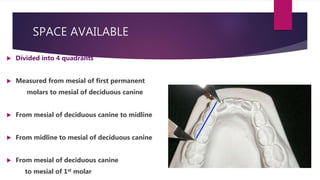
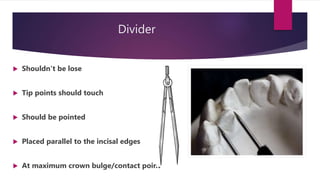
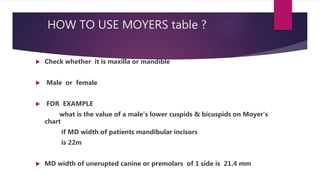
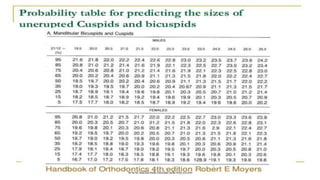
The document discusses mixed dentition analysis, which involves estimating space requirements for permanent teeth based on measurements of primary teeth. It describes three main methods: arch length discrepancy, Moyer's predictability tables, and radiographic analysis. Arch length discrepancy involves measuring the space available between molars and comparing to the summed widths of teeth in between. Moyer's tables provide predicted widths of unerupted canines and premolars based on measured primary tooth widths. Radiographic analysis uses dental casts and x-rays to directly measure unerupted tooth sizes and correct for magnification.











![Tanaka and Johnston
Measure mesiodistal width of mandibular incisors
[Not maxillary as their sizes varies]
Sum the mesiodistal widths of mandibular incisors and divide by 2
For mandibular canine and premolars MD width add 10.5
For maxillary canine and premolars MD width add 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mixeddentitionanalysis-201223153426/85/Mixed-dentition-analysis-16-320.jpg)


![FOR MAXILLARY UNERUPTED CANINES AND
PREMOLARS:
Now here we will put the MD width of Mandibular incisors for
formula correction i.e. 22mm
22/2=11
ADD 11
11+11= 22mm [for one side]
FOR BOTH SIDES X 2 = 22X2 =44mm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mixeddentitionanalysis-201223153426/85/Mixed-dentition-analysis-19-320.jpg)




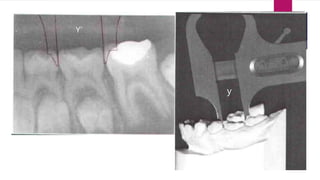
![Radiographic Method
[HUCKABA’S]
Dental cast and patient radiograph is required
Radiograph may be periapical or OPG
Reaquired Mesiodistal width of each tooth is measured separately
on the cast and radiograph.
Calculate with formula x = x’y/y’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mixeddentitionanalysis-201223153426/85/Mixed-dentition-analysis-26-320.jpg)