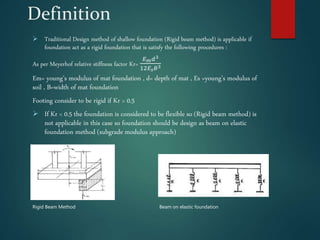
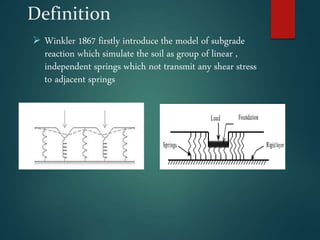
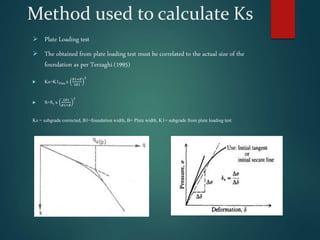
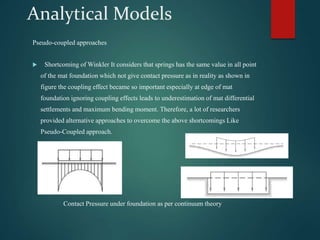
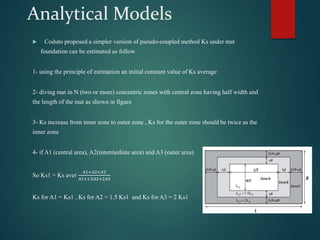
This document discusses the modulus of subgrade reaction (Ks), which represents the relationship between applied stress and associated soil settlement beneath foundations. It defines Ks and describes several analytical models and methods for calculating Ks values, including plate loading tests, correlations with soil properties, and pseudo-coupled approaches that assign different Ks values depending on location beneath the foundation. Factors that influence Ks include soil type, moisture content, and foundation geometry.