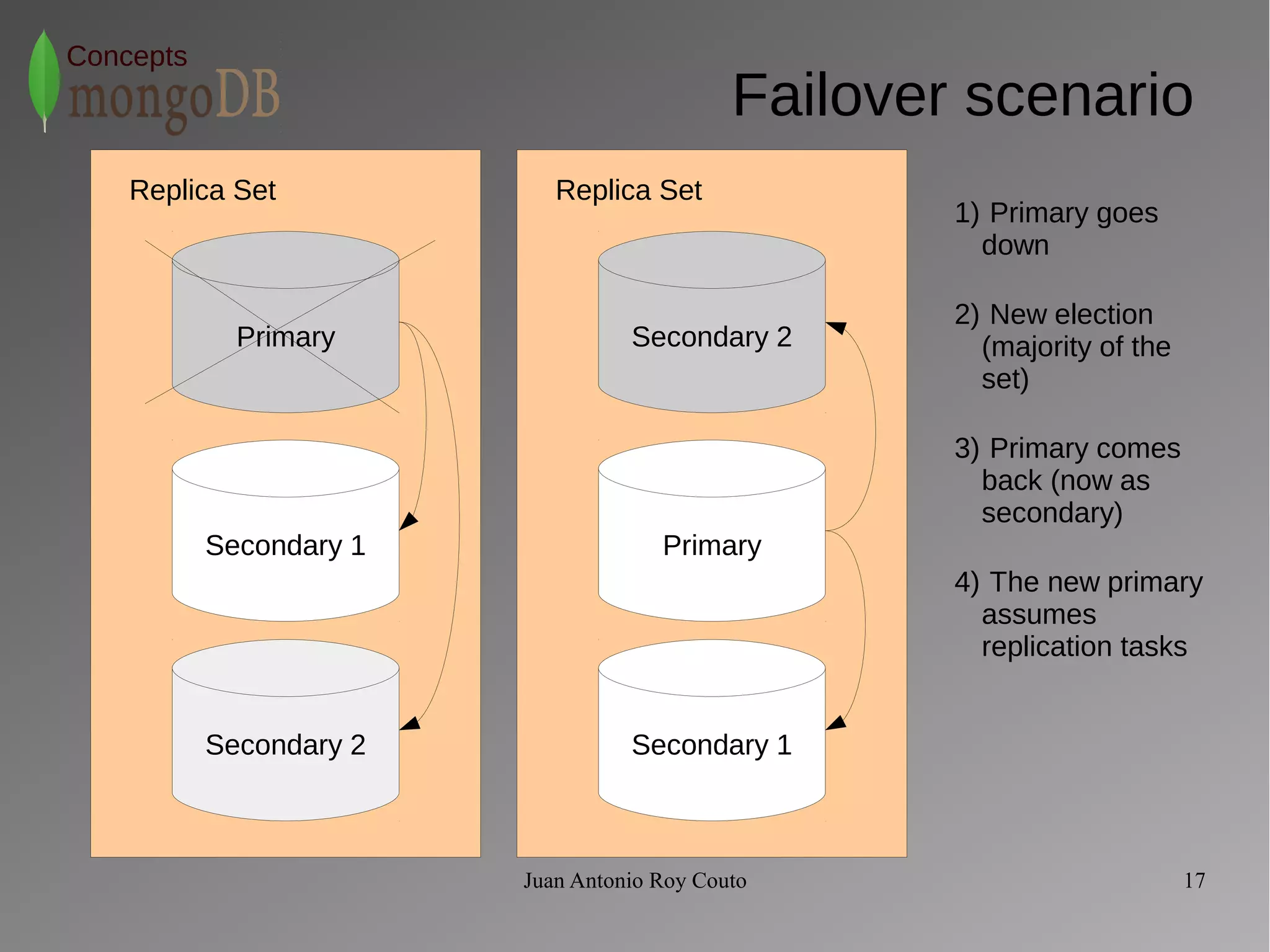
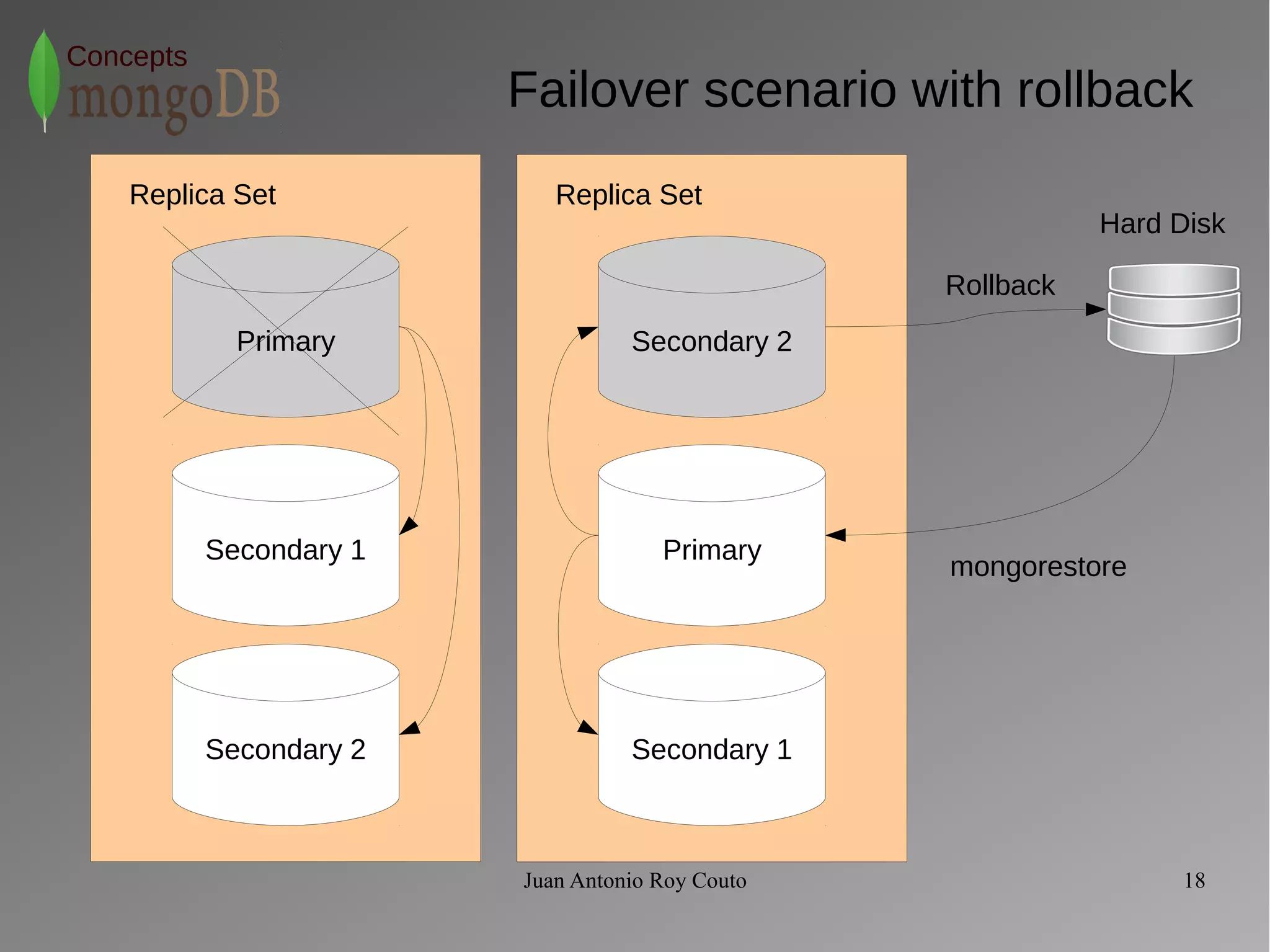
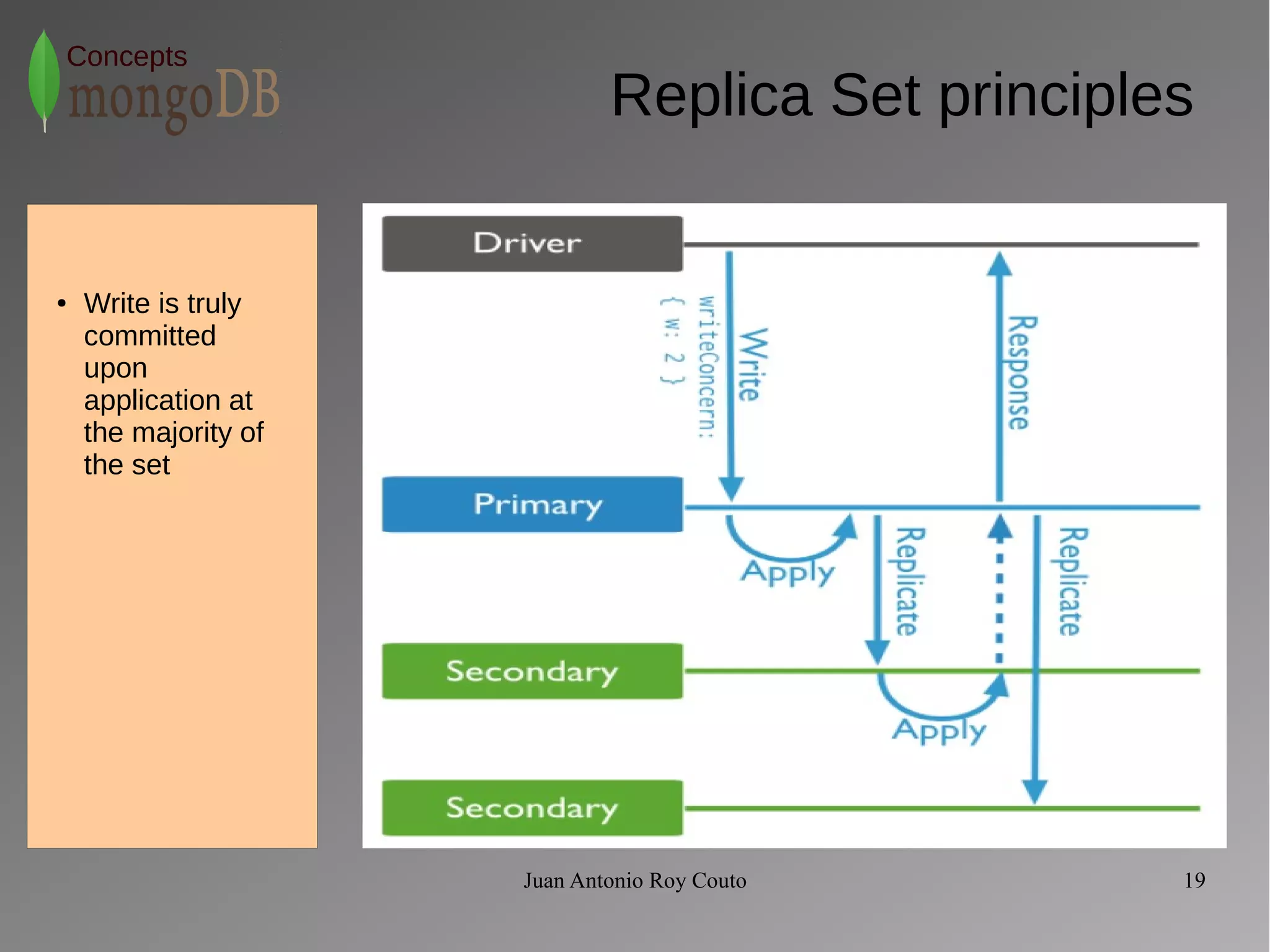
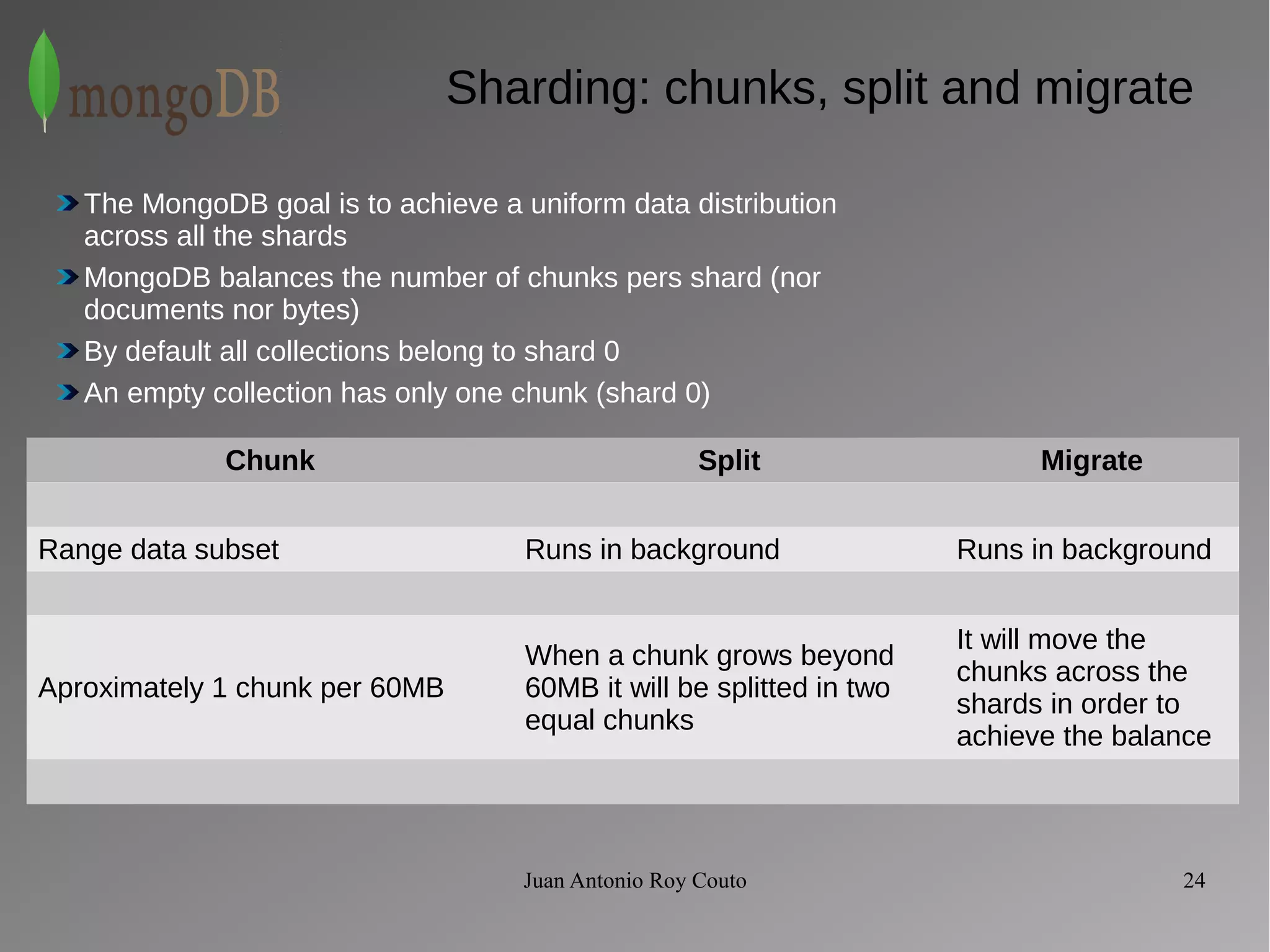
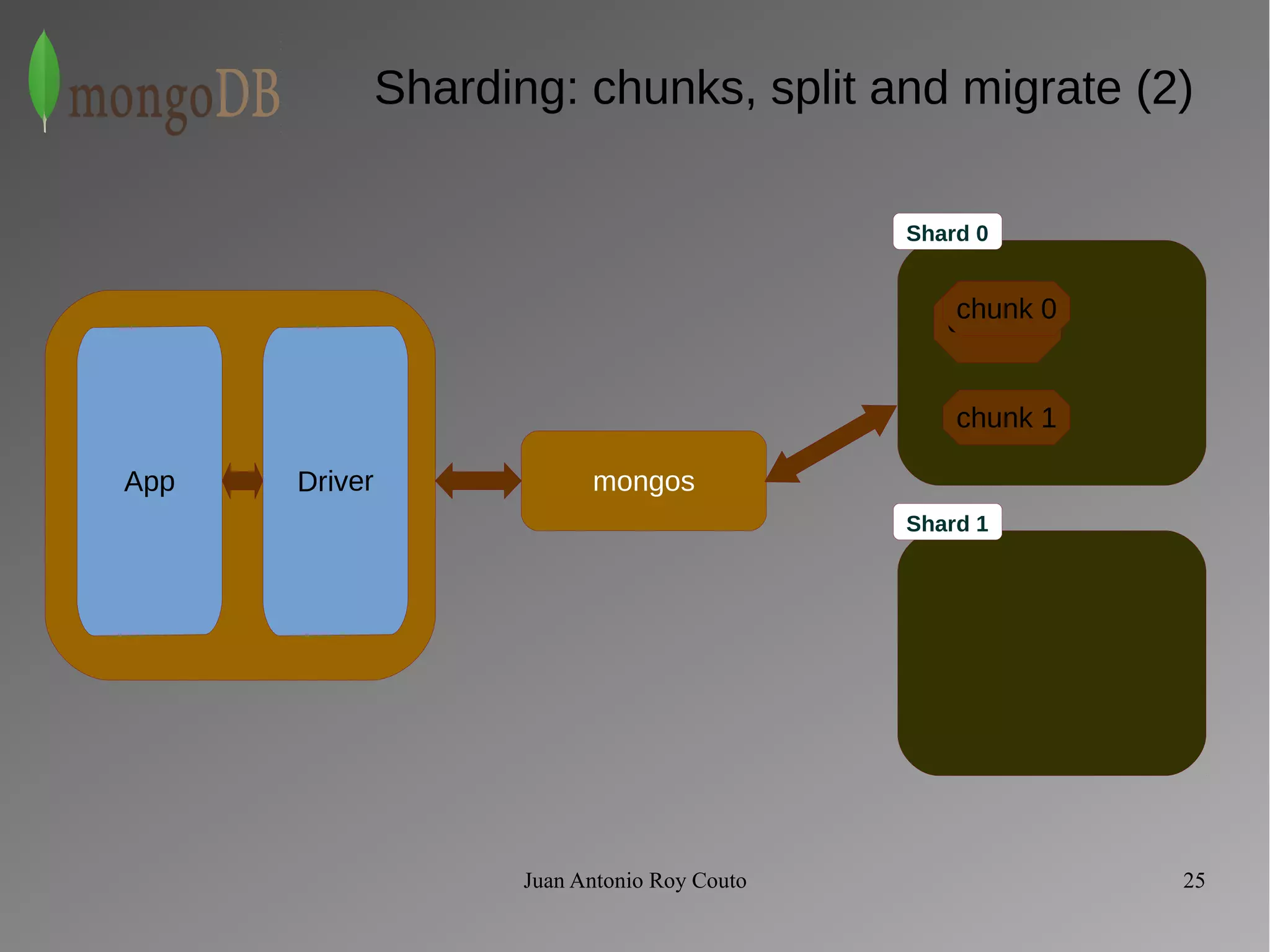
