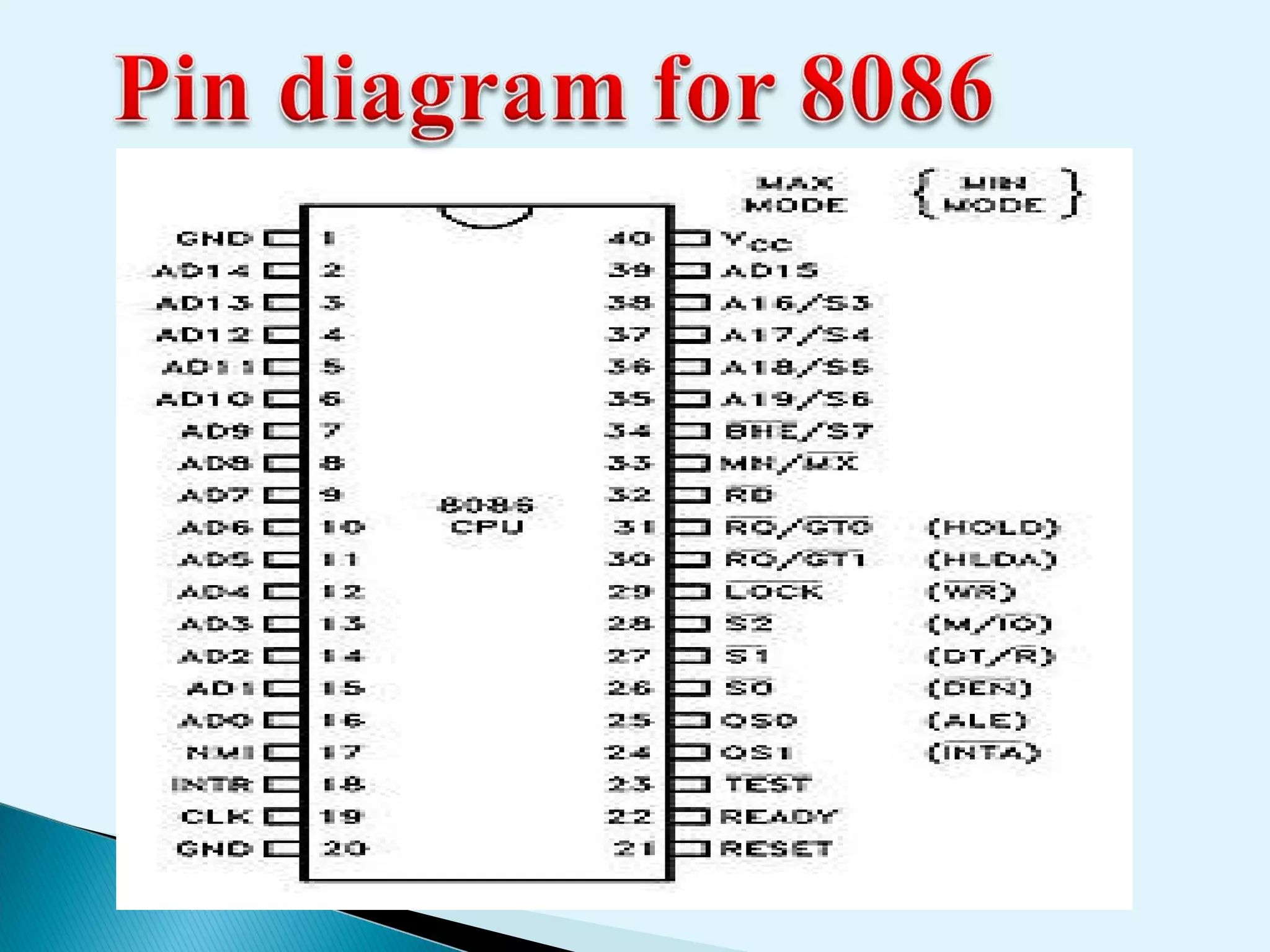
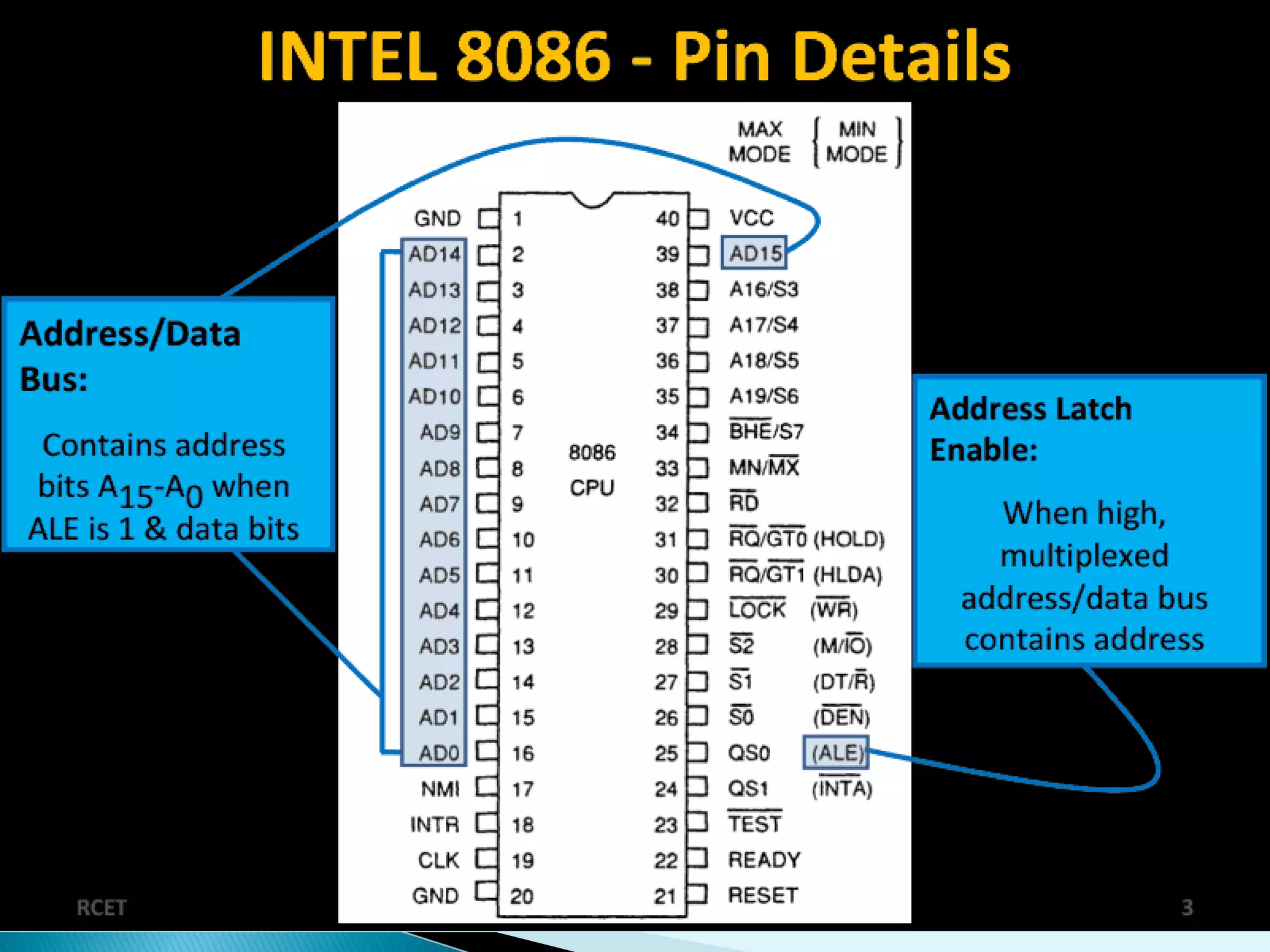
