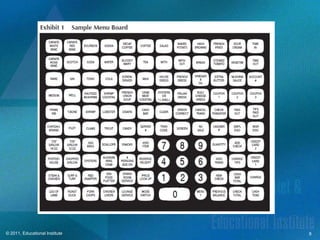
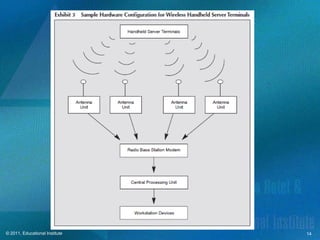
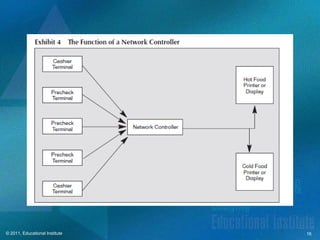
This document discusses point-of-sale technology used in hospitality businesses. It describes the key components of a POS system including touchscreen and wireless terminals, various types of printers, payment processing devices like magnetic stripe readers, and data security standards. The document also outlines important files maintained by POS software such as open checks, menu items, and employee information that managers can use to generate sales and productivity reports.