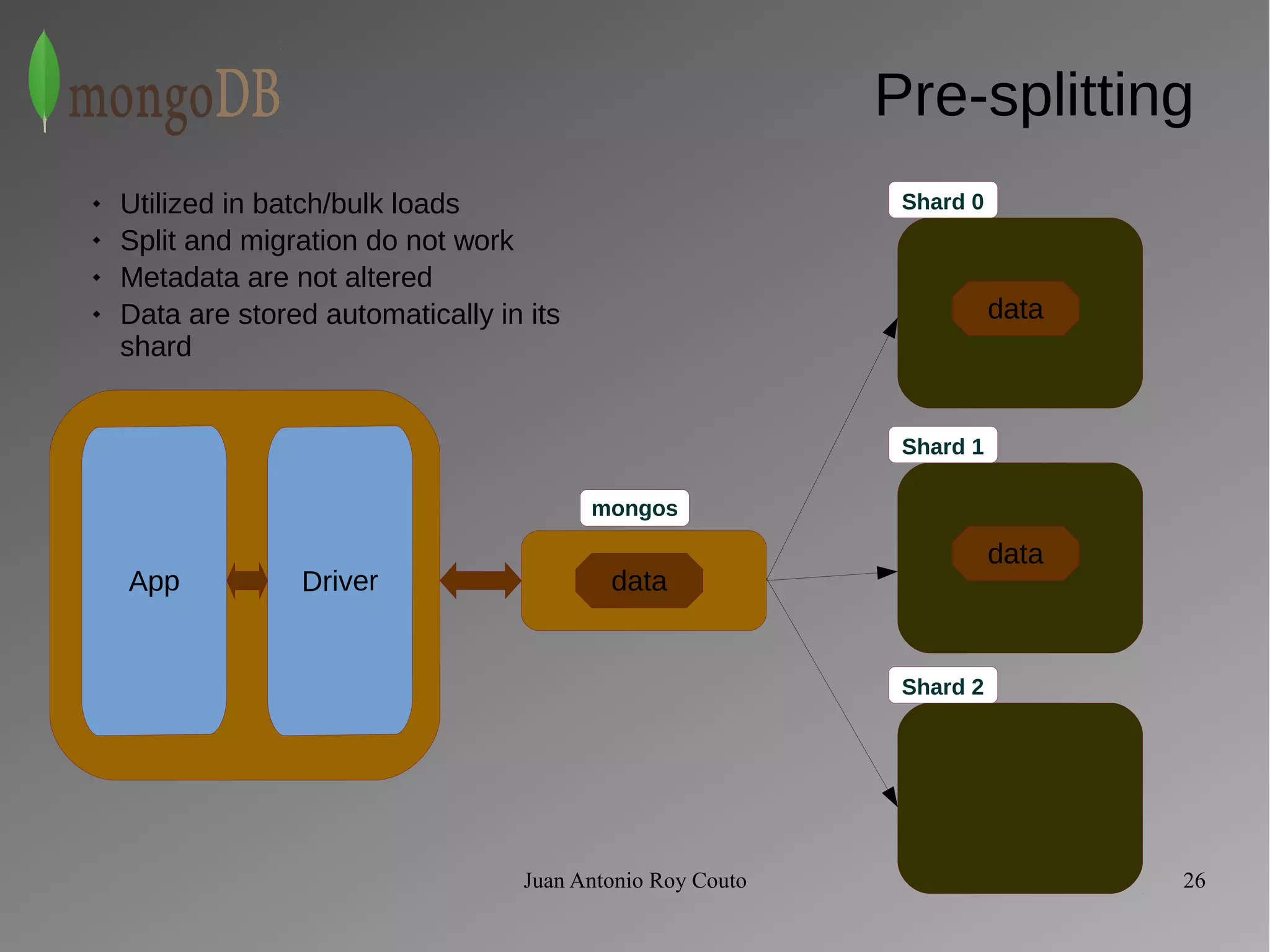
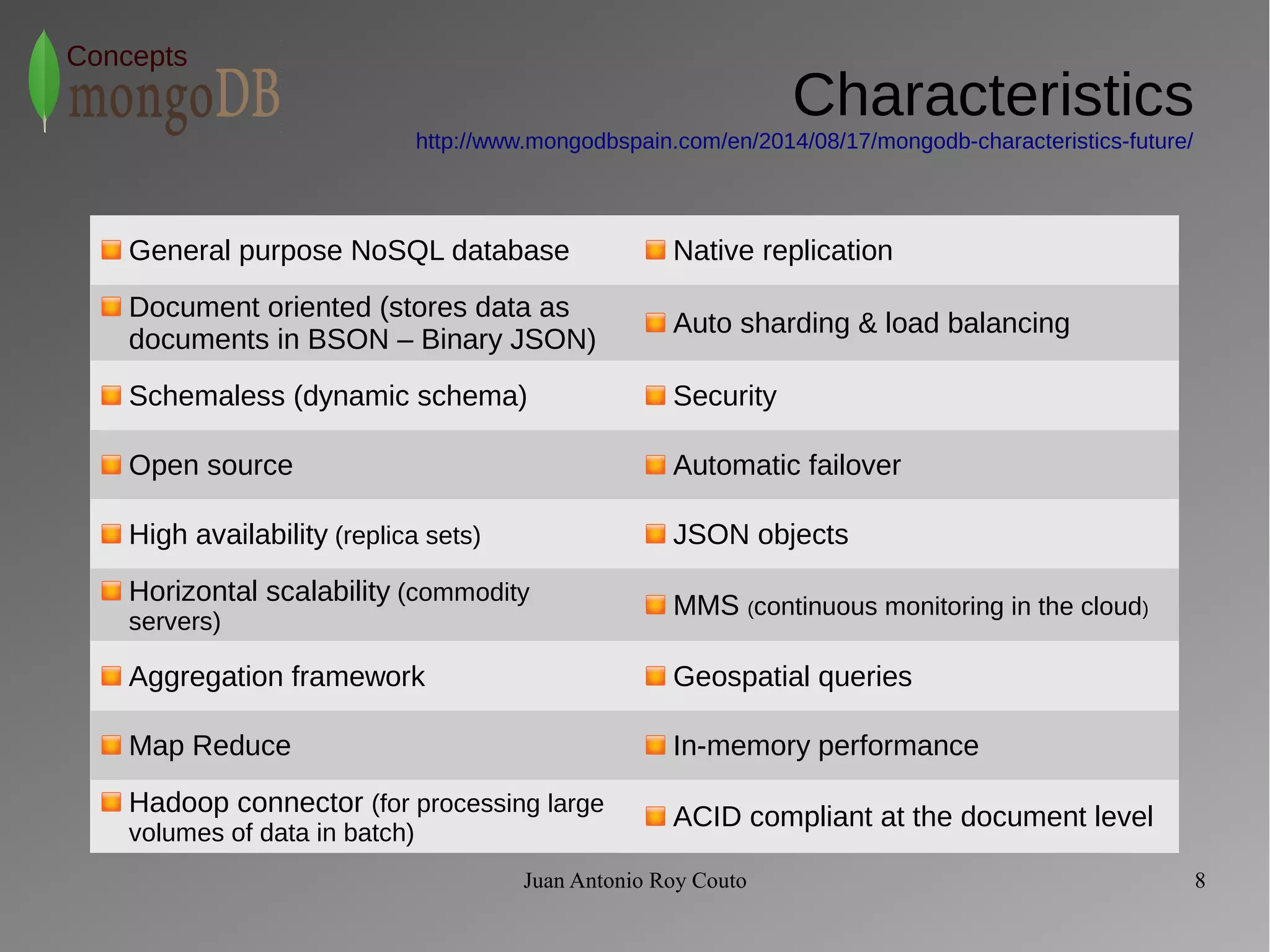
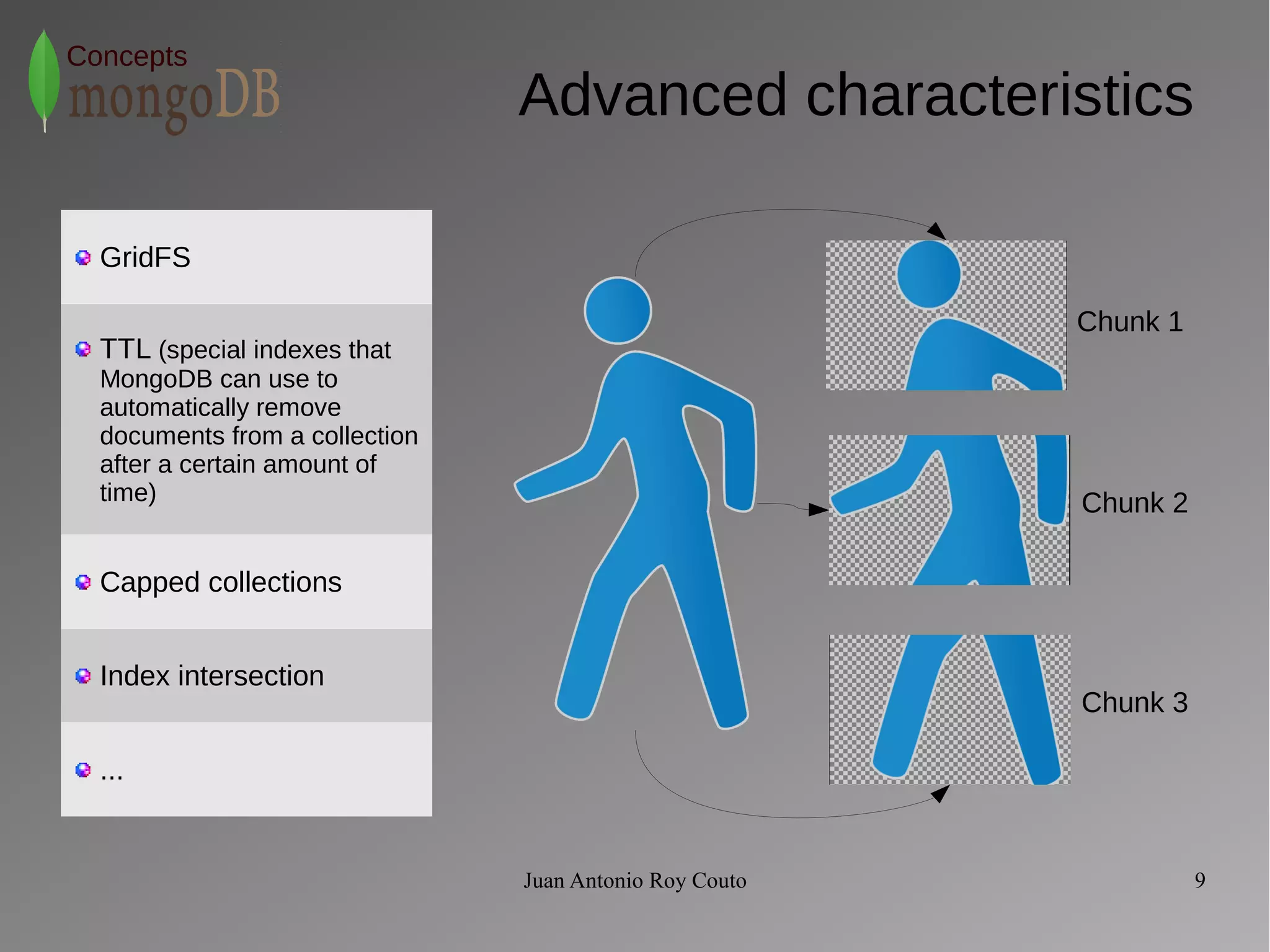
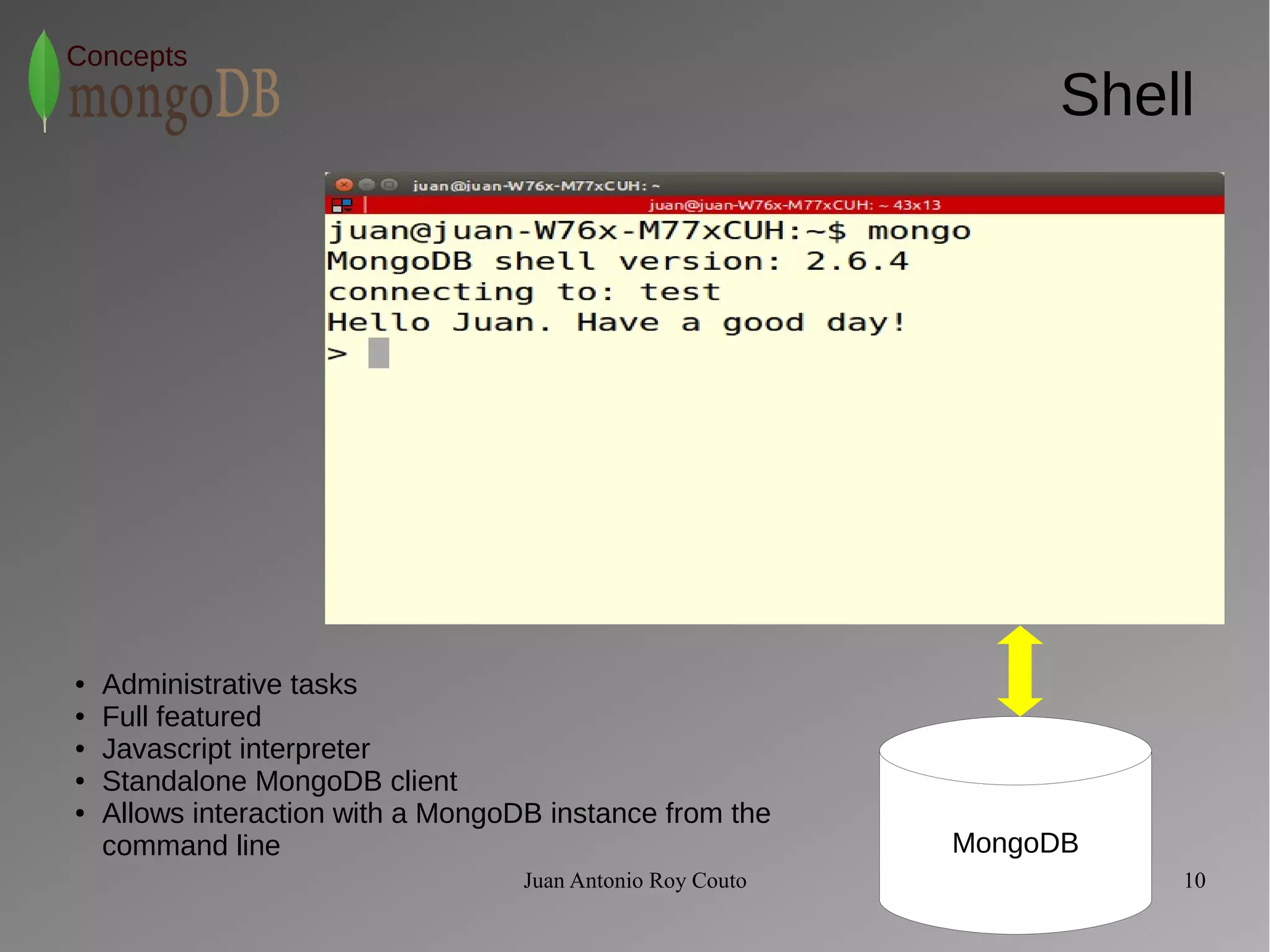
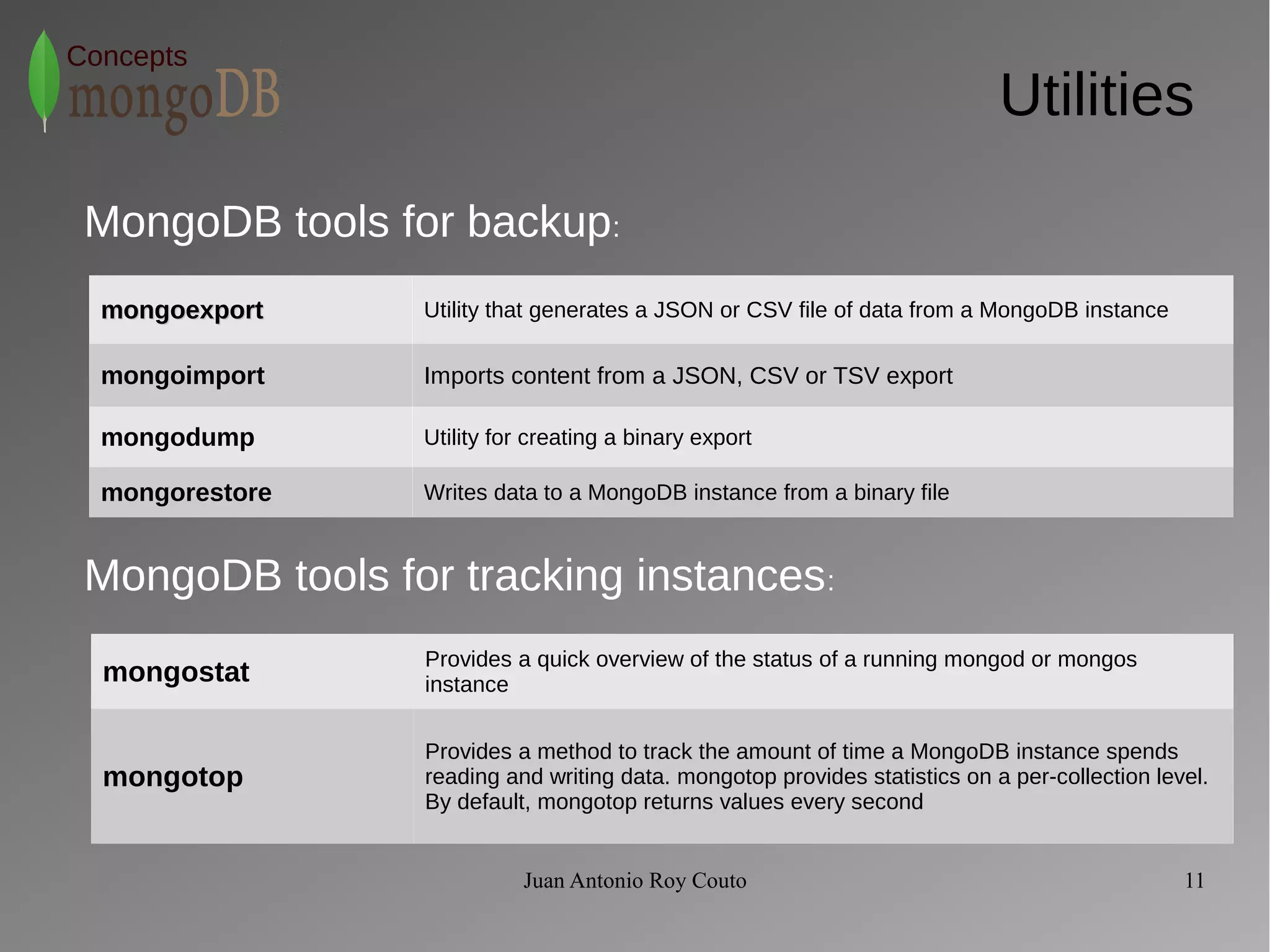