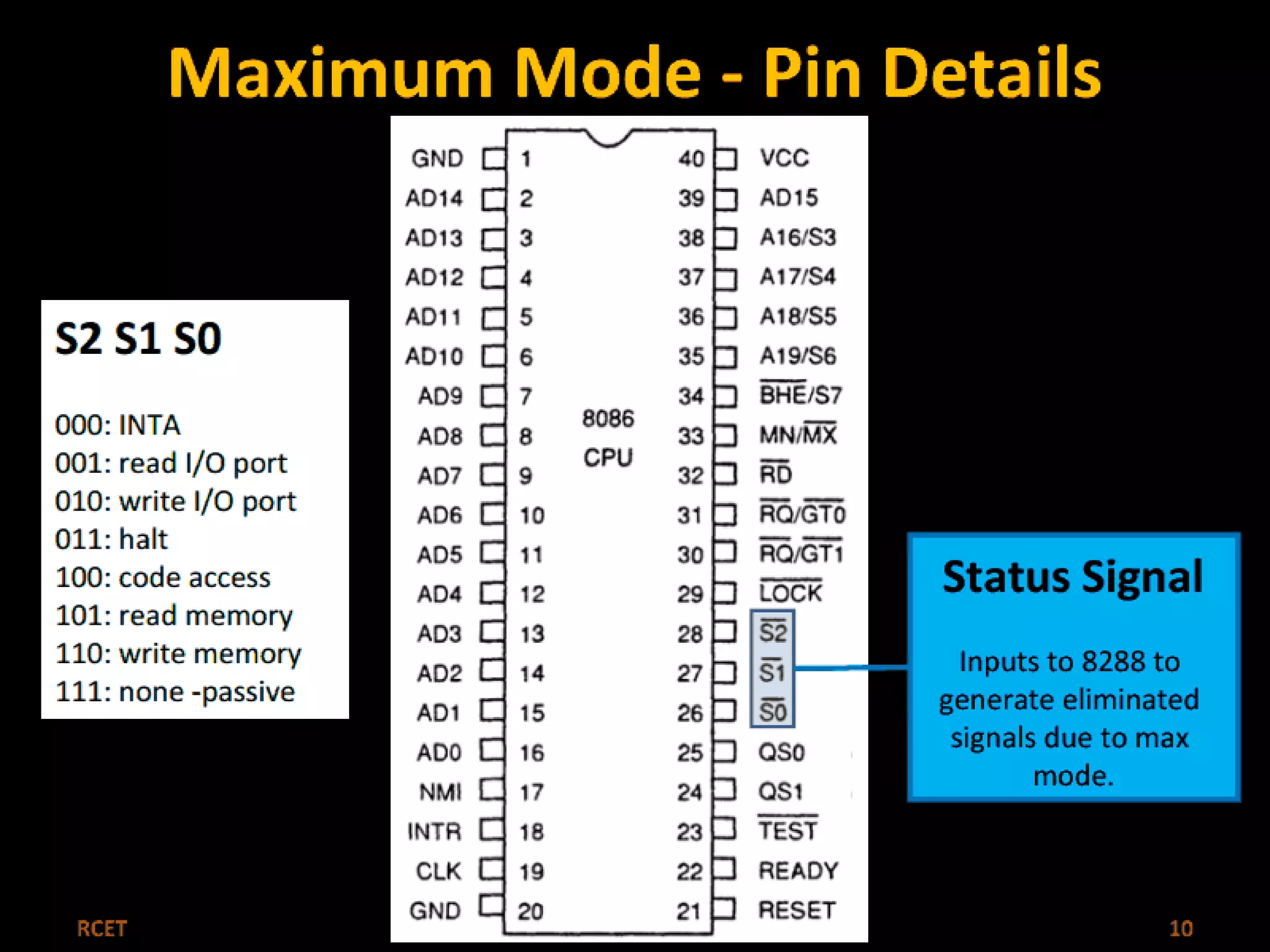
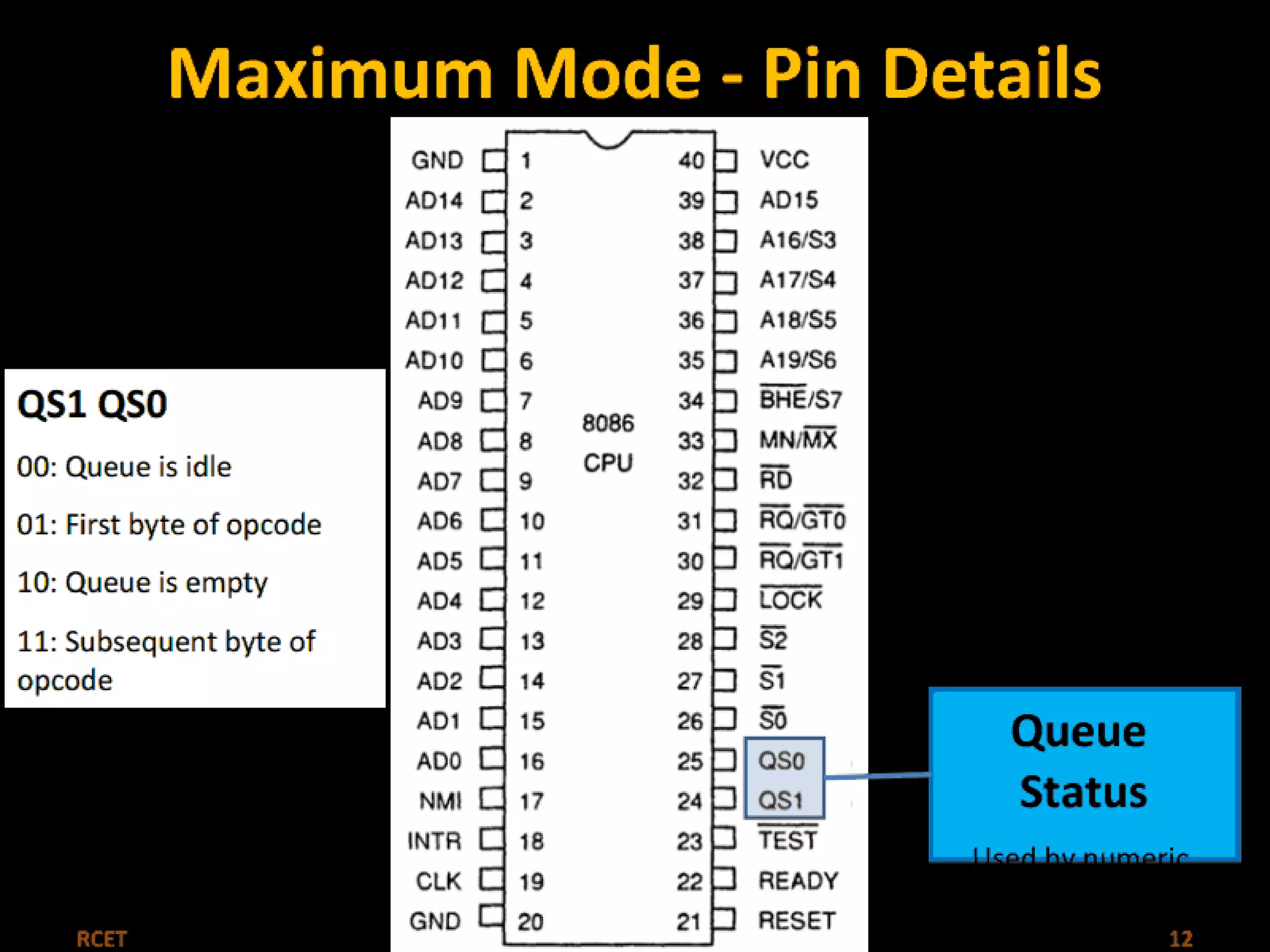
