Mobile Technology
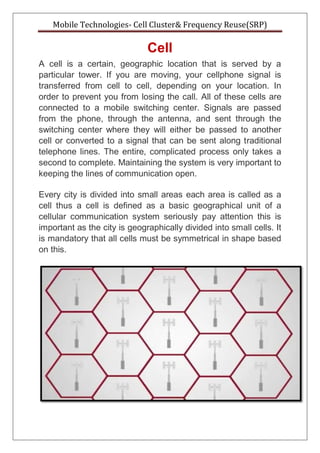
- 1. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) Cell A cell is a certain, geographic location that is served by a particular tower. If you are moving, your cellphone signal is transferred from cell to cell, depending on your location. In order to prevent you from losing the call. All of these cells are connected to a mobile switching center. Signals are passed from the phone, through the antenna, and sent through the switching center where they will either be passed to another cell or converted to a signal that can be sent along traditional telephone lines. The entire, complicated process only takes a second to complete. Maintaining the system is very important to keeping the lines of communication open. Every city is divided into small areas each area is called as a cell thus a cell is defined as a basic geographical unit of a cellular communication system seriously pay attention this is important as the city is geographically divided into small cells. It is mandatory that all cells must be symmetrical in shape based on this.
- 2. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) We have four geometrical shapes such as Circle Square equilateral triangle and hexagon. If we select the shape of a cell as a circle then the area between the two circles will not get covered by the base station and any attempt of communication from that area will fail. Thus we eliminate the circular shape. Hexagon has the highest area as compared to the other two shapes. Thus we divide the geographical area into hexagonal cells. Cluster group: The next concept is a cluster a group of cells is called as a cluster. The cluster size is not fixed. It depends on the requirements of the area.
- 3. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) Basic structure of mobile phone: Let’s study the mobile phone system now the basic structure of the mobile phone system is as shown. Where MS means mobile station BTS is base transceiver station. BSC is base station controller and MSC is mobile switching center. In this diagram MS is nothing but the mobile phone of a user. Call from one mobile to another mobile: Every cell has its own base transceiver station at its center. Whenever a call is set up the first signal is sent to the base transceiver station of the cell from this base transceiver station it goes to the central base station controller which controls the working of all the base stations from BSC it then goes to MSC or mobile switching center which is the master controller of the entire system. These MSC s are different for different areas from MSC of area one the signal is transmitted to MSC of area 2 where it follows the reverse sequence as MSC to BSC, BSC to BTS and from BTS – MS. Whenever a user makes an attempt to call someone a separate channel is assigned to the user by the MSC if all the channels are already occupied by other users then this user has to wait for a channel to become
- 4. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) free in such a case the user gets the notification such as call cannot be completed or network error etc Features of cellular concept: Frequency reuse: Now let’s see the features of the cellular concept its first feature is frequency reuse in frequency reuse same set of frequencies are used for radio channels located in different areas as shown in the diagram below. Every cell named as a uses the same set of frequencies the advantages of frequency reuse are many transmitters of small output power operating at the same frequency can be used. It reduces the minimum height of the transmitting antenna as each antenna has to cover a small distance but the disadvantage is that if the system is not properly designed then it may lead to co-channel interference. Co-channel interference is a phenomenon in which two frequency signals of adjacent channels interfere with each other.
- 5. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) Cell splitting: The second feature of the cellular concept is cell splitting. In cell splitting technique each cell is divided into smaller cells known as micro cells. The radius of these small cells is half of the original radius. Cell splitting technique proves advantages when the traffic of cell phone users increases beyond the limit of a regular cell. Handoff: Let’s see what do we mean by a handoff procedure consider a situation where we are traveling from place A to place B via a car. Sometimes it happens that for a short period of 2 or 3 seconds the signal strength on mobiles becomes very low and again it increases and reaches its normal level. Have you ever thought why this happens? The answer to this question is the handoff procedure when someone user X travels in area A he receives the signal from base station that is antenna a has a stronghold on out devices signal but as he moves away from antenna a the signal strength gradually decreases at a boundary of cell a the whole of antenna a on the device is minimum at the same time when the device is about to enter into cell B base station B starts to take hold on the device thus at the border of cell a and cell B. Both the antennas have equal amount of hold on the device of user X as user X crosses the border and enters into cell be area B strength of base station. A very rapidly decreases and strength of base station B rapidly increases in short the device receives the signal network from base station B. But during this procedure the call is still on. Hence base station a handovers this call to base station B without any effect on a call this procedure is known as the handoff procedure. This process happens so rapidly that the user never notices it.