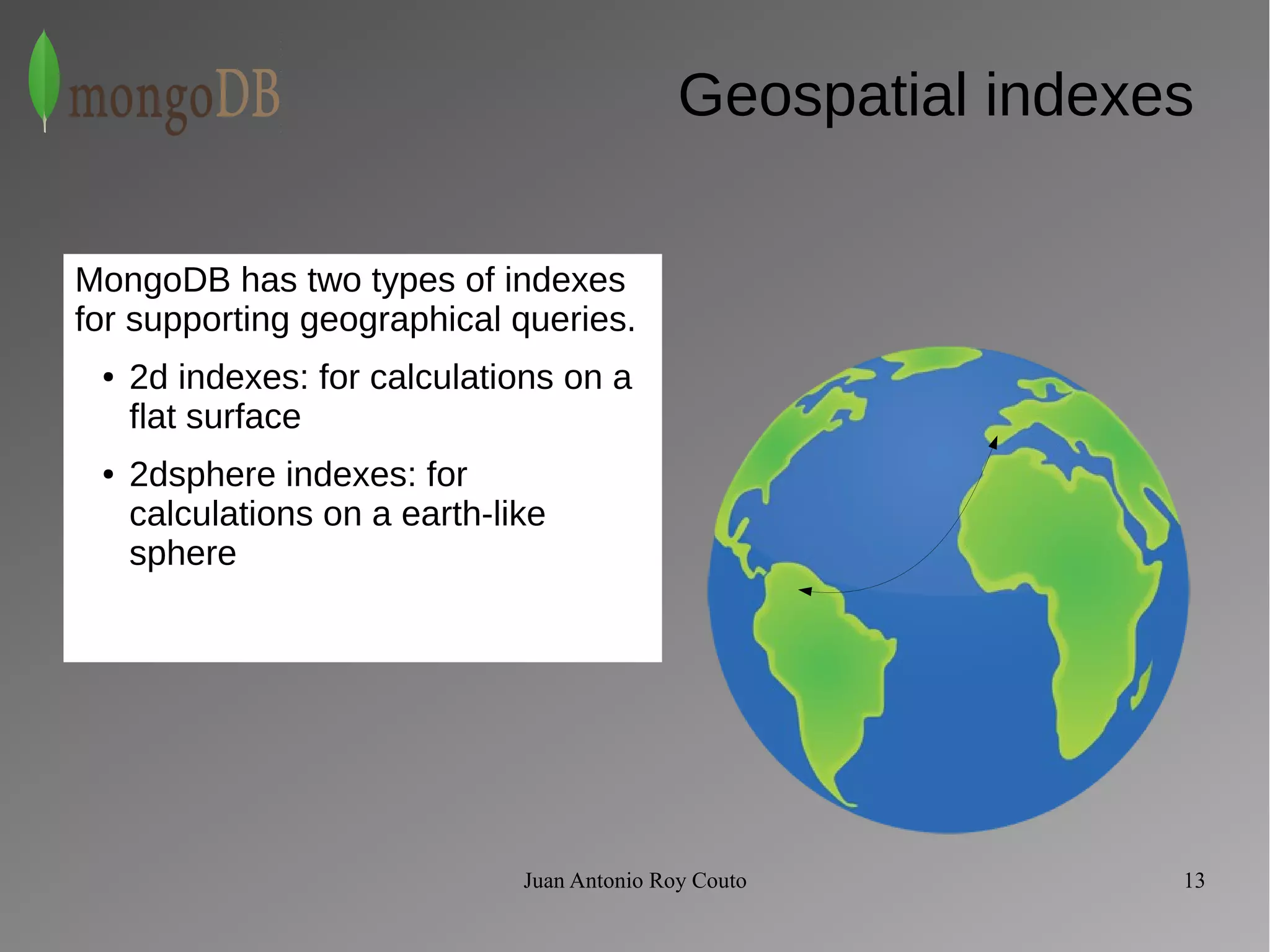
The document discusses key concepts related to MongoDB including its characteristics, replication, sharding, and utilities. MongoDB is a fast, flexible, scalable database designed