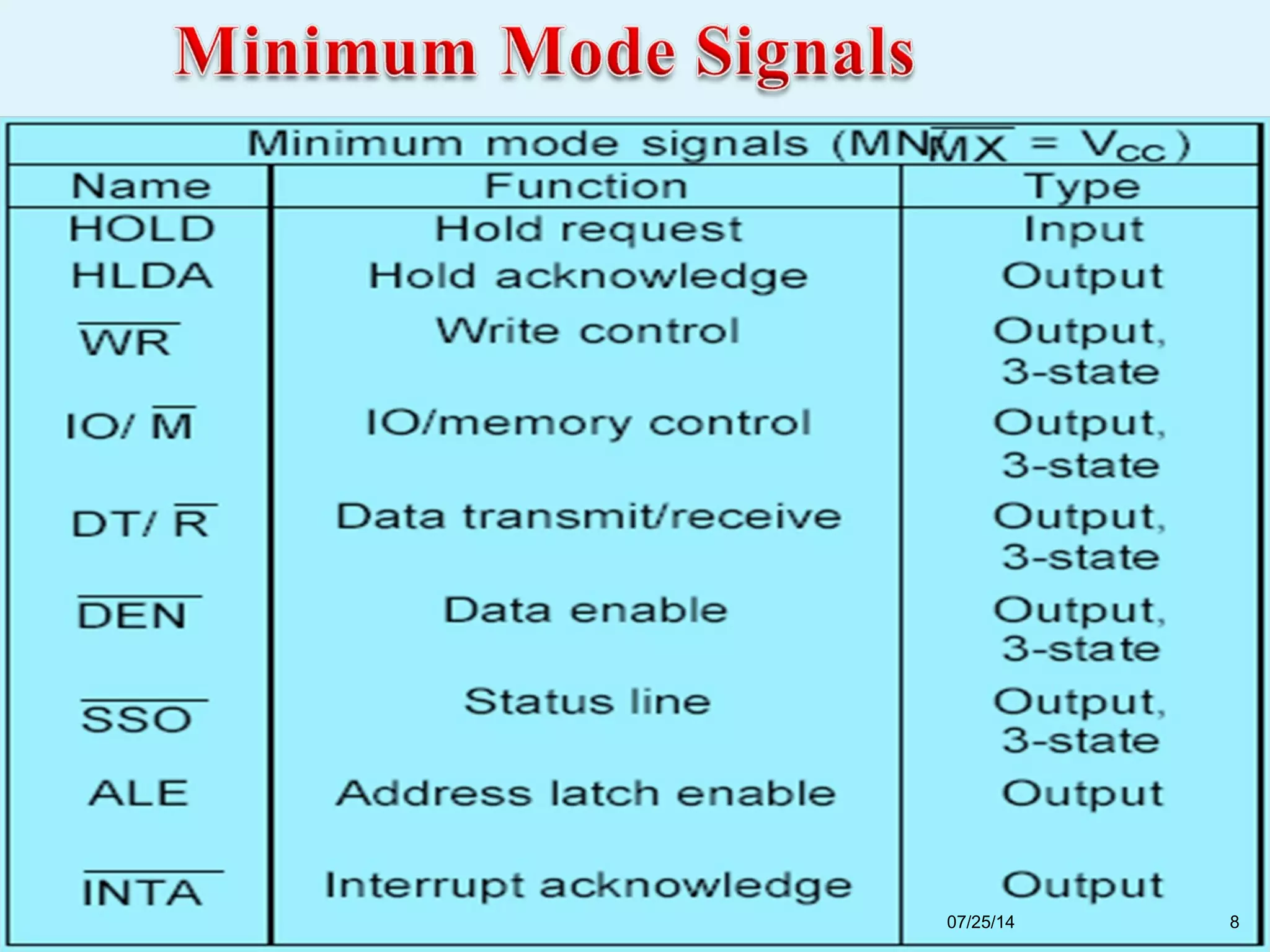
