Embed presentation
Downloaded 20 times



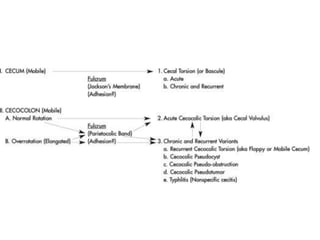
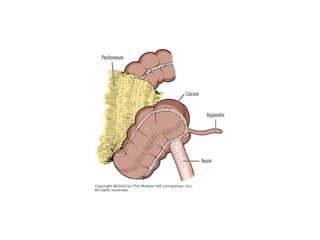
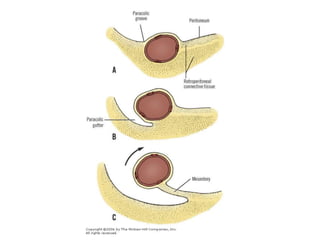

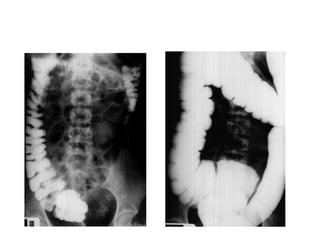


Mobile cecum syndrome is an embryological variation where the cecum is improperly fixed to the lateral abdominal wall, leaving it redundant and prone to twisting around its axis. It affects 10% of the population and more commonly females, with 2% presenting as acute intestinal obstruction. Patients often experience right lower quadrant pain, colicky pain, and alternating constipation and diarrhea. Treatment involves surgical fixation of the cecum to the lateral abdominal wall to prevent further twisting.