- 6. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) We all know that there are two types of systems available as GSM and CDMA. We will only study the basics of GSM system GSM stands for global system for mobile GSM is nothing but a big system made up of few small systems. Such as mobile stations MS base station subsystem, BSS network and switching subsystem NSS operating subsystems OSS. The architecture of this GSM network is as shown mobile station MS nothing but the device used for communication. Such as cell phone fax machine etc base station subsystem BSS. BSS gets connected to ms wire radio interface. it has two different blocks as BTS base transceiver system and BSC base station controller practically. Every MS gets connected to BTS of that area this beauty s sends the signal to BSC many BTS are connected to one BSC and at the end of this BSC is connected to MSC. Hence BSS system consists of BTS and BSC network and switching subsystem NSS. This system mainly contains MSC. MSC is the backbone of the entire network it controls all the operations from setting up a call till the handoff procedure other blocks of NSS are h l our home location register which keeps the database of all the users who reside in the same geographical area VL our visitor location register keeps the track of all the users who are visitors for that particular geographical area mainly roaming customers authentication center mainly controls. The authentication of the users by checking their sim numbers etc and sends the required information to the MSC SIM: what does a SIM card actually do we all know a mobile would not work without one but why let’s start by looking at what SIM actually stands for it stands for subscriber identity module. So fundamentally it identifies your phone so when you send a message. Your phone knows which network to use and your operator knows who to bail for it though SIM contains more
- 7. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) information. It contains of course your number the information needed to bill you for a lot SIM. The SIM obviously knows the unlock pin though you can’t get it out even if you use scissors and it typically has contacts and messages saves on its memory because of this you can easily move the SIM between phones and keep your number. A simple way to think about it is that once you insert a SIM card the phone becomes your phone. The carrier extracts the information from a number this number is written on the SIM card. It is called the integrated circuit card identifier the shiny bit is an integrated circuit basically just a bunch of transistors and this is mounted on a card. It is a pointless name really but Telkom people seem to love the raku names anyway the number is made up of an issuer identification number and IIN more acronyms starting with an industry identifier which is almost always 89 have a look at your SIM card it probably starts with 89 then the country code, 44 for United Kingdom then we have the individual account identification number that is unique to you and finally we have a check digit that ensures that the previous numbers are correct. So it checks for any miss prints or errors and this is done using a clever algorithm developed IBM which is Lunz checksum. Finally let’s look at something the very few people know about there are two main ways of managing a network GSM and CDMA. GSM is a global system for mobile that requires a SIM and is used by almost everyone
- 8. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) but you also have the entirely valid code division multiple access system which does not require a SIM how is this possible it’s quite complicated but basically what is going on is the phone has a serial number and the carriers have a list of the phone’s if your phone is on the list you can use the network.
- 9. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) Cells A cell can be defined as an area of radio coverage from one BTS antenna system. It is the smallest building block in a mobile network and a cell can be represented by a hexagon. There are two types of cells; 1. Omni directional cell: An omni-directional cell (or omnicell) is served by a BTS with an antenna which transmits equally in all directions (360 degrees). 2. Sector cell: A sector cell is the area of coverage from an antenna, which transmits, in a given direction only. For example, this may be equal to 120 degrees or 180 degrees of an equivalent omni- directional cell. One BTS can serve one of these sector cells with a collection of BTS’s at a site serving more than one, leading to terms such as two-sectored sites and more commonly, three-sectored sites.