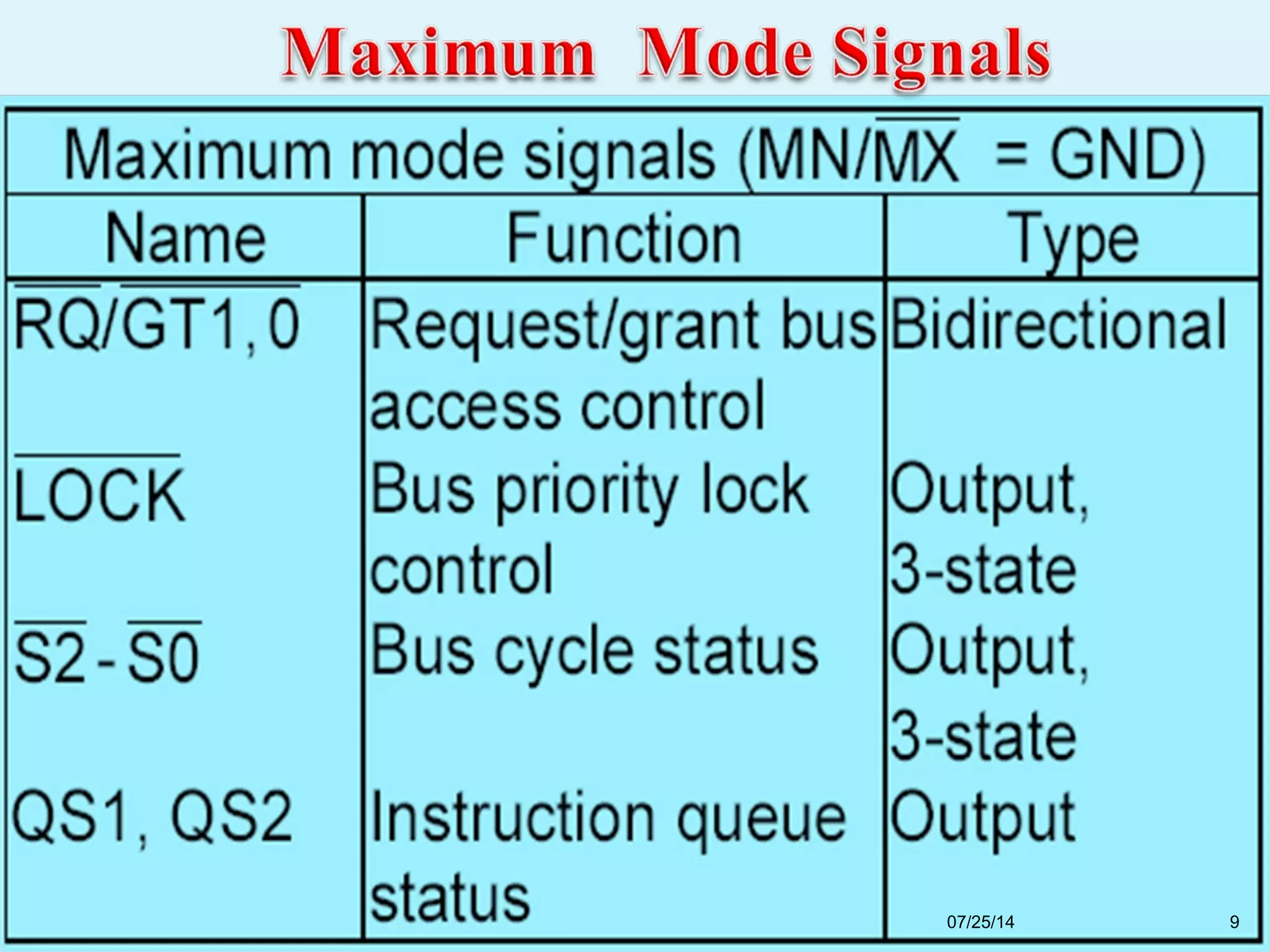
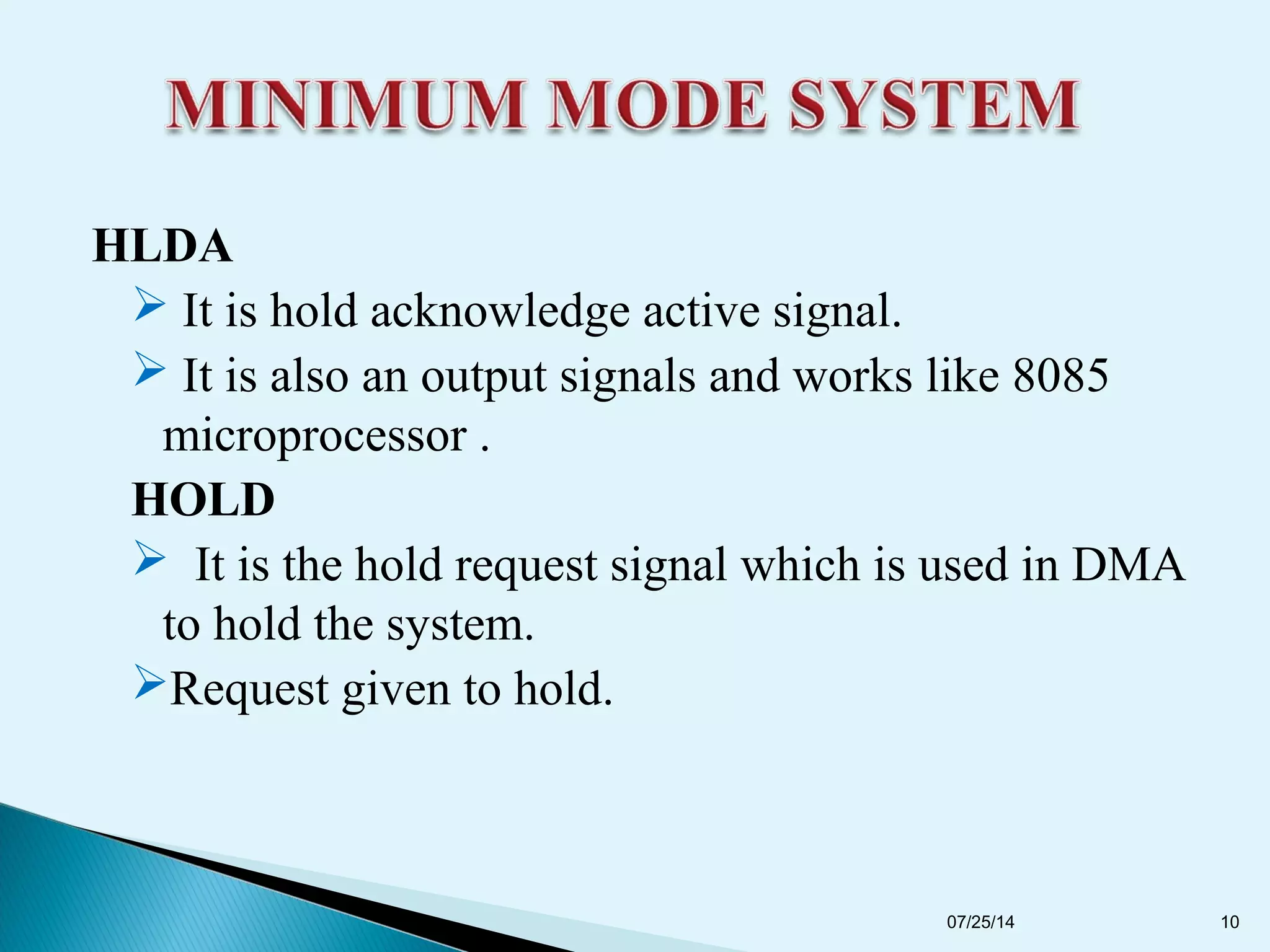
