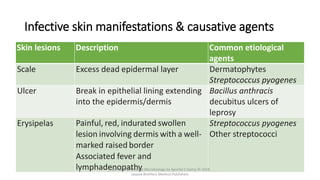
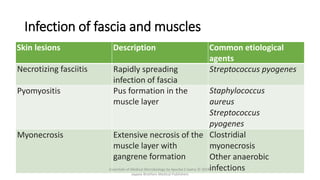
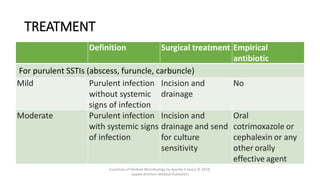
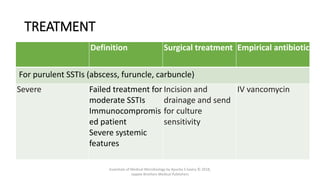
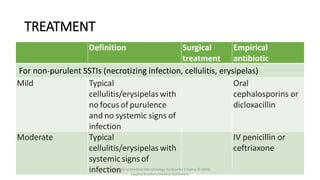
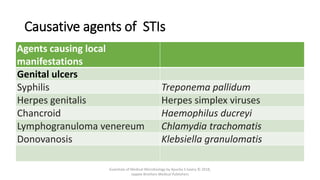
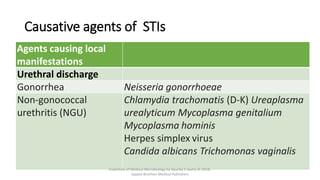
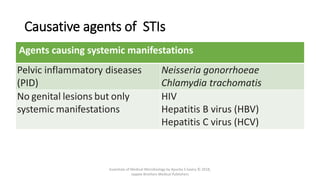
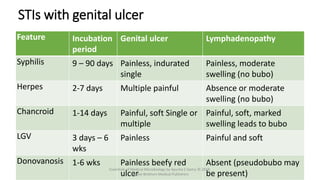
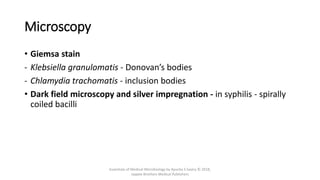
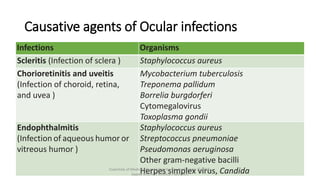
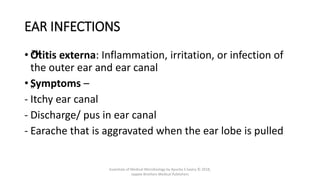
The document discusses skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs). It describes various skin lesions such as macules, papules, plaques, nodules, vesicles, bullae, pustules, and abscesses. It lists the common etiological agents that cause each type of lesion. It also discusses specific infections including folliculitis, furuncles, carbuncles, cellulitis, and impetigo. The document provides guidance on laboratory diagnosis, treatment and antibiotics for purulent and non-purulent SSTIs of varying severity.