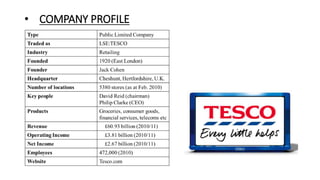
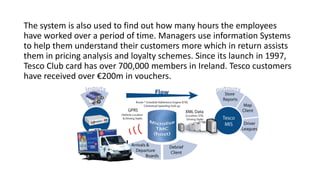
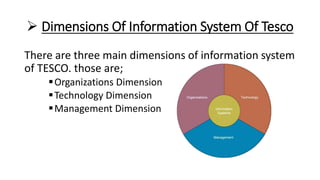
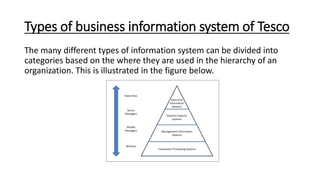
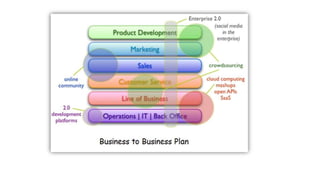
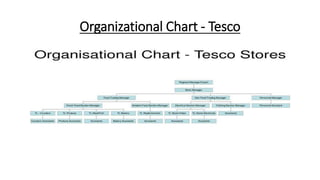
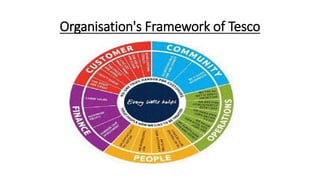
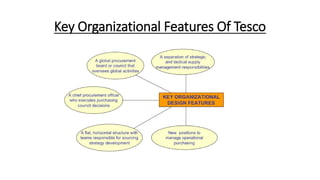
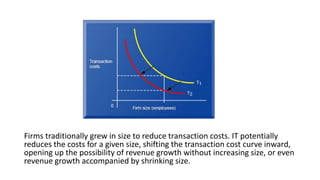
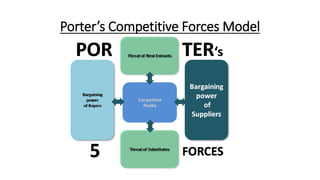
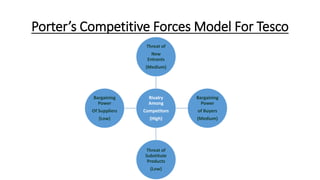
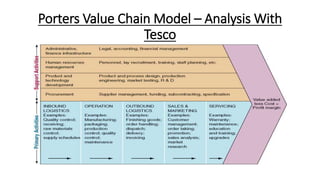
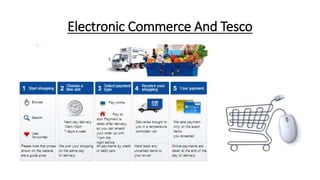
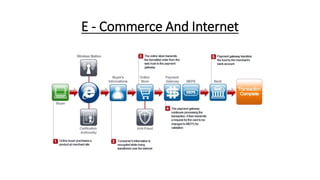
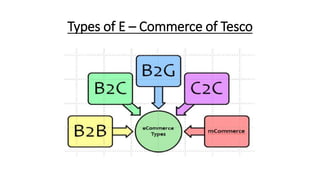
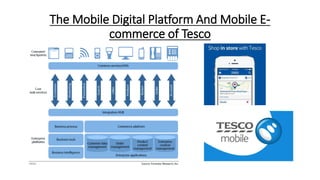
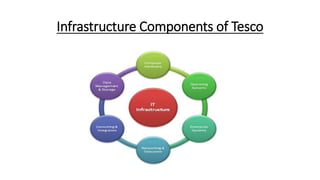
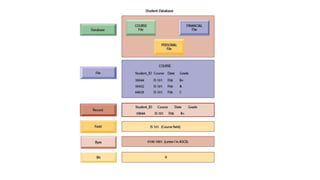
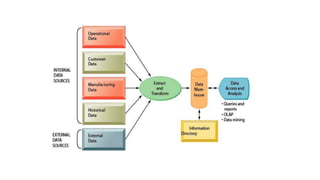
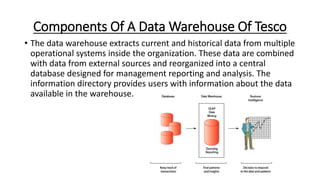
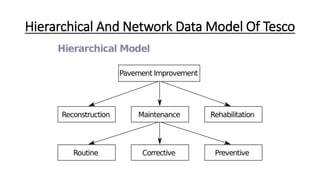
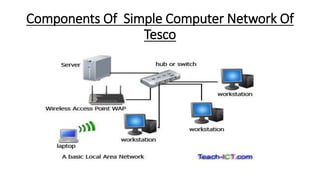
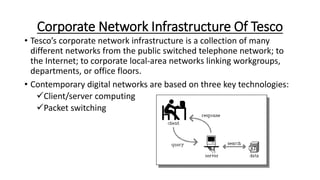
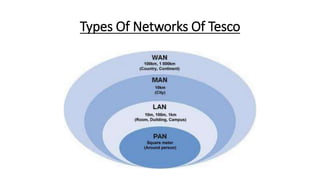
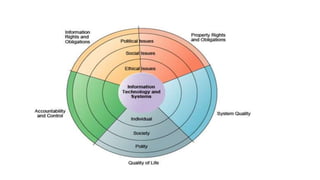
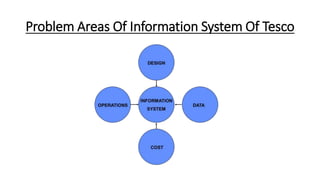
Tesco is a large global grocery retailer headquartered in the UK. It uses various information systems throughout its operations for functions like inventory management, supply chain management, sales and checkout, financial reporting, HR, and more. Information systems are critical to Tesco's success and have helped increase efficiency, automate processes, and enable new capabilities like e-commerce. Some key systems used include GOLD for warehouse management, their customer loyalty program, and online shopping platforms. Challenges include maintaining system integrity and performance across Tesco's large global operations.