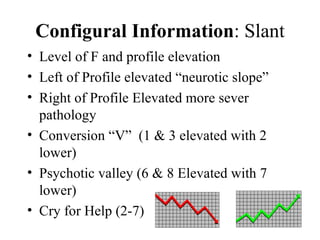
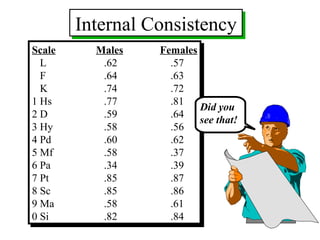
The MMPI-2 is a widely used psychological assessment that was first published in 1943 and revised in 1989. It consists of 567 true/false questions and measures personality traits and psychopathology. The revision process involved updating outdated items and adding new scales. The MMPI-2 maintains good reliability and comparability to the original MMPI, while improving representation of special populations. Interpretation involves examining validity, clinical, content, and supplemental scale scores.












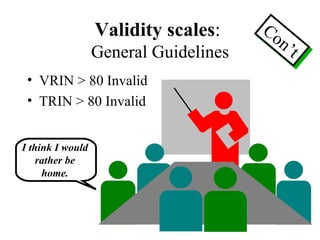
![Deviant Response Sets : General Random : F >100, Fb >100, F(p)> 100 VRIN >80 All True : F > 100, Fb > 100, TRIN > 80 All False : L > 65, F > 100, Fb > 100, TRIN > 80 Negative Impression : F > 100, F(p) < 100, K Low, VRIN & TRIN Acceptable; Exaggeration : Clinical Judgment Positive Impression : L > 65, K > 65, Low F Defensiveness : K & L 10 points higher than F; either F or K elevated (experimental: S [superlative] greater than 29).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mmpi-101015025617-phpapp01/85/Mmpi-22-320.jpg)