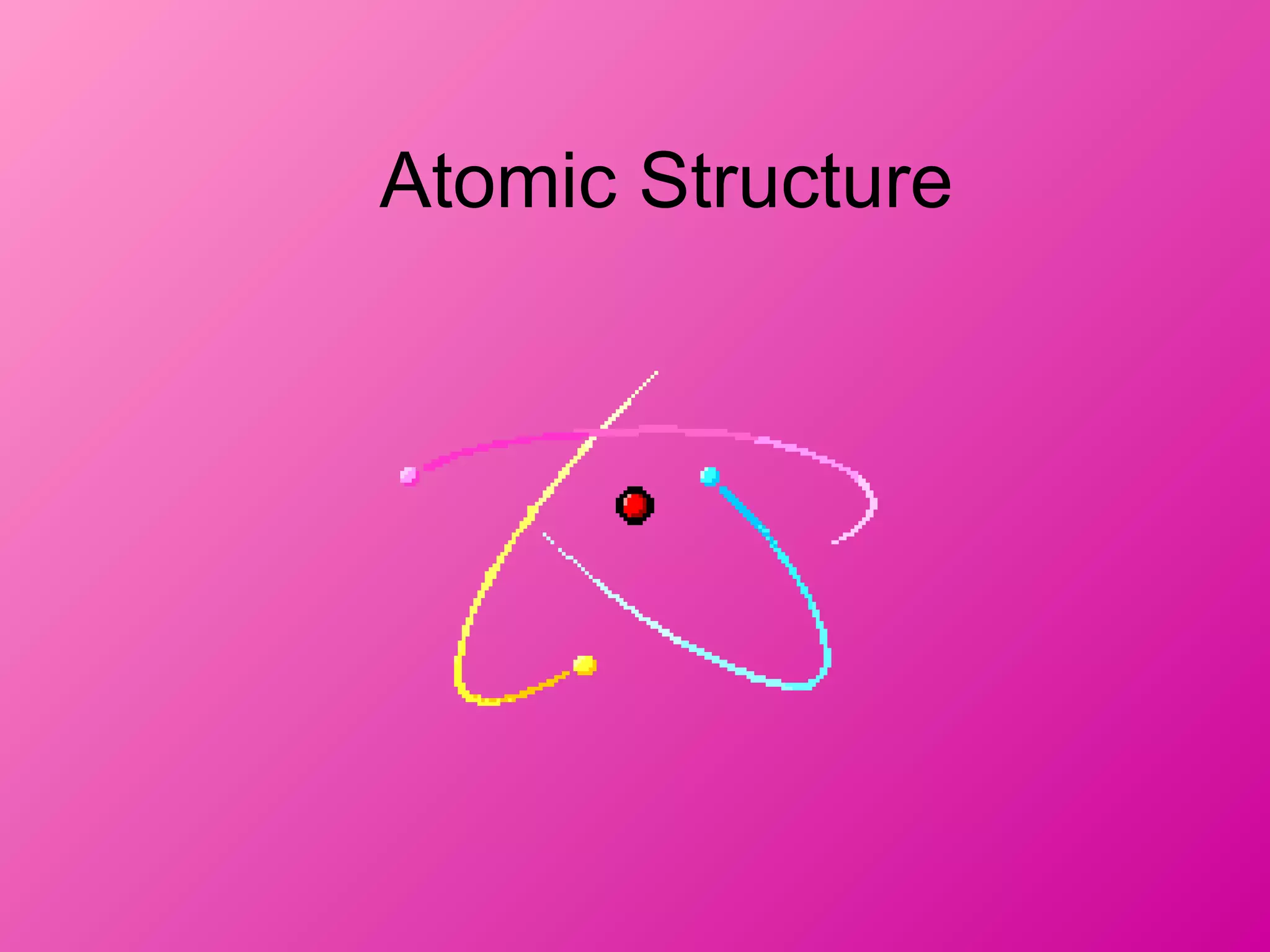
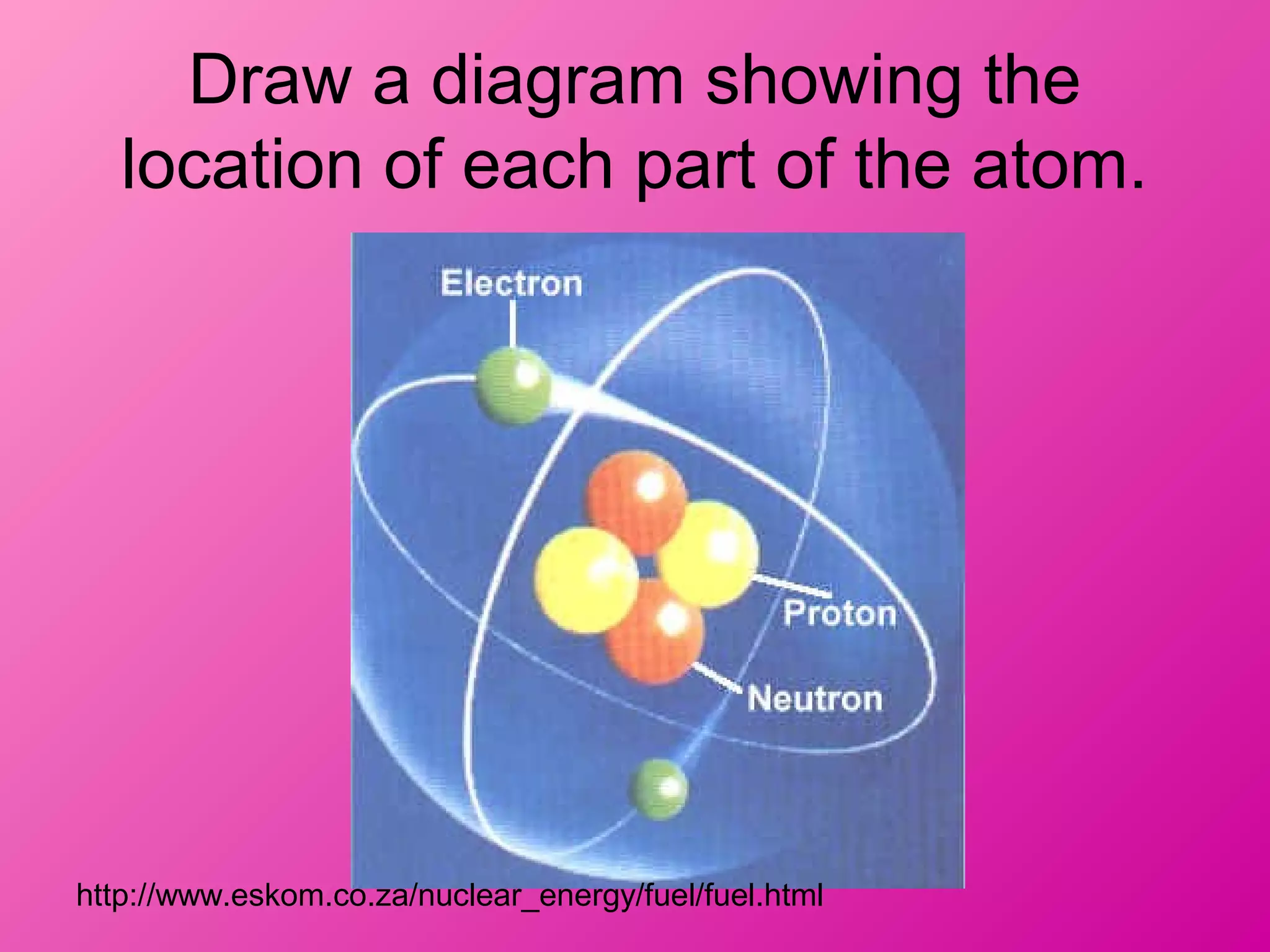
