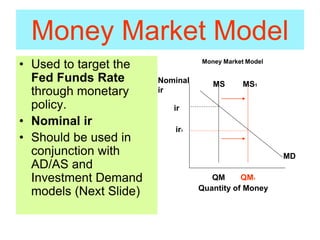
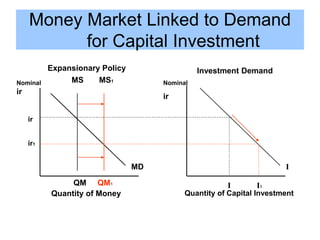
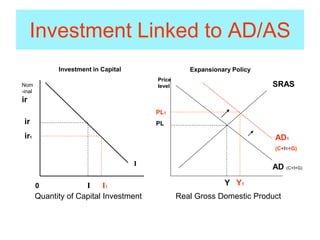
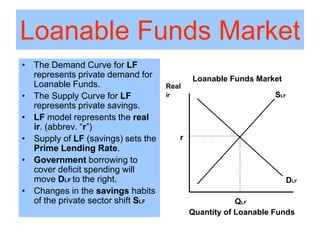
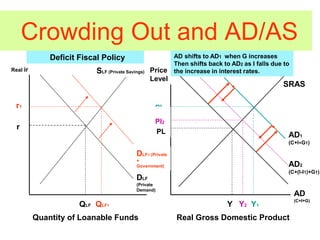
This document provides an overview of interest rates and their impact on the economy. It discusses how interest rates act as signals in the market, helping to allocate resources efficiently. The key models used to demonstrate how interest rates work include the money market model, loanable funds market, and aggregate demand/aggregate supply. Monetary and fiscal policy can influence interest rates. For example, deficit spending by the government increases demand for loanable funds, putting upward pressure on rates. Higher interest rates can then "crowd out" private investment. The document defines important terms and concepts related to nominal and real interest rates, money supply, demand for money, and how the Federal Reserve uses tools like the discount rate and required reserve ratio to implement monetary policy.