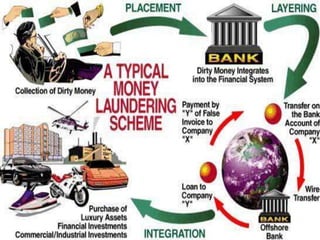
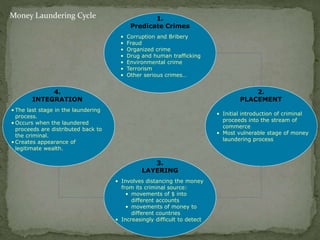
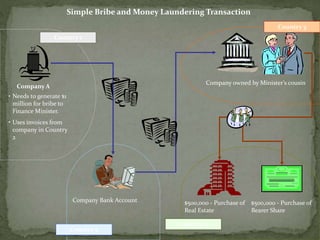
Money laundering is defined as the process of disguising illegally obtained money to make it appear legitimate. It originated from mafia ownership of laundromats in the US and can involve complex techniques to conceal the illicit origins of funds. Money laundering is estimated to cost between $500 billion to $1.5 trillion annually worldwide and poses significant social and economic threats. Countries like India have established agencies and laws to help prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.