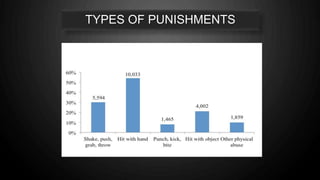
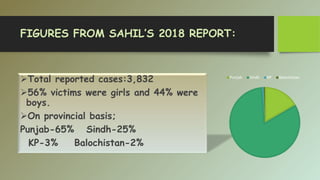
The document discusses the issue of child abuse, including its widespread prevalence and harmful impacts. It notes that millions of children worldwide experience abuse, neglect, exploitation and violence in their homes, schools, and communities each day. This takes a significant toll on their physical and mental health as well as their overall quality of life. The consequences of this violence can also be intergenerational, as those abused as children are more likely to become abusive adults. The stakes are high, as the experiences children have in their childhood will shape the future society they construct as adults.