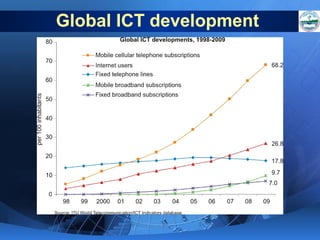
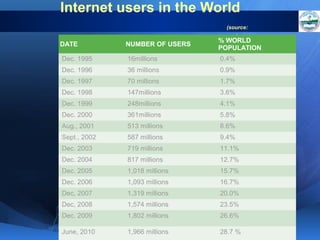
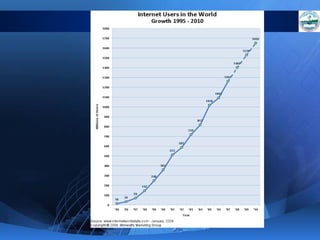
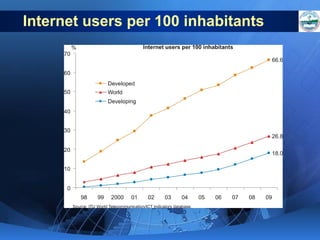
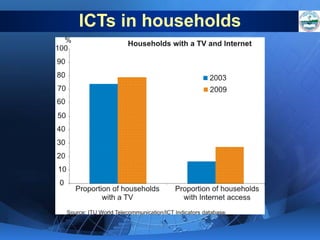
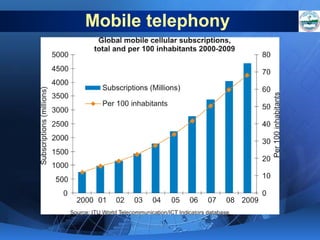
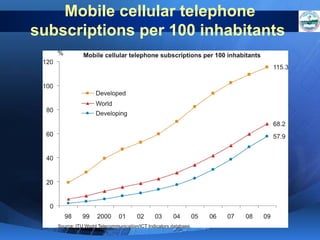
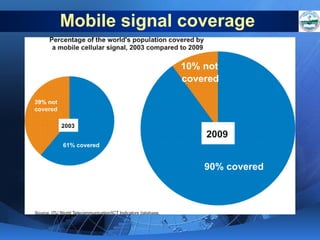
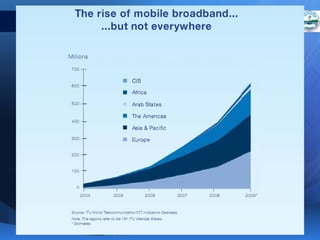
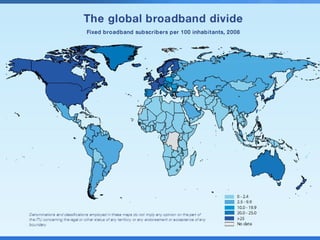
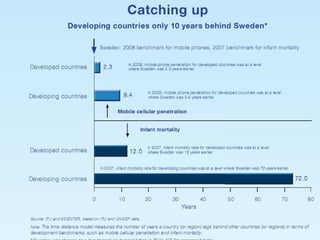
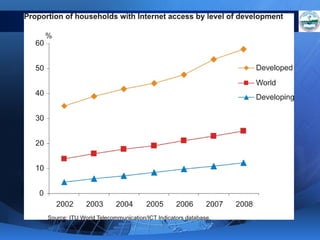
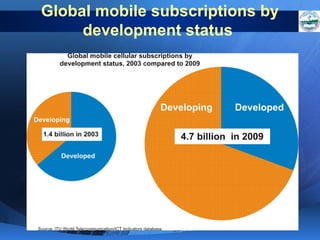
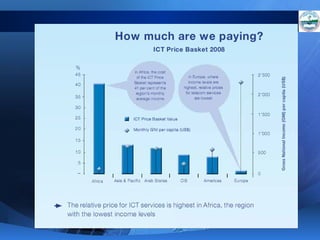
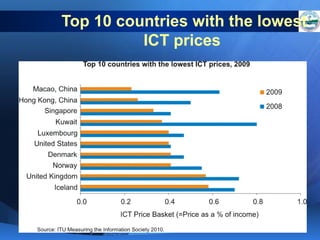
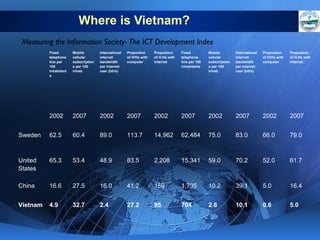
ICTs such as the internet, mobile phones, and digital technologies have eroded barriers of time and space, allowing for swift global communication flows. ICTs play an important role in globalization by facilitating the sharing of information worldwide and enabling real-time interaction across borders. While ICTs can promote development by increasing access to information, a digital divide still exists between developed and developing nations in infrastructure and skills. Both positive and negative consequences can arise from increased global media, including greater connectivity but also risks of exclusion.