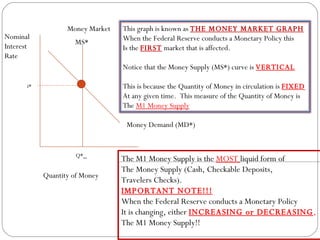
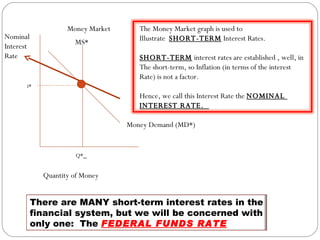
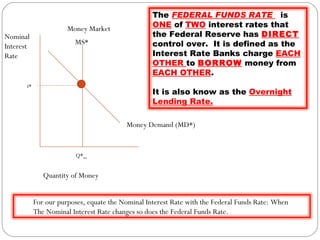
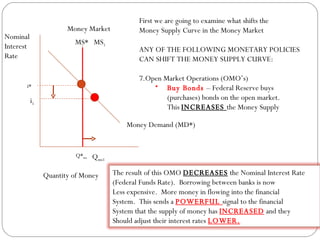
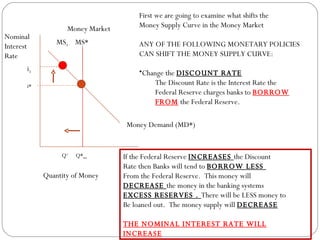
The document discusses the money market graph and how it is used to illustrate short-term interest rates. It explains that the Federal Reserve has three main policy tools to change the money supply curve: open market operations, changing the discount rate, and changing reserve requirements. Adjusting these tools can shift the money supply curve to either increase or decrease the money supply and nominal interest rates, pursuing either an expansionary or contractionary monetary policy.