- 10. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) Clusters Groups of frequencies can be placed together into patterns of cells called clusters. A cluster is a group of cells in which all available frequencies have been used once and only once. Since the same frequencies can be used in neighboring clusters, interference may become a problem. Therefore, the frequency re-use distance must be kept as large as possible. However, to maximize capacity the frequency re-use distance should be kept as low as possible. The re-use patterns recommended for GSM are the 4/12 and the 3/9 pattern. 4/12 means that there are four three-sector sites supporting twelve cells using twelve frequency groups. In the 3/9 cell pattern there are always 9 channels separating each frequency in a cell. However, when compared with the 4/12 pattern, cells A1 and C3 are neighbors and use adjacent frequencies. Therefore, the C/A interference will increase. In this case, an operator may use frequency hopping which, if planned correctly, could reduce the possibility of such adjacent channel interference
- 11. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) Frequency Reuse Frequency Reuse is the scheme in which allocation and reuse of channels throughout a coverage region is done. Each cellular base station is allocated a group of radio channels or Frequency sub-bands to be used within a small geographic area known as a cell. The shape of the cell is Hexagonal. The process of selecting and allocating the frequency sub-bands for all of the cellular base station within a system is called Frequency reuse or Frequency Planning. Silent Features of using Frequency Reuse: Frequency reuse improve the spectral efficiency and signal Quality (QoS). Frequency reuse classical scheme proposed for GSM systems offers a protection against interference. The number of times a frequency can be reused is depend on the tolerance capacity of the radio channel from the nearby transmitter that is using the same frequencies. In Frequency Reuse scheme, total bandwidth is divided into different sub-bands that are used by cells. Frequency reuse scheme allow WiMax system operators to reuse the same frequencies at different cell sites. Cell with the same letter uses the same set of channels group or frequencies sub-band.
- 12. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) TOTAL NUMBER OF CHANNELS (S) To find the total number of channel allocated to a cell: S = Total number of duplex channels available to use k = Channels allocated to each cell (k<S) N = Total number of cells or Cluster Size Then Total number of channels (S) will be, S = kN FREQUENCY REUSE FACTOR Frequency Reuse Factor = 1/N In the above diagram cluster size is 7 (A,B,C,D,E,F,G) thus frequency reuse factor is 1/7. THE NUMBER OF CELLS N is the number of cells which collectively use the complete set of available frequencies is called a Cluster. The value of N is calculated by the following formula: N = I2 + I*J + J2 Where I,J = 0,1,2,3…
- 13. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) CAPACITY(C)- Hence, possible values of N are 1,3,4,7,9,12,13,16,19 and so on. If a Cluster is replicated or repeated M times within the cellular system, then Capacity, C, will be, C = MkN = MS In Frequency reuse there are several cells that use the same set of frequencies. These cells are called Co-Channel Cells. These Co-Channel cells results in interference. So to avoid the Interference cells that use the same set of channels or frequencies are separated from one another by a larger distance. The distance between any two Co-Channels can be calculated by the following formula: D = R * (3 * N)1/2 Where, R = Radius of a cell N = Number of cells in a given cluster