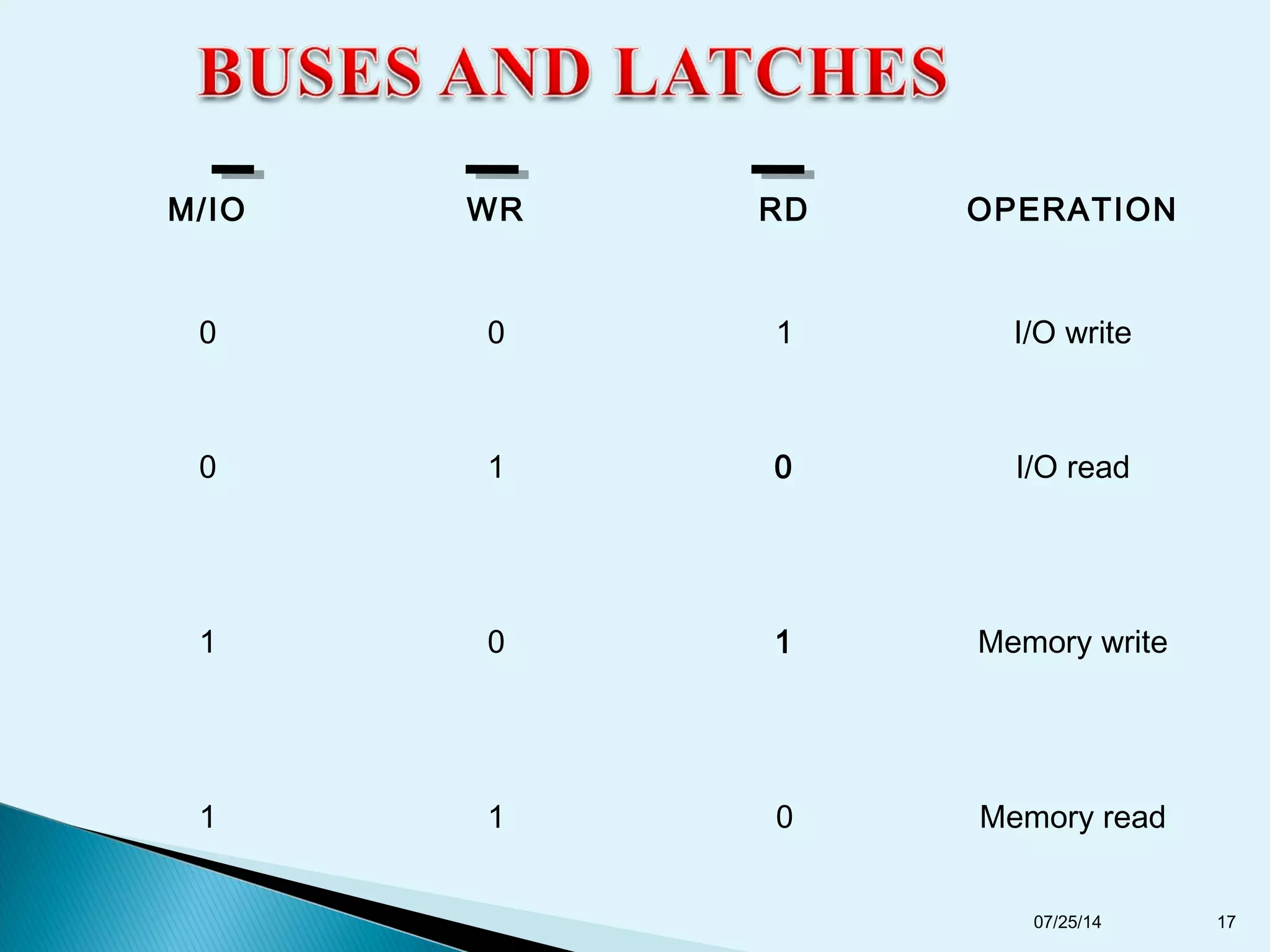
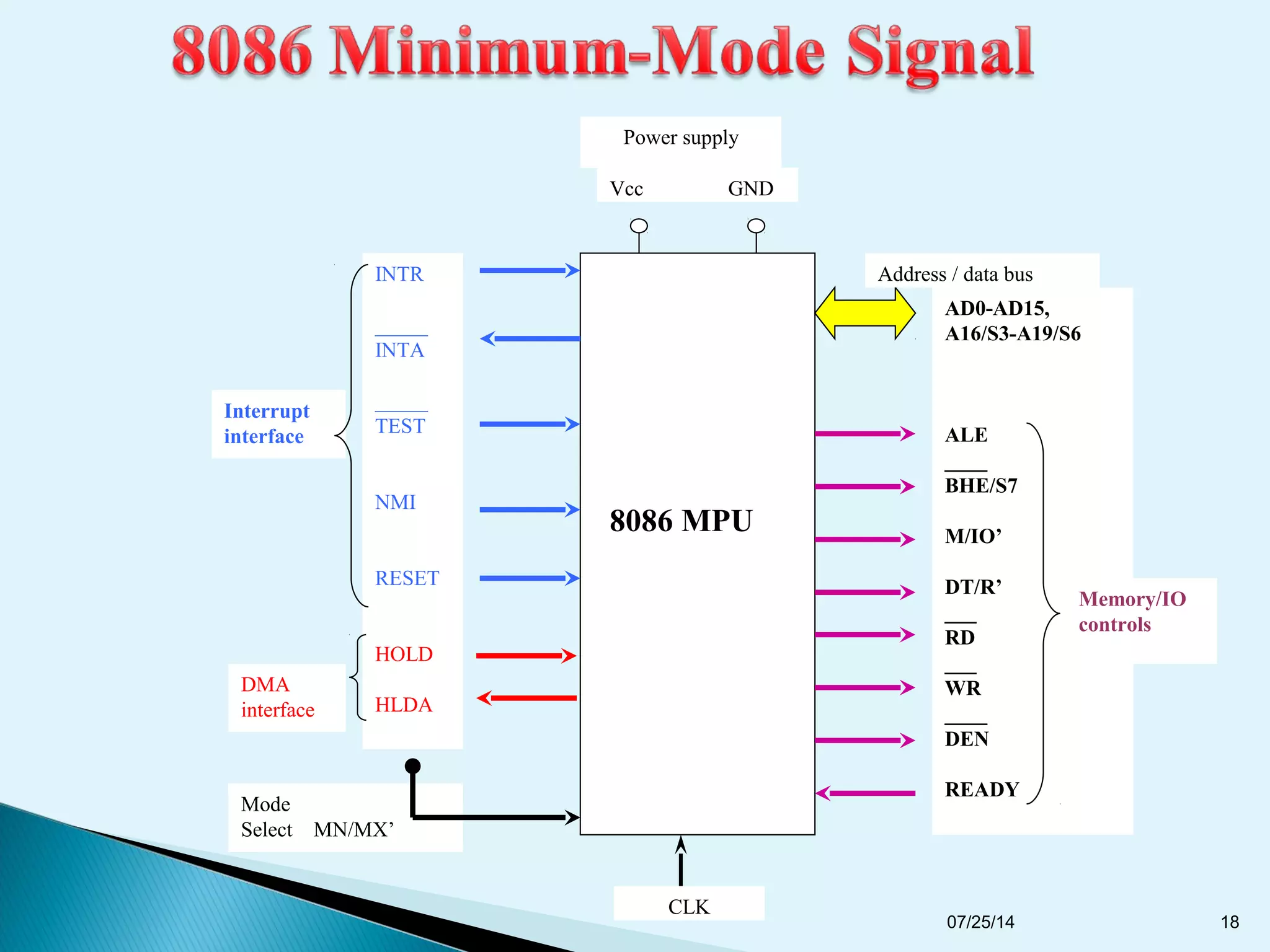
