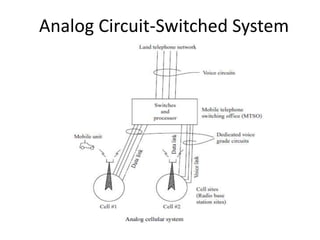
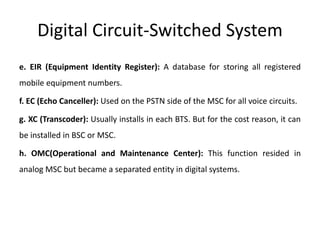
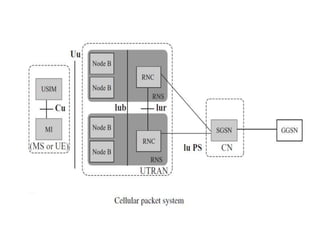
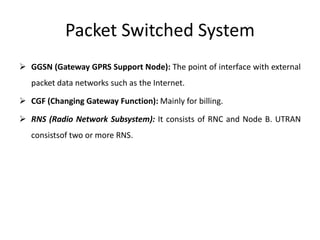
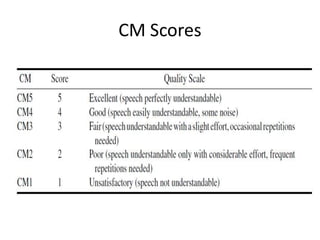
The document discusses the key components of basic cellular systems including circuit-switched and packet-switched systems. It describes the main elements of analog circuit-switched systems including mobile units, cell sites, and mobile telephone switching offices. For digital circuit-switched systems, it outlines the mobile station, base transceiver station, base station controller, and switching subsystems. It also summarizes the mobile station, radio network controller, support nodes, and gateway for packet-switched systems and reviews performance criteria such as voice quality, data quality, coverage, and special features.