- 14. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) BELOW IS THE PYTHON CODE FOR VISUALIZING THE FREQUENCY REUSE CONCEPT #!/usr/bin/python from math import * # import everything from Tkinter module from tkinter import * # Base class for Hexagon shape class Hexagon(object): def __init__(self, parent, x, y, length, color, tags): self.parent = parent self.x = x self.y = y self.length = length self.color = color self.size = None self.tags = tags self.draw_hex() # draw one hexagon def draw_hex(self): start_x = self.x start_y = self.y angle = 60 coords = [] for i in range(6):
- 15. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) end_x = start_x + self.length * cos(radians(angle * i)) end_y = start_y + self.length * sin(radians(angle * i)) coords.append([start_x, start_y]) start_x = end_x start_y = end_y self.parent.create_polygon(coords[0][0], coords[0][1], coords[1][0], coords[1][1], coords[2][0], coords[2][1], coords[3][0], coords[3][1], coords[4][0], coords[4][1], coords[5][0], coords[5][1], fill=self.color, outline="black", tags=self.tags) # class holds frequency reuse logic and related methods class FrequencyReuse(Tk): CANVAS_WIDTH = 800 CANVAS_HEIGHT = 650 TOP_LEFT = (20, 20) BOTTOM_LEFT = (790, 560)
- 16. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) TOP_RIGHT = (780, 20) BOTTOM_RIGHT = (780, 560) def __init__(self, cluster_size, columns=16, rows=10, edge_len=30): Tk.__init__(self) self.textbox = None self.curr_angle = 330 self.first_click = True self.reset = False self.edge_len = edge_len self.cluster_size = cluster_size self.reuse_list = [] self.all_selected = False self.curr_count = 0 self.hexagons = [] self.co_cell_endp = [] self.reuse_xy = [] self.canvas = Canvas(self, width=self.CANVAS_WIDTH, height=self.CANVAS_HEIGHT, bg="#4dd0e1") self.canvas.bind("<Button-1>", self.call_back) self.canvas.focus_set() self.canvas.bind('<Shift-R>', self.resets) self.canvas.pack() self.title("Frequency reuse and co-channel selection") self.create_grid(16, 10)
- 17. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) self.create_textbox() self.cluster_reuse_calc() # show lines joining all co-channel cells def show_lines(self): # center(x,y) of first hexagon approx_center = self.co_cell_endp[0] self.line_ids = [] for k in range(1, len(self.co_cell_endp)): end_xx = (self.co_cell_endp[k])[0] end_yy = (self.co_cell_endp[k])[1] # move i^th steps l_id = self.canvas.create_line(approx_center[0], approx_center[1], end_xx, end_yy) if j == 0: self.line_ids.append(l_id) dist = 0 elif i >= j and j != 0: self.line_ids.append(l_id) dist = j # rotate counter-clockwise and move j^th step l_id = self.canvas.create_line( end_xx, end_yy, end_xx + self.center_dist * dist * cos(radians(self.curr_angle - 60)), end_yy + self.center_dist * dist *
- 18. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) sin(radians(self.curr_angle - 60))) self.line_ids.append(l_id) self.curr_angle -= 60 def create_textbox(self): txt = Text(self.canvas, width=80, height=1, font=("Helvatica", 12), padx=10, pady=10) txt.tag_configure("center", justify="center") txt.insert("1.0", "Select a Hexagon") txt.tag_add("center", "1.0", "end") self.canvas.create_window((0, 600), anchor='w', window=txt) txt.config(state=DISABLED) self.textbox = txt def resets(self, event): if event.char == 'R': self.reset_grid() # clear hexagonal grid for new i/p def reset_grid(self, button_reset=False): self.first_click = True self.curr_angle = 330 self.curr_count = 0
- 19. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) self.co_cell_endp = [] self.reuse_list = [] for i in self.hexagons: self.canvas.itemconfigure(i.tags, fill=i.color) try: self.line_ids except AttributeError: pass else: for i in self.line_ids: self.canvas.after(0, self.canvas.delete, i) self.line_ids = [] if button_reset: self.write_text("Select a Hexagon") # create a grid of Hexagons def create_grid(self, cols, rows): size = self.edge_len for c in range(cols): if c % 2 == 0: offset = 0 else: offset = size * sqrt(3) / 2 for r in range(rows): x = c * (self.edge_len * 1.5) + 50