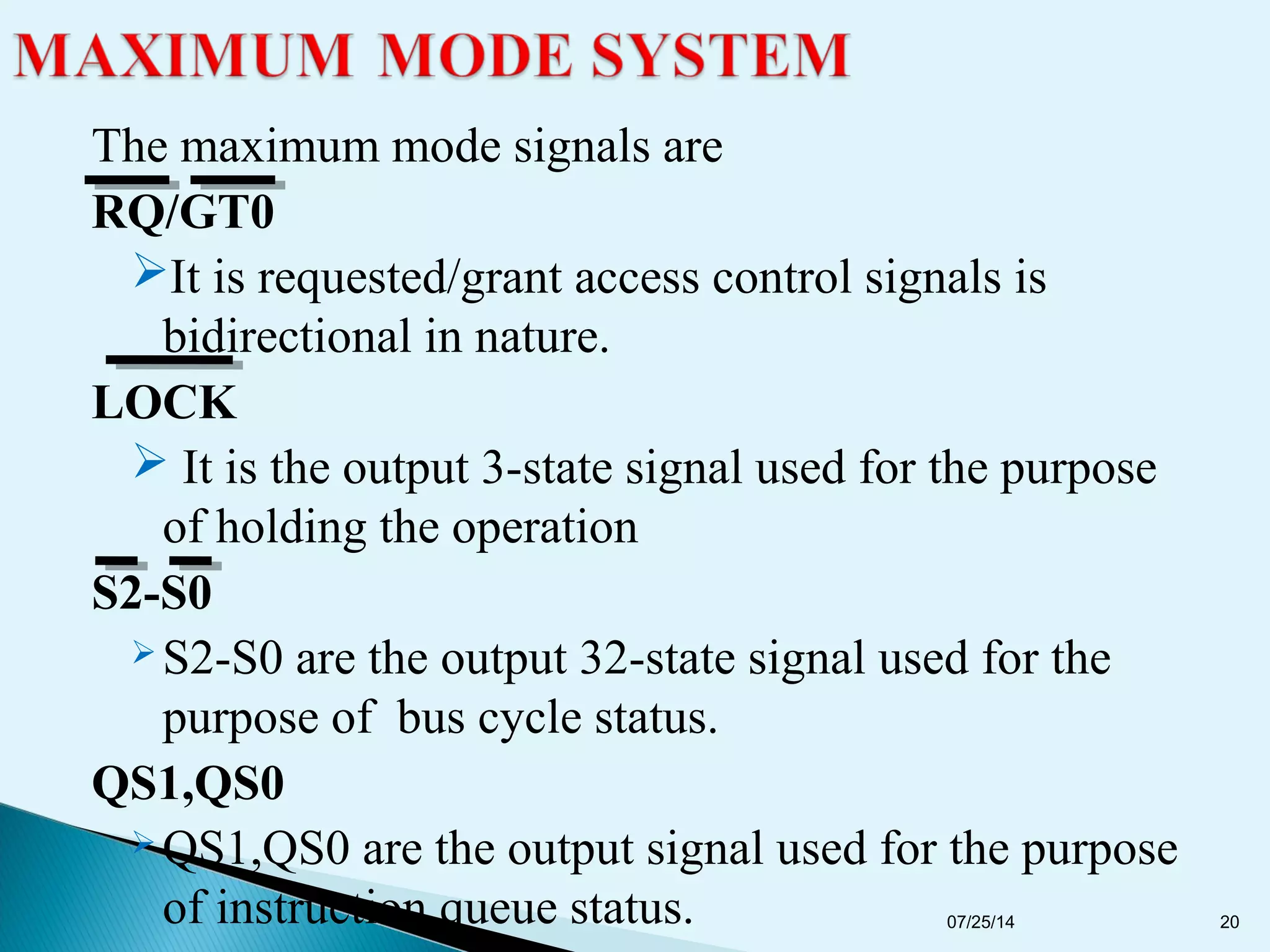
