This document discusses the workings of MongoDB indexing and the query optimizer, focusing on version 1.8 and its similarities to earlier versions. It covers various functionalities, including different query types, indexing behaviors, and query optimization techniques through examples and explanations. The document aims to help users understand how to make effective optimizations using these MongoDB features.








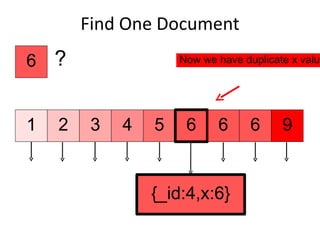

![Find One Document > db.c.find( {x:6} ).limit( 1 ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 1, "nscannedObjects" : 1, "n" : 1, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : false, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ 6, 6 ] ] } } Uses a btree cursor to find the object. Index ranges are around a single value.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-11-320.jpg)








![Equality Match > db.c.find( {x:6} ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 3, "nscannedObjects" : 3, "n" : 3, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : false, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ 6, 6 ] ] } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-20-320.jpg)





![Full Document Matcher > db.c.find( {x:6,y:1} ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 3, "nscannedObjects" : 3, "n" : 1, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : false, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ 6, 6 ] ] } } Documents for all matching index keys are scanned, but only one document matched on non index keys.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-26-320.jpg)



![Range Match > db.c.find( {x:{$gte:4,$lte:7}} ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 4, "nscannedObjects" : 4, "n" : 4, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : false, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ 4, 7 ] ] } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-30-320.jpg)






![documents contain lists with several values like [8,9].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-38-320.jpg)
![Multikeys 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 ? > 7 {_id:4,x:[8,9]} 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-39-320.jpg)
![Multikeys > db.c.find( {x:{$gt:7}} ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 2, "nscannedObjects" : 2, "n" : 1, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : true, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ 7, 1.7976931348623157e+308 ] ] } } All keys in valid range are scanned, but the matcher rejects duplicate documents making n == 1.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-40-320.jpg)




![Range Types db.c.find( {x:/^a/} ) "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ "a", "b" ], [ /^a/, /^a/ ] ] } 2 ranges scanned of 2 different types: string and regex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-45-320.jpg)
![Range Types db.c.find( {x:/a/} ) "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ "", { } ], [ /a/, /a/ ] ] } Here the index only helps to restrict type, not efficient in practice](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-46-320.jpg)
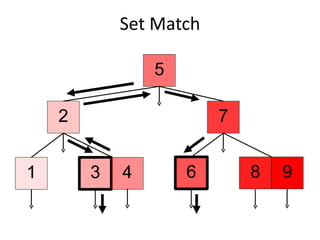
![Set Match db.c.find( {x:{$in:[3,6]}} )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-47-320.jpg)


![Set Match > db.c.find( {x:{$in:[3,6]}} ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1 multi", "nscanned" : 3, "nscannedObjects" : 2, "n" : 2, "millis" : 8, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : false, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ 3, 3 ], [ 6, 6 ] ] }} Why is nscanned 3? This is an algorithmic detail, when there are disjoint ranges for a key nscanned may be higher than the number of matching keys.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-50-320.jpg)

![All Match db.c.find( {x:{$all:[3,6]}} )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-52-320.jpg)

![All Match 8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 3 ? {_id:4,x:[3,6]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-54-320.jpg)
![All Match > db.c.find( {x:{$all:[3,6]}} ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 1, "nscannedObjects" : 1, "n" : 1, "millis" : 0, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : true, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ 3, 3 ] ] } } The first entry in the $all match array is always used for index bounds. Note this may not be the least numerous indexed value in the $all array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-55-320.jpg)




![Limit > db.c.find( {x:{$lt:6},y:3} ).limit( 3 ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 4, "nscannedObjects" : 4, "n" : 3, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : true, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ -1.7976931348623157e+308, 6 ] ] } } Scan until three matches are found, then stop.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-60-320.jpg)



![Skip > db.c.find( {x:{$lt:6},y:3} ).skip( 3 ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 5, "nscannedObjects" : 5, "n" : 1, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : true, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ -1.7976931348623157e+308, 6 ] ] } } All skipped documents are scanned.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-64-320.jpg)




![Sort > db.c.find( {x:{$lt:6},y:3} ).sort( {x:1} ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 5, "nscannedObjects" : 5, "n" : 4, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : true, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ -1.7976931348623157e+308, 6 ] ] } } Find uses the btree cursor to easily sort data](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-69-320.jpg)




![Sort Results are sorted on the fly to match requested order. The scanAndOrder field is only printed when its value is true. > db.c.find( {x:{$lt:6},y:3} ).sort( {y:1} ).explain() { "cursor" : "BtreeCursor x_1", "nscanned" : 5, "nscannedObjects" : 5, "n" : 4, "scanAndOrder" : true, "millis" : 1, "nYields" : 0, "nChunkSkips" : 0, "isMultiKey" : true, "indexOnly" : false, "indexBounds" : { "x" : [ [ -1.7976931348623157e+308, 6 ] ] } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingmongosv-110325053243-phpapp02/85/2011-Mongo-FR-Indexing-in-MongoDB-74-320.jpg)