- 20. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) y = (r * (self.edge_len * sqrt(3))) + offset + 15 hx = Hexagon(self.canvas, x, y, self.edge_len, "#fafafa", "{},{}".format(r, c)) self.hexagons.append(hx) # calculate reuse distance, center distance and radius of the hexagon def cluster_reuse_calc(self): self.hex_radius = sqrt(3) / 2 * self.edge_len self.center_dist = sqrt(3) * self.hex_radius self.reuse_dist = self.hex_radius * sqrt(3 * self.cluster_size) def write_text(self, text): self.textbox.config(state=NORMAL) self.textbox.delete('1.0', END) self.textbox.insert('1.0', text, "center") self.textbox.config(state=DISABLED) #check if the co-channels are within visible canvas def is_within_bound(self, coords): if self.TOP_LEFT[0] < coords[0] < self.BOTTOM_RIGHT[0] and self.TOP_RIGHT[1] < coords[1] < self.BOTTOM_RIGHT[1]: return True return False #gets called when user selects a hexagon #This function applies frequency reuse logic in order to #figure out the positions of the co-channels
- 21. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) def call_back(self, evt): selected_hex_id = self.canvas.find_closest(evt.x, evt.y)[0] hexagon = self.hexagons[int(selected_hex_id - 1)] s_x, s_y = hexagon.x, hexagon.y approx_center = (s_x + 15, s_y + 25) if self.first_click: self.first_click = False self.write_text( """Now, select another hexagon such that it should be a co-cell of the original hexagon.""" ) self.co_cell_endp.append(approx_center) self.canvas.itemconfigure(hexagon.tags, fill="green") for _ in range(6): end_xx = approx_center[0] + self.center_dist * i * cos( radians(self.curr_angle)) end_yy = approx_center[1] + self.center_dist * i * sin( radians(self.curr_angle)) reuse_x = end_xx + (self.center_dist * j) * cos( radians(self.curr_angle - 60)) reuse_y = end_yy + (self.center_dist * j) * sin(
- 22. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) radians(self.curr_angle - 60)) if not self.is_within_bound((reuse_x, reuse_y)): self.write_text( """co-cells are exceeding canvas boundary. Select cell in the center""" ) self.reset_grid() break if j == 0: self.reuse_list.append( self.canvas.find_closest(end_xx, end_yy)[0]) elif i >= j and j != 0: self.reuse_list.append( self.canvas.find_closest(reuse_x, reuse_y)[0]) self.co_cell_endp.append((end_xx, end_yy)) self.curr_angle -= 60 else: curr = self.canvas.find_closest(s_x, s_y)[0] if curr in self.reuse_list: self.canvas.itemconfigure(hexagon.tags, fill="green") self.write_text("Correct! Cell {} is a co-cell.".format( hexagon.tags)) if self.curr_count == len(self.reuse_list) - 1:
- 23. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) self.write_text("Great! Press Shift-R to restart") self.show_lines() self.curr_count += 1 else: self.write_text("Incorrect! Cell {} is not a co-cell.".format( hexagon.tags)) self.canvas.itemconfigure(hexagon.tags, fill="red") if __name__ == '__main__': print( """Enter i & j values. common (i,j) values are: (1,0), (1,1), (2,0), (2,1), (3,0), (2,2)""" ) i = int(input("Enter i: ")) j = int(input("Enter j: ")) if i == 0 and j == 0: raise ValueError("i & j both cannot be zero") elif j > i: raise ValueError("value of j cannot be greater than i") else: N = (i**2 + i * j + j**2) print("N is {}".format(N)) freqreuse = FrequencyReuse(cluster_size=N) freqreuse.mainloop() OUTPUT:
- 24. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP) Useful Study links- 1. Mobile Communication – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tt1- Ohe9QQU&list=RDCMUCpuCKBmQA70bNy39- VJU_4g&index=2 2. Frequency Reuse - Cell Splitting - Handoff Procedure https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ioj6F1v59yw 3. How Mobile Phone Works https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1JZG9x_VOwA 4. Cellular Concepts https://www.tutorialspoint.com/umts/umts_cellular_c oncepts_introduction.htm
- 25. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP)
- 26. Mobile Technologies- Cell Cluster& Frequency Reuse(SRP)