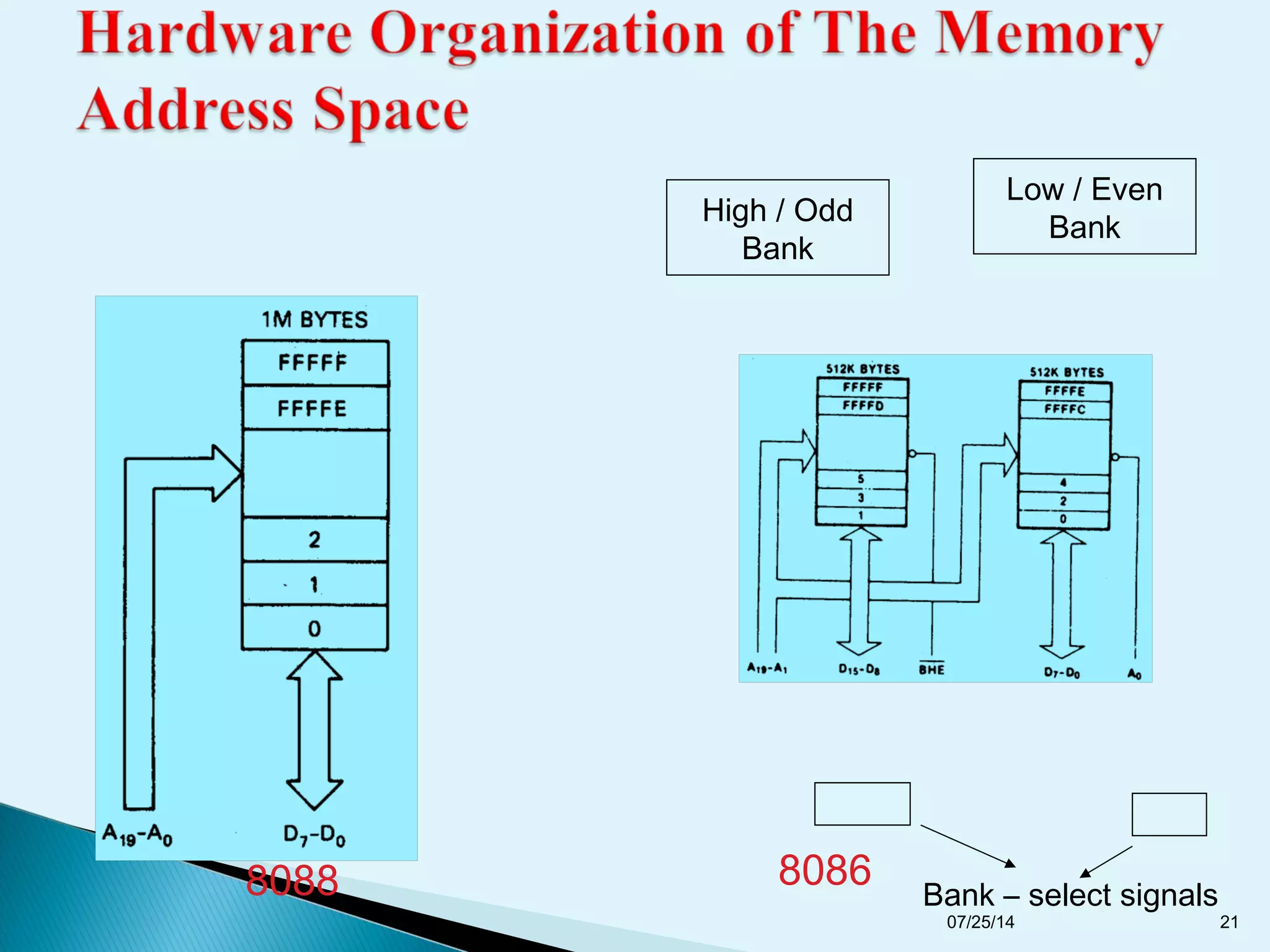
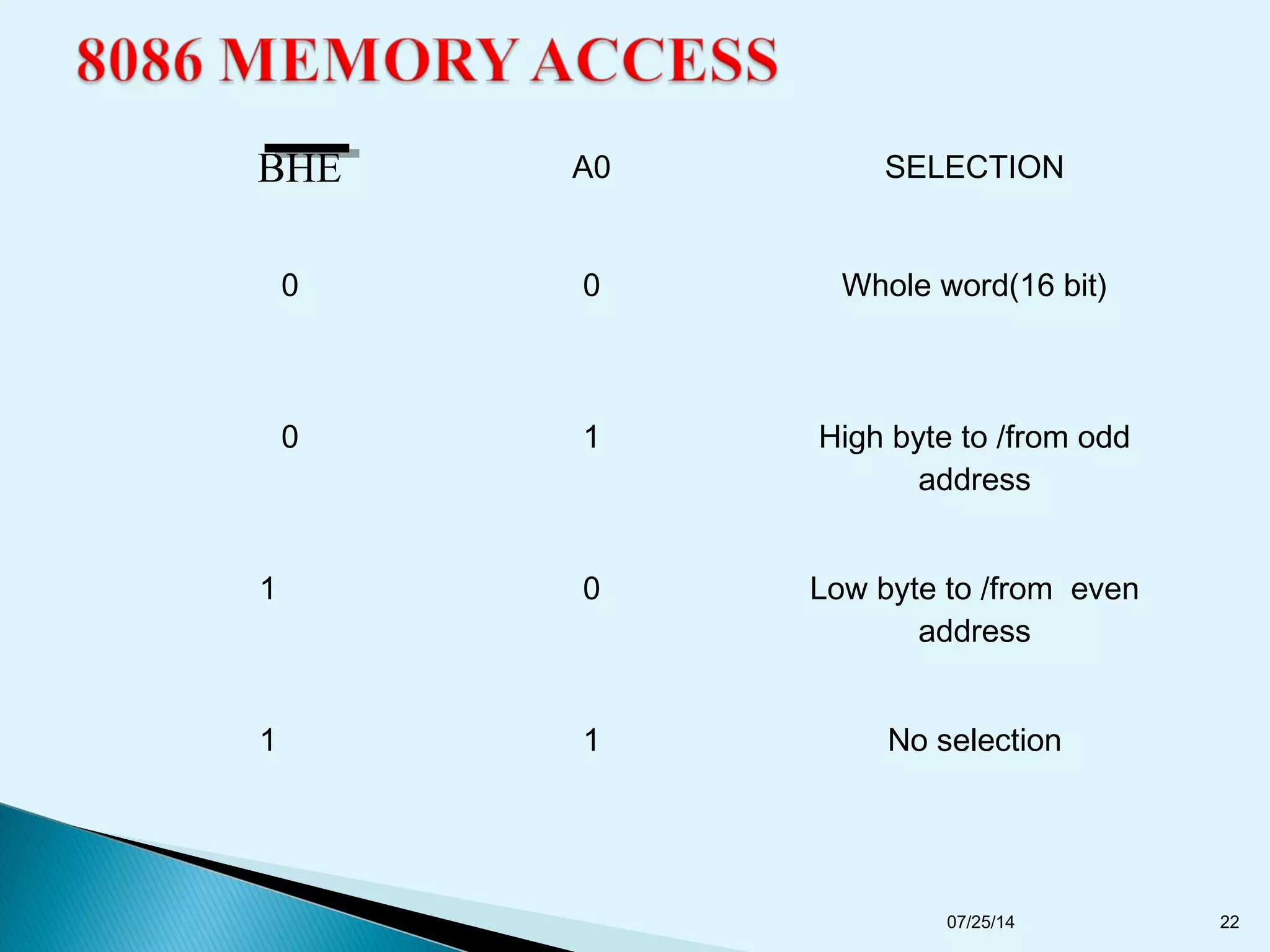
