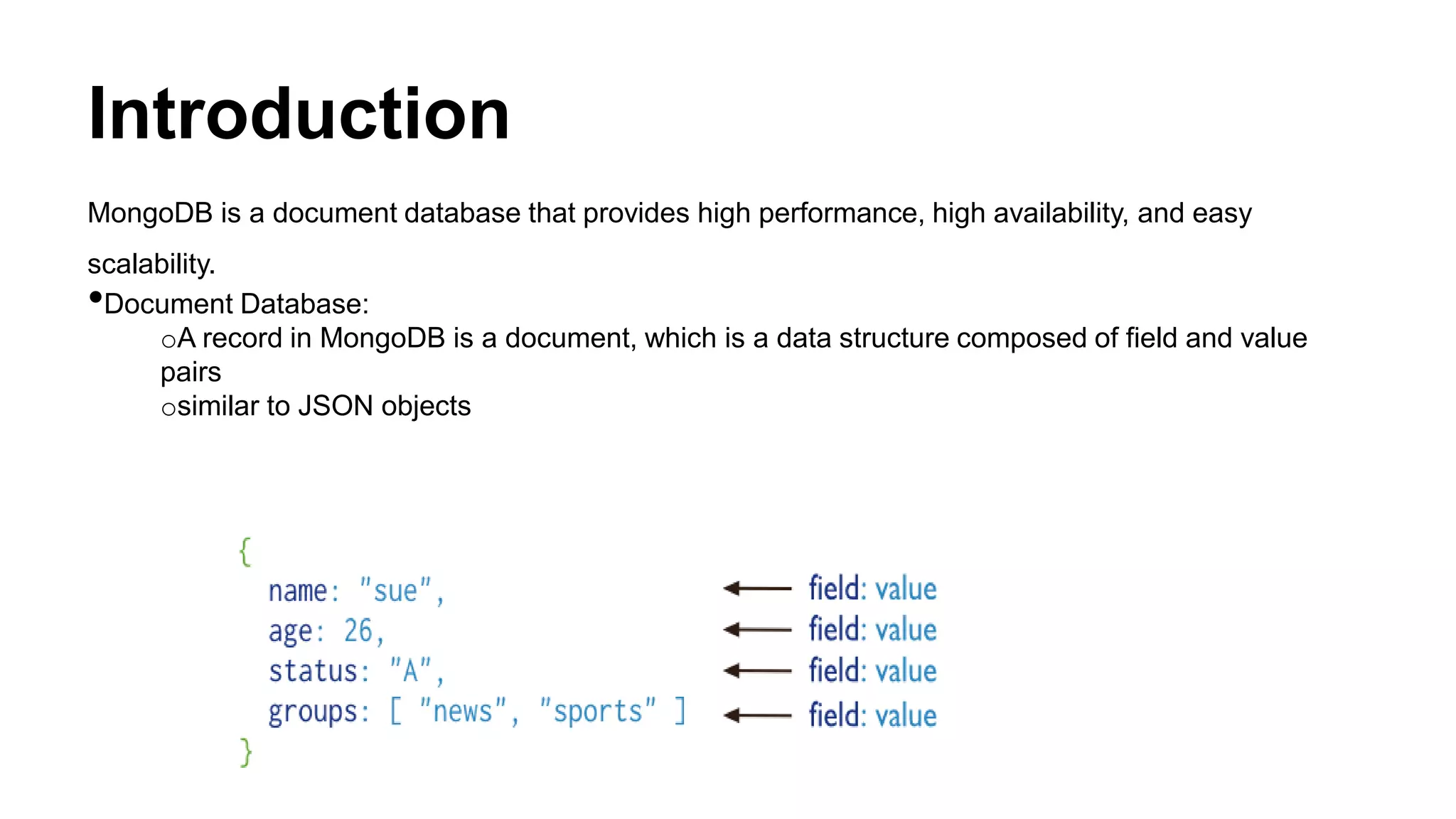
MongoDB is a document database that provides high performance, high availability, and easy scalability. It uses a document-oriented data model where records are stored as documents (similar to JSON objects) which are organized into collections. Key features include embedding for fast reads/writes, indexing, replication for high availability, automatic sharding for scalability, and eventual consistency. Documents contain fields, embedded documents, and arrays. Queries use operators like $lt, $gte, $ne to filter results similar to SQL WHERE clauses. Records can be inserted, updated, deleted, sorted, limited, and projected. MongoDB can be backed up using mongodump which dumps collections to files that can be restored using mongorestore.





![Data Types
•date
oDate are stored in milliseconds since the epoch. The time zone is not stored.
o{“x”:new Date()}
•code
oDocument can also contain JavaScript code
o{“x”: function() {/*.......*/}}
•binary data
•undefined
o{“x”: undefined}
•array
o{“x”: [“a”, “b”, “c”]}
•embedded document
oDocument can contain entire documents, embedded as values in the parent document.
o{“x”: {“name” : “Your Name”}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mondodb-140430123400-phpapp01/75/Mondodb-7-2048.jpg)

![MongoDB Query
•Insert Document
>db.collection_name.insert(document)
•Example;
>db.mycol.insert({
_id: ObjectId(7df78ad8902c),
title: 'MongoDB Overview',
description: 'MongoDB is no sql database',
by: ganesh kunwar,
url: 'http://www.ganeshkunwar.com.np',
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 100
})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mondodb-140430123400-phpapp01/75/Mondodb-9-2048.jpg)
![MongoDB Query
•Find()
oquery data from collection
o> db.COLLECTION_NAME.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("53371ed996322bd29e878e2b"), "title" : "MongoDB Overview",
"description" : "MongoDB is no sql database", "by" : "ganesh kunwar", "url" :
"http://www.ganeshkunwar.com.np", "tags" : [ "mongodb", "database", "NoSQL" ], "likes" : 100 }
•Pretty()
odisplay the result in formatted way
o> db.COLLECTION_NAME.find().pretty()
{
_id: ObjectId(7df78ad8902c),
title: 'MongoDB Overview',
description: 'MongoDB is no sql database',
by: ganesh kunwar,
url: 'http://www.ganeshkunwar.com.np',
tags: ['mongodb', 'database', 'NoSQL'],
likes: 100
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mondodb-140430123400-phpapp01/75/Mondodb-10-2048.jpg)
![MongoDB Query
•findOne()
oreturns only one document.
•And in MongoDB
o> db.mycol.find(key1: value1, key2: value2)
•OR in MongoDB
o> db.mycol.find($or: [{key1: value1}, {key2, value2}] )
•And and OR together
o> db.myclo.find(key1: val1, $or: [{key2: value2}, {key3, value3}] )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mondodb-140430123400-phpapp01/75/Mondodb-11-2048.jpg)