to reduce administrative tasks through features like replica sets, sharding, and disaster recovery. It also includes powerful analysis tools and indexes that allow for queries on non-relational data structures.


![Customers collection
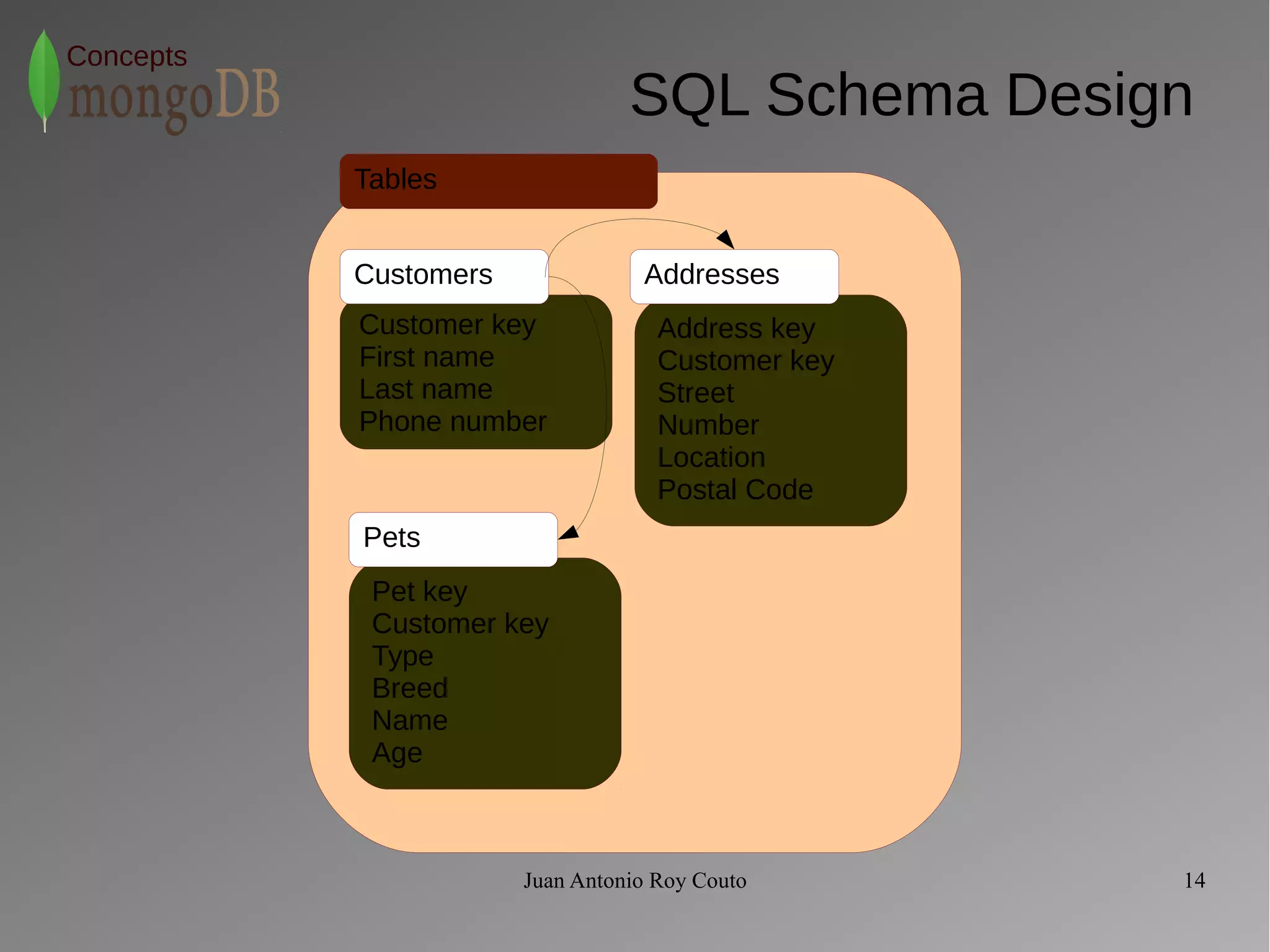
Customer info Addresses
Juan Antonio Roy Couto 15
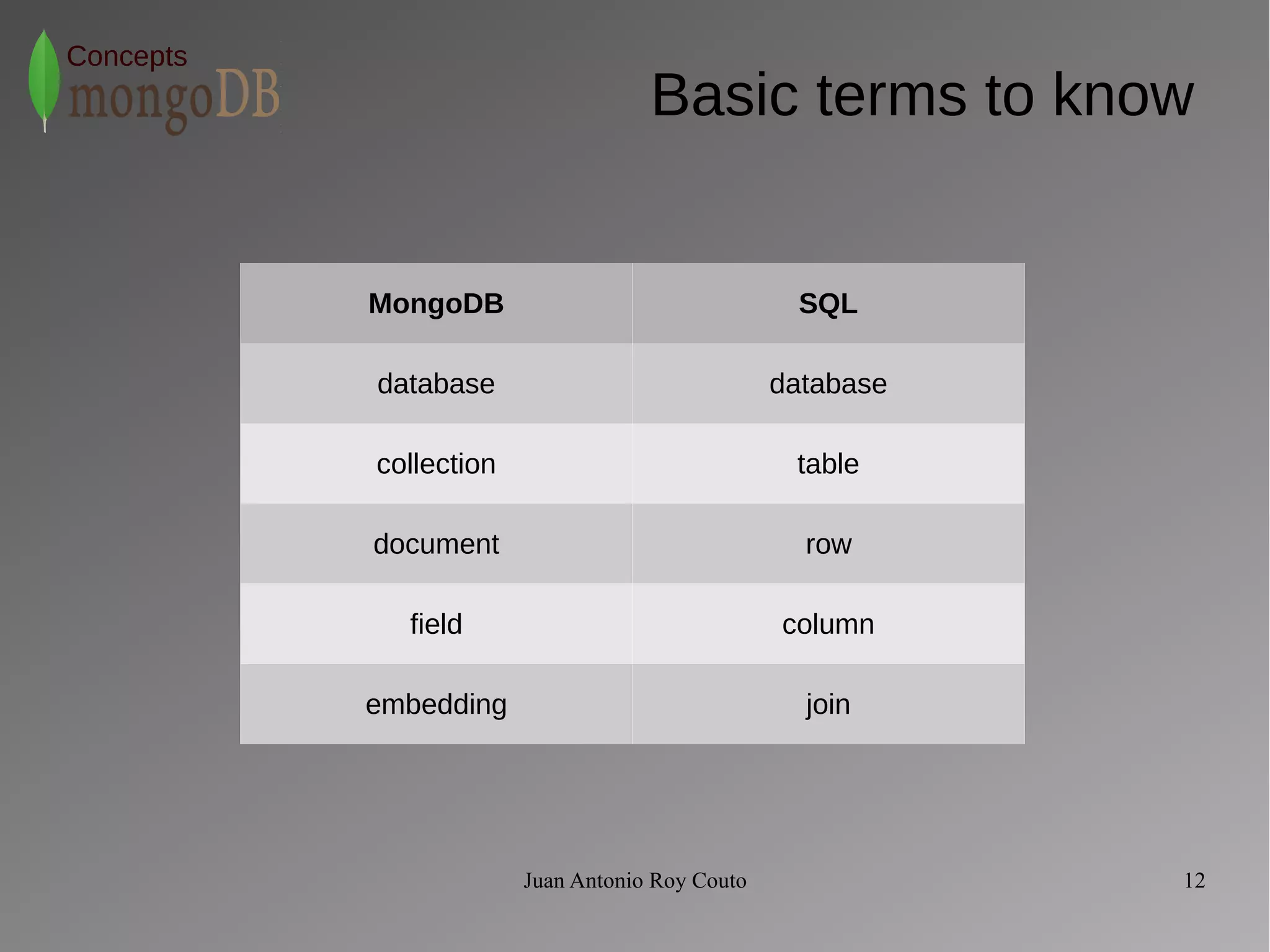
Concepts
MongoDB Schema Design
> db.customers.findOne()
{
"_id" : ObjectId("54131863041cd2e6181156ba"),
"first_name" : "Peter",
"last_name" : "Keil",
"phone_number" : 619123456,
"address" : {
"street" : "C/Alcalá",
"number" : 123,
"location" : "Madrid",
"postal_code" : 12345
},
"pets" : [
{
"type" : "Dog",
"breed" : "Airedale Terrier",
"name" : "Linda",
"age" : 2
},
{
"type" : "Dog",
"breed" : "Akita",
"name" : "Bruto",
"age" : 10
}
]
}
>
First name
Last name
Phone number
Street
Number
Location
Postal Code
Type
Breed
Name
Age
Type
Breed
Name
Age
Pets](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongodbconcepts-140930111407-phpapp01/75/MongoDB-Concepts-15-2048.jpg)