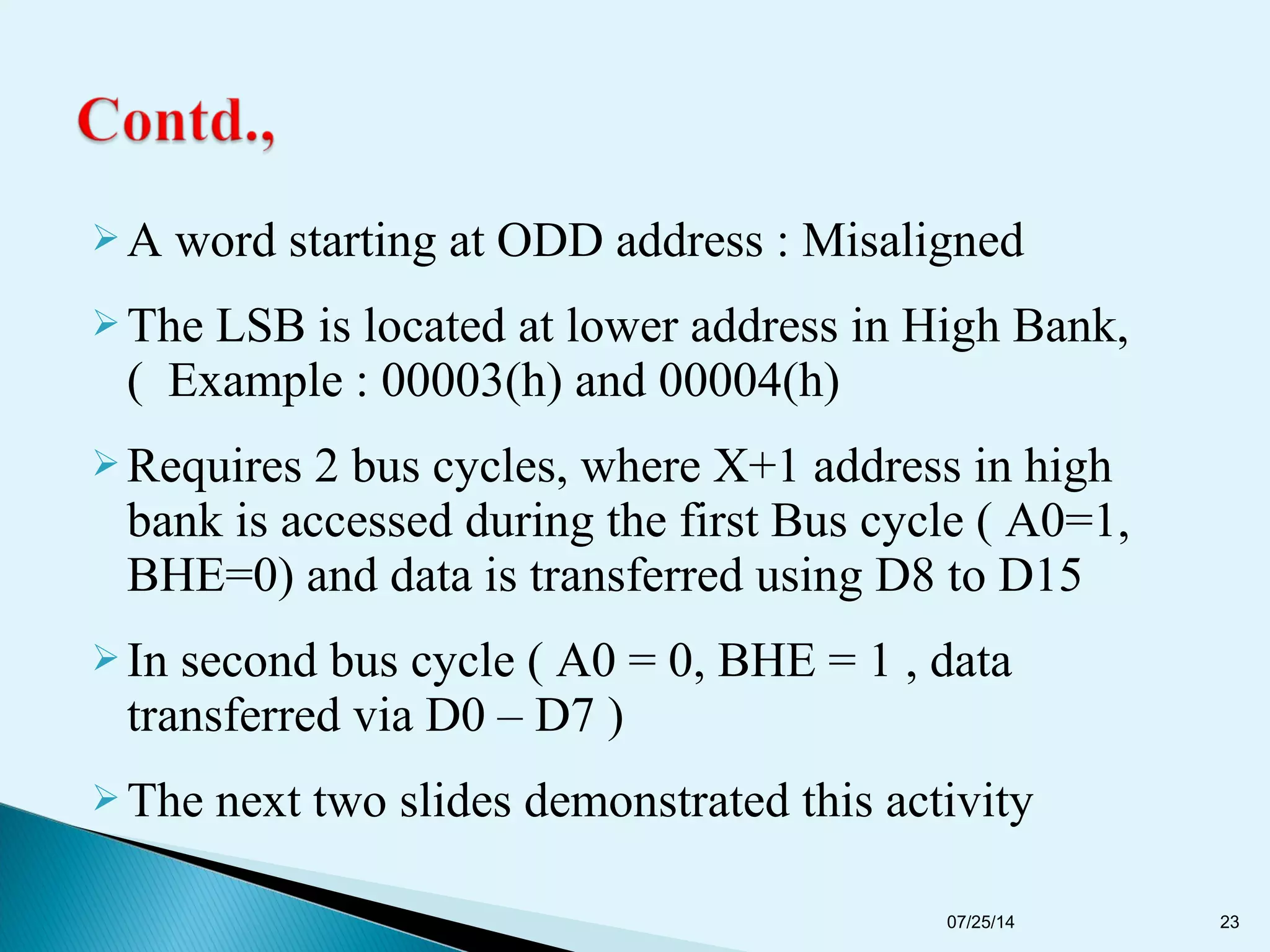
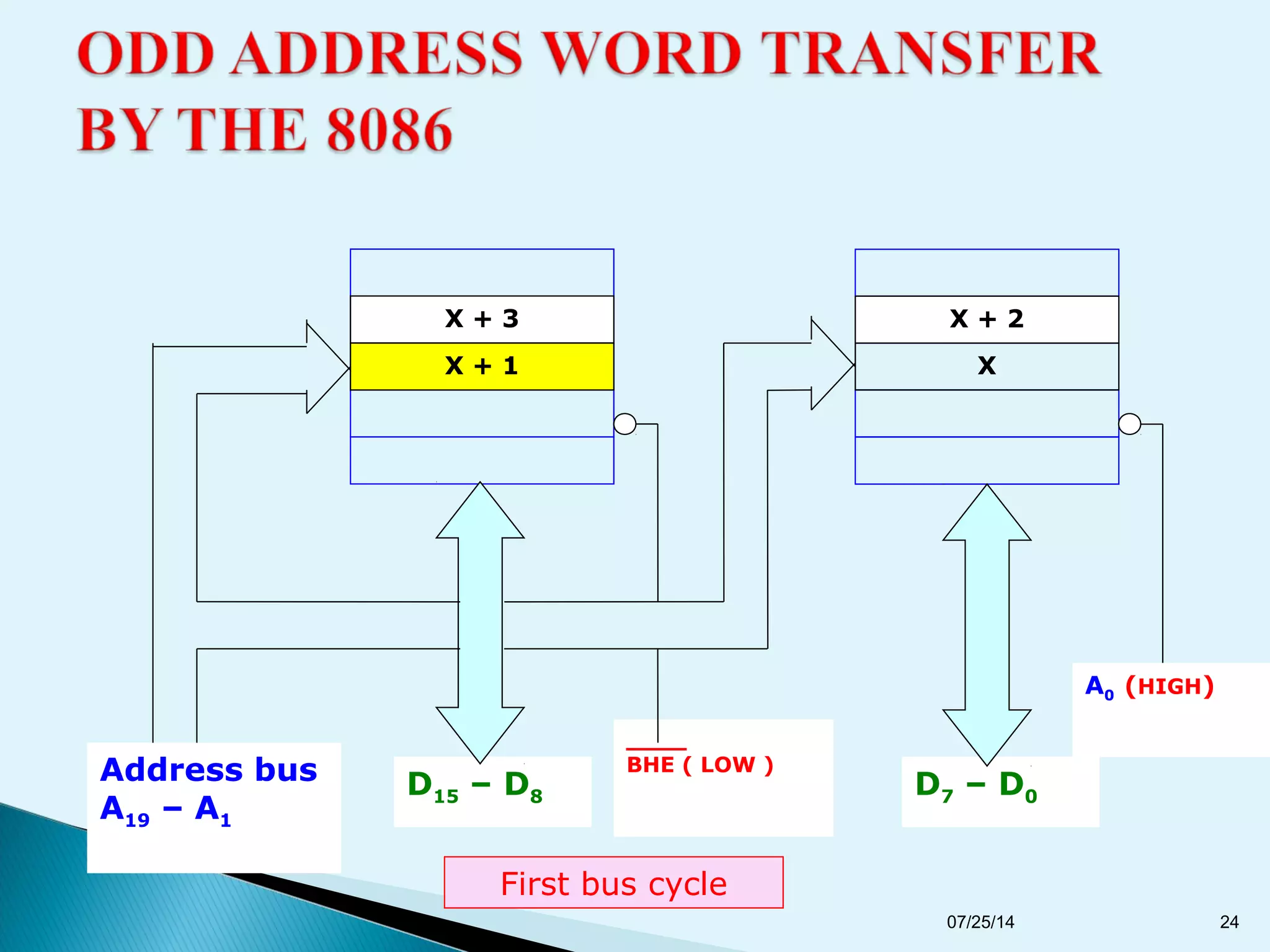
