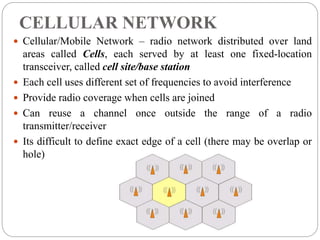
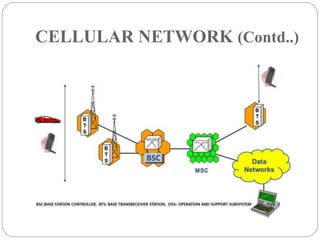
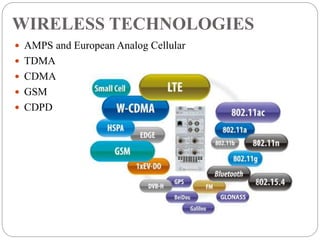
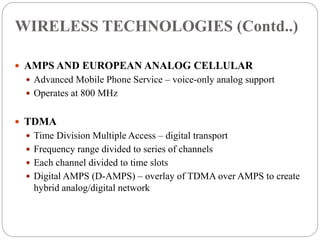
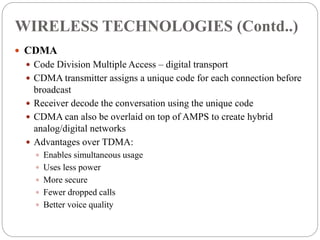
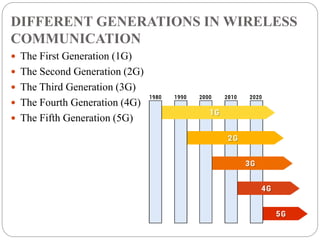
The document provides an overview of mobile commerce, detailing its wireless applications, cellular network structure, and various technologies involved. It covers generations of wireless communication from 1G to 5G, highlighting security issues, portals, and human resource management systems related to mobile commerce. Various modules of HRIS are also discussed, emphasizing the need for efficient management of human resources in organizations.