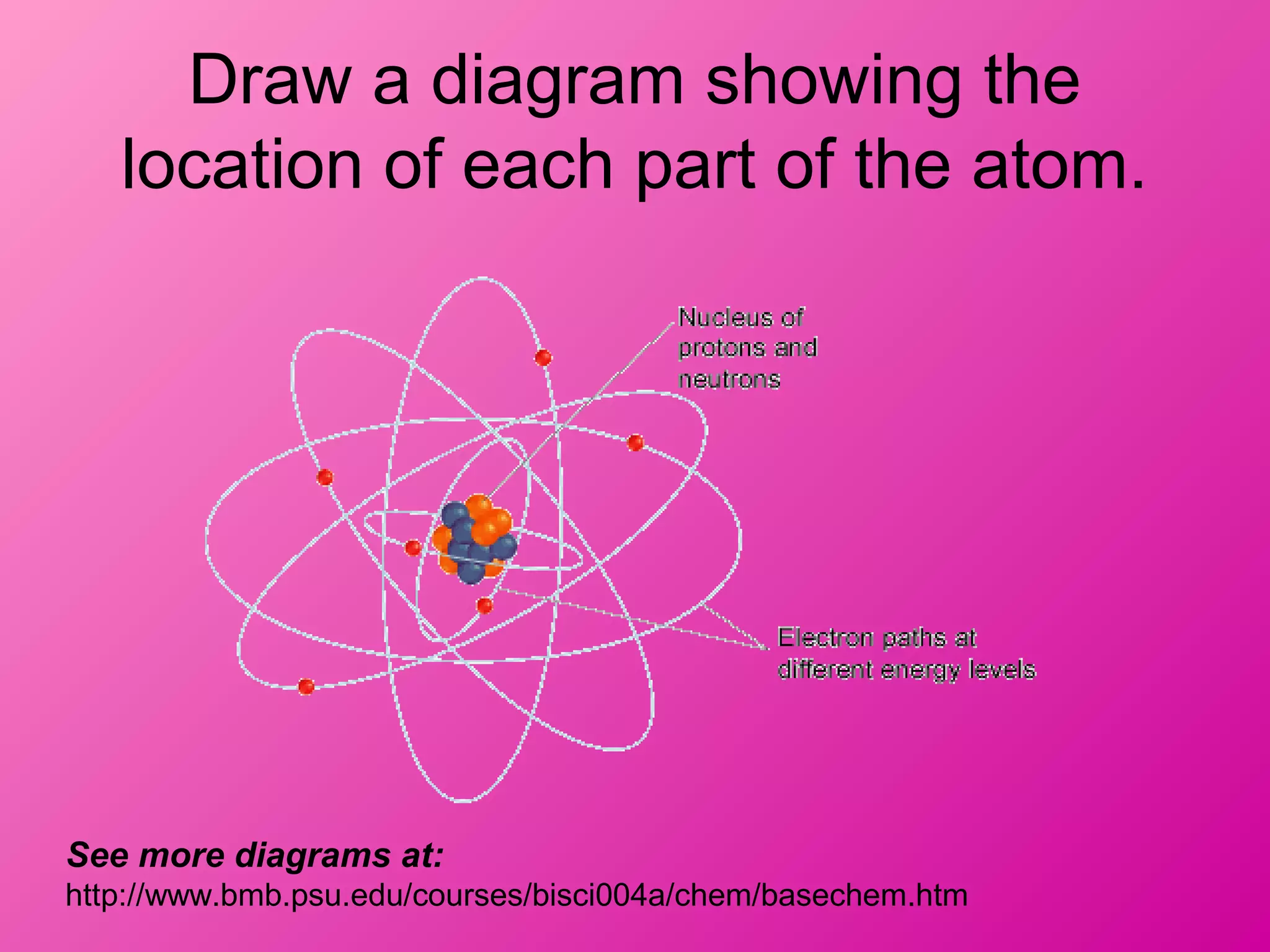
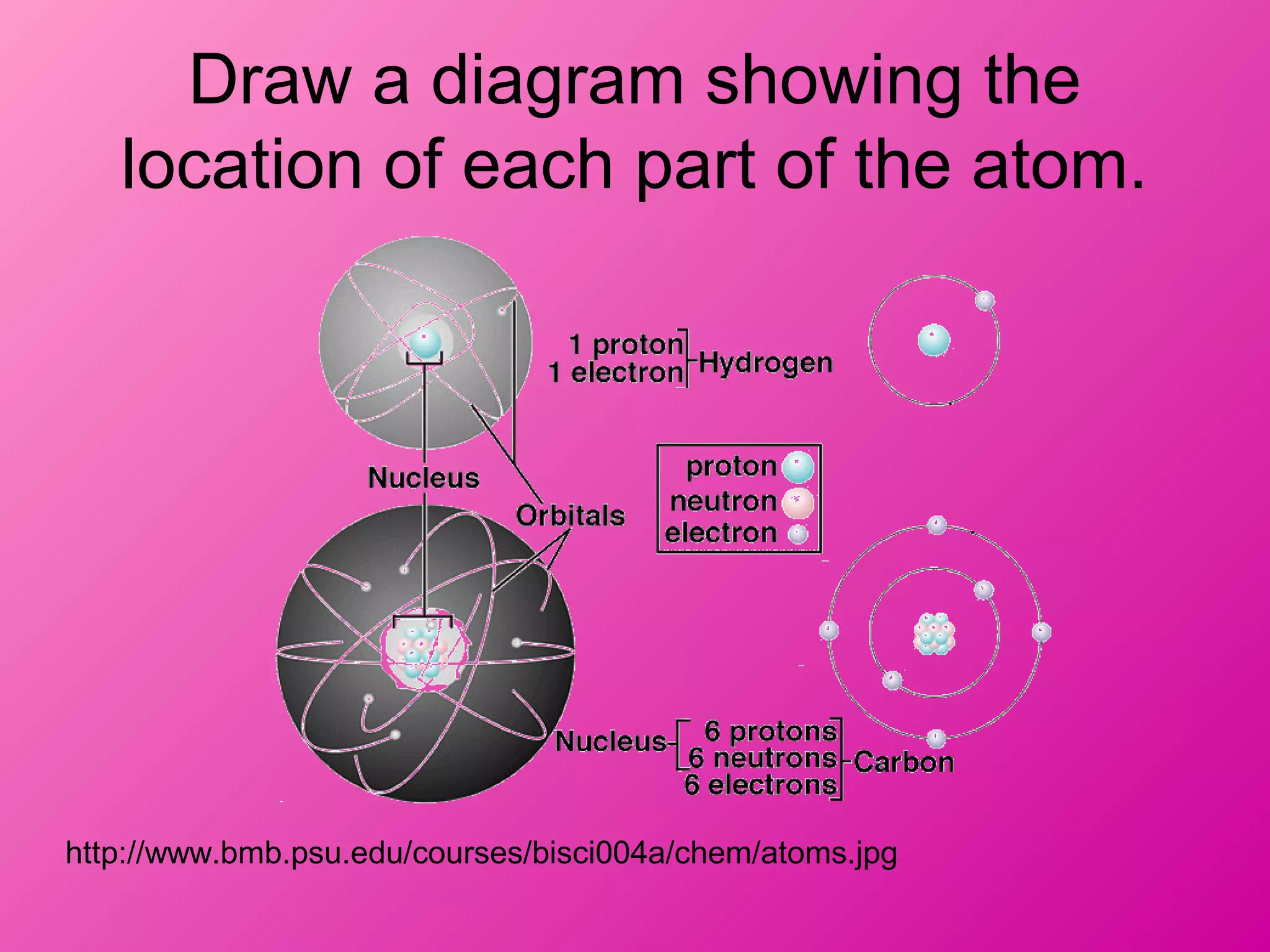
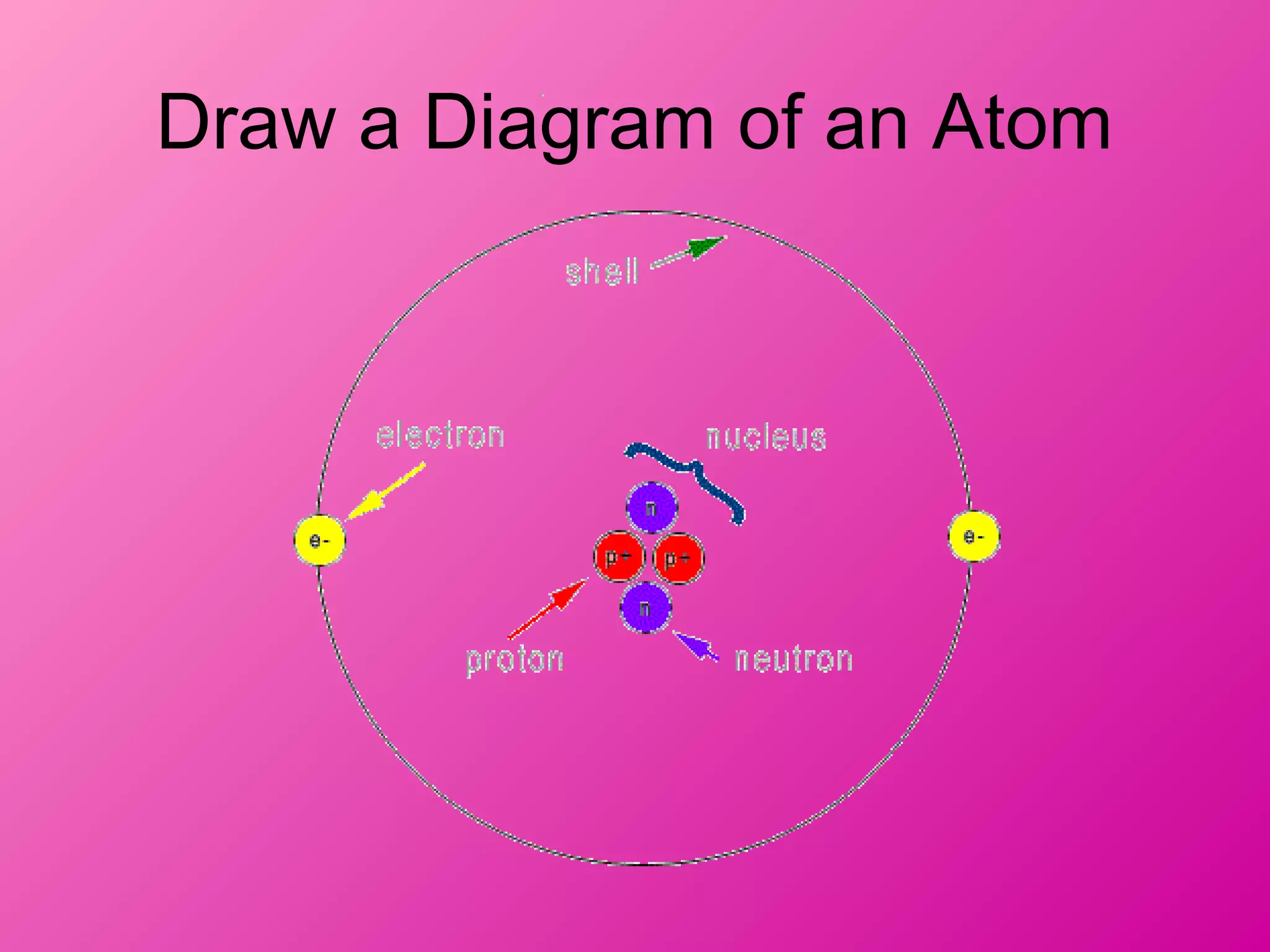
