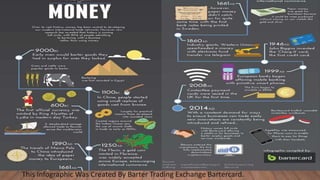
The document provides a comprehensive overview of money, including its history, meaning, functions, and various types. It explains that money serves as a medium of exchange, a measure of value, and a store of value, among other roles, and traces the evolution of money from cattle and coins to paper currency and cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Additionally, it discusses the emotional and behavioral implications of money in individual lives and relationships.