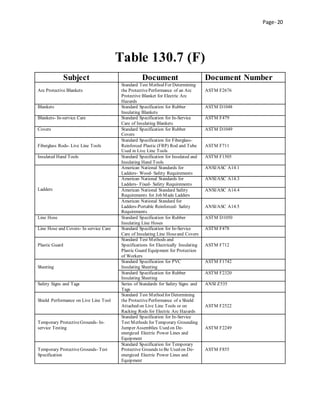
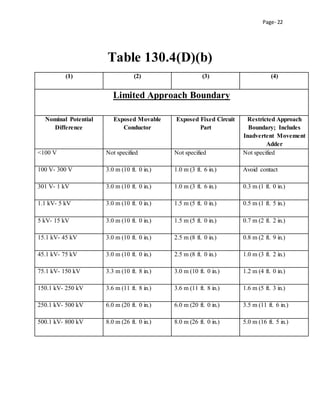
This document outlines an electrical safety policy and procedures for Midwest Manufacturing. It aims to establish standards to prevent electrical hazards and ensure compliance with OSHA and NFPA regulations. The policy requires that electrical circuits be de-energized before work, unless doing so would increase hazards or is infeasible. It assigns responsibilities to different departments to implement the policy and train employees. The procedures section specifies requirements for inspecting equipment, locking out tag out procedures, use of personal protective equipment, and energized work permits.