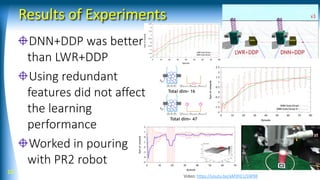
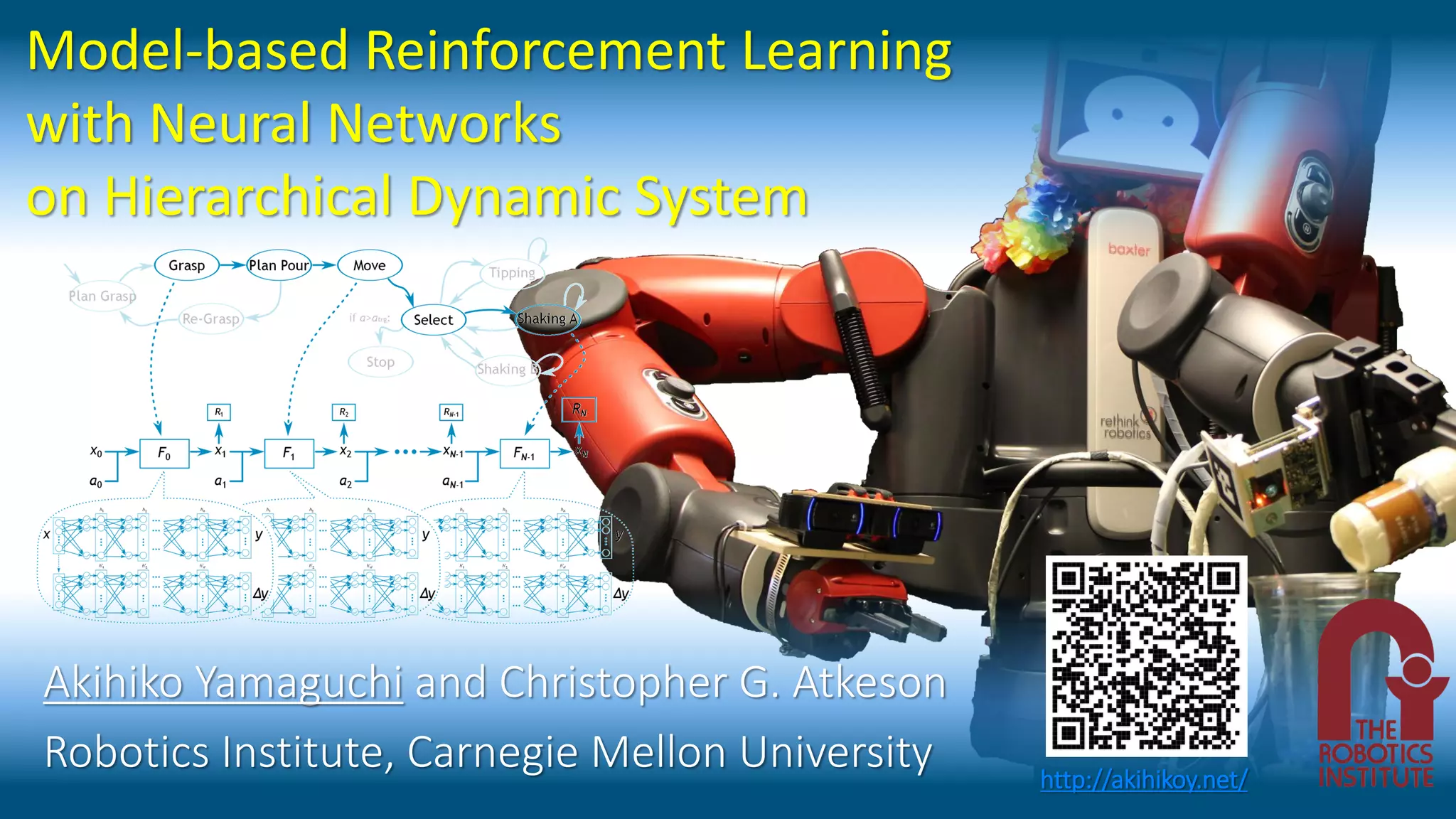
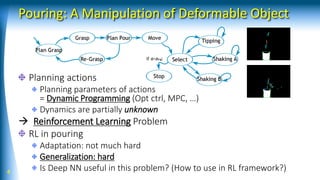
This document discusses model-based reinforcement learning using neural networks for hierarchical dynamic systems. It proposes using stochastic neural networks to model subsystem dynamics and handle uncertainty. Stochastic differential dynamic programming is also introduced to deal with simulation biases from learned models. Experiments show deep neural networks with differential dynamic programming worked better than other methods for learning a pouring task with a robot.


![Remarks of Reinforcement Learning
Good to think about Model-free RL v.s.
Model-based RL
Successful robot-learning RL is model-free
(direct policy search) [cf. Kober et al. 2013]
Good at fine-tuning, Less computation cost (at
execution)
Robust to PoMDP
Model-based: Simulation biases
Model-based:
1. Generalization ability
2. Sharable / Reusable
3. Capable to reward changes
2 and 3: Thanks to symbolic (hierarchical)
representation
5
input
output
hidden
- u
update
FK ANN
[Magtanong et al. 2012]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijcai2016drlspot-160710184728/85/Model-based-Reinforcement-Learning-with-Neural-Networks-on-Hierarchical-Dynamic-System-5-320.jpg)
![How to deal with simulation biases?
Do not learn dx/dt = F(x,u) (dt: small like xx ms)
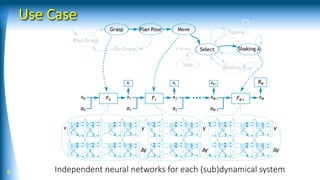
Learn (sub)task-level dynamics
Parameters F_grasp Grasp result
Parameters F_flow_ctrl Flow ctrl result
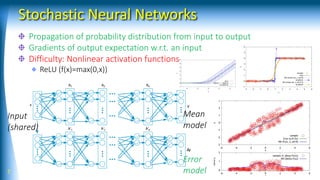
Use stochastic models
Gaussian F Gaussian
Stochastic Neural Networks [Yamaguchi, Atkeson, ICRA 2016]
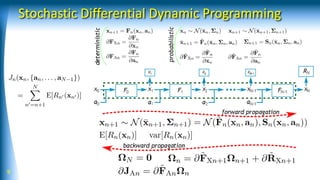
Use stochastic dynamic programming
Stochastic Differential Dynamic Programming
[Yamaguchi, Atkeson, Humanoids 2015]
6 Model-based RL with Neural Networks for Hierarchical Dynamic System](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ijcai2016drlspot-160710184728/85/Model-based-Reinforcement-Learning-with-Neural-Networks-on-Hierarchical-Dynamic-System-6-320.jpg)