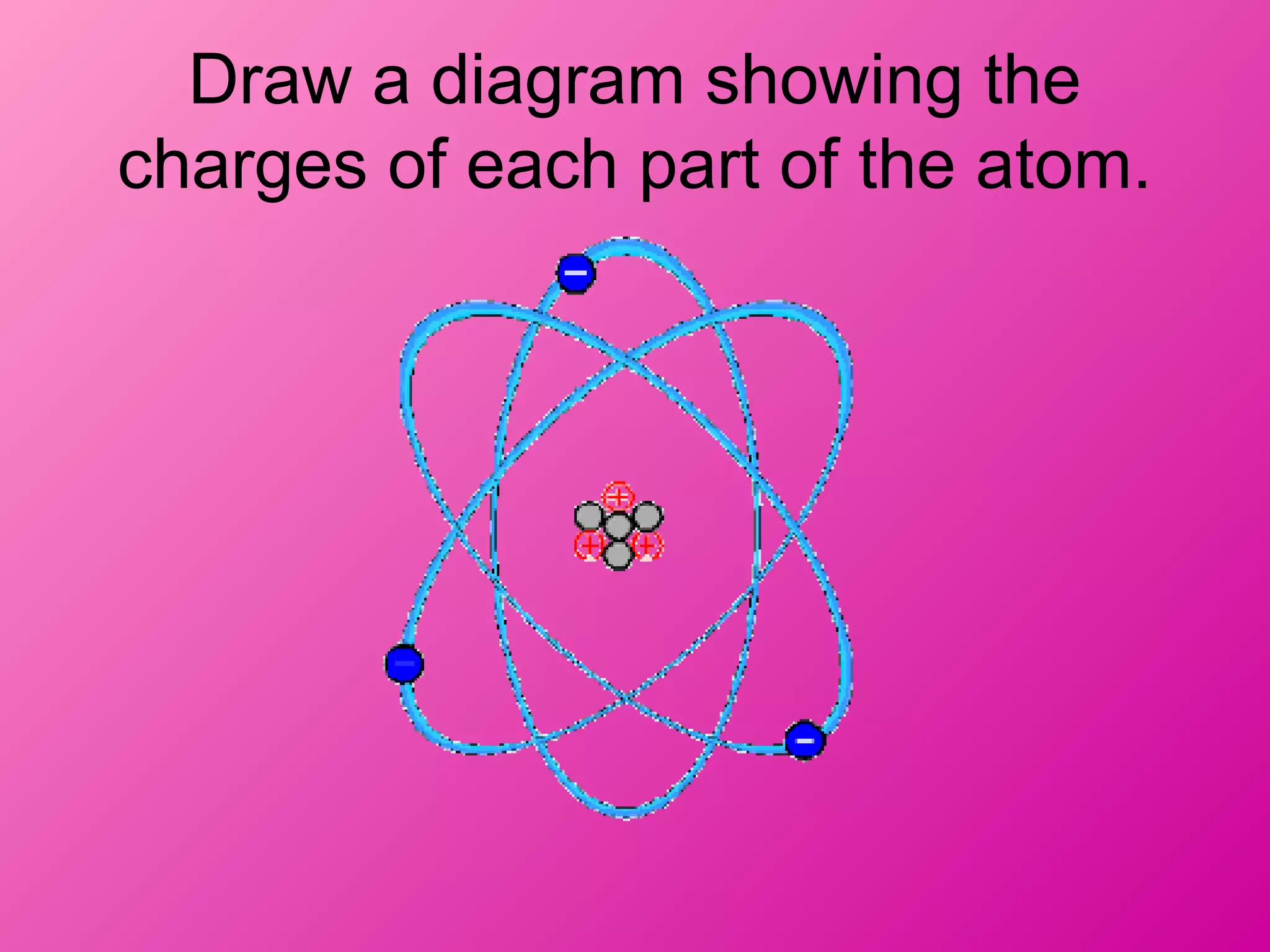
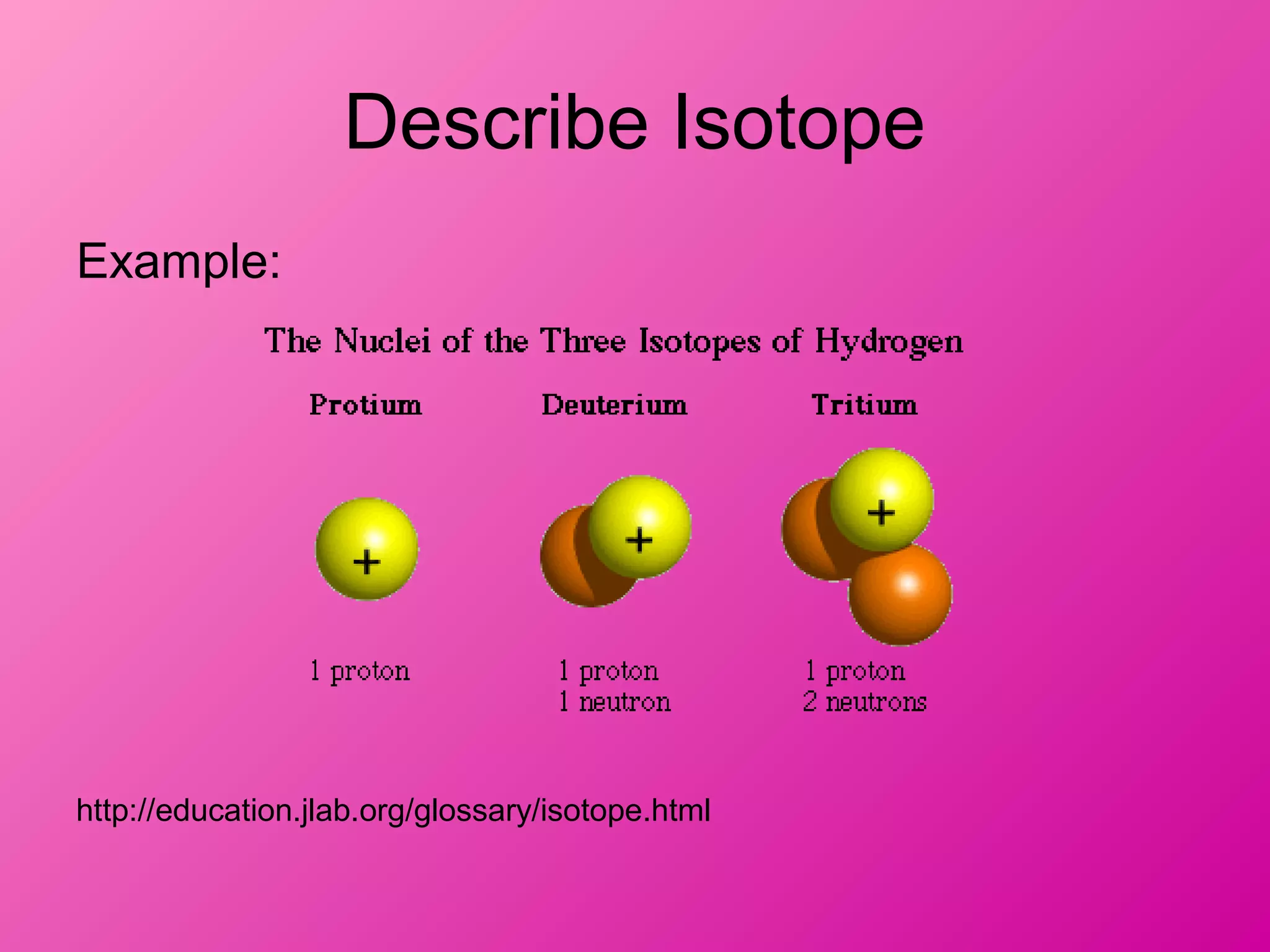
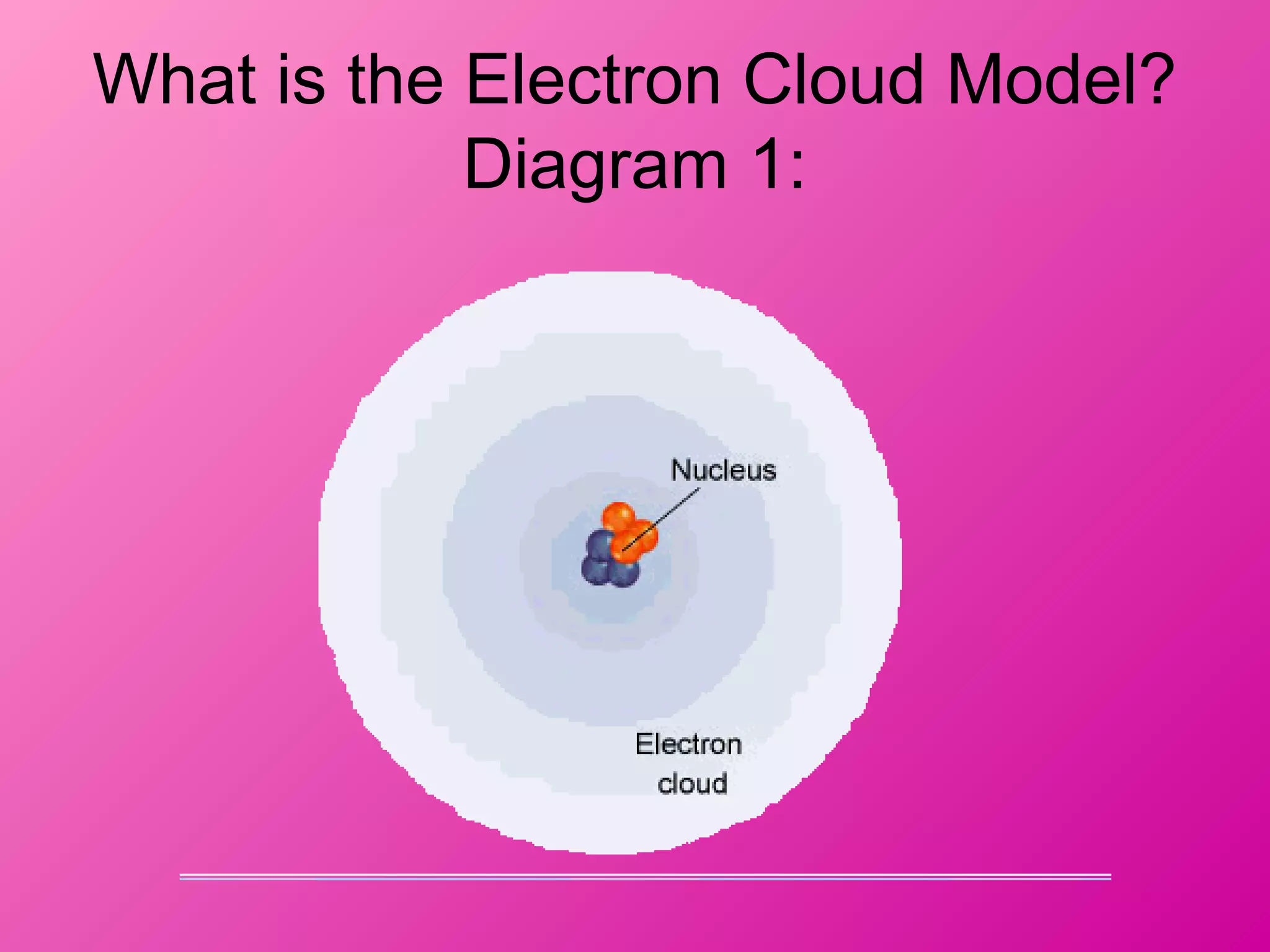
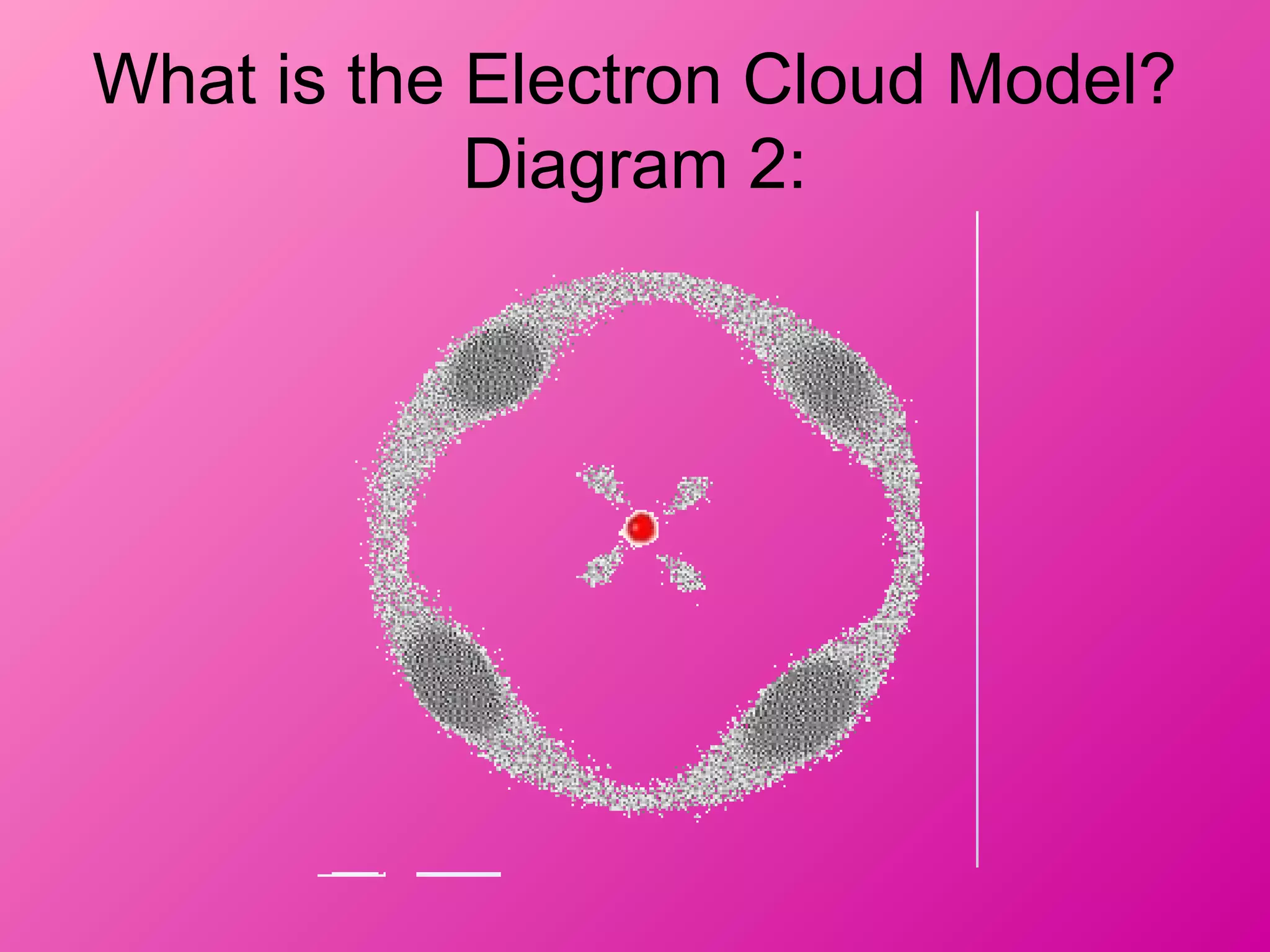
The document discusses the major parts of an atom: protons, neutrons, and electrons. It provides descriptions of each part, including their composition and location within the atom. Diagrams are included to illustrate the structure of the atom and the positions of the subatomic particles. Additional topics covered include isotopes, quarks, and the electron cloud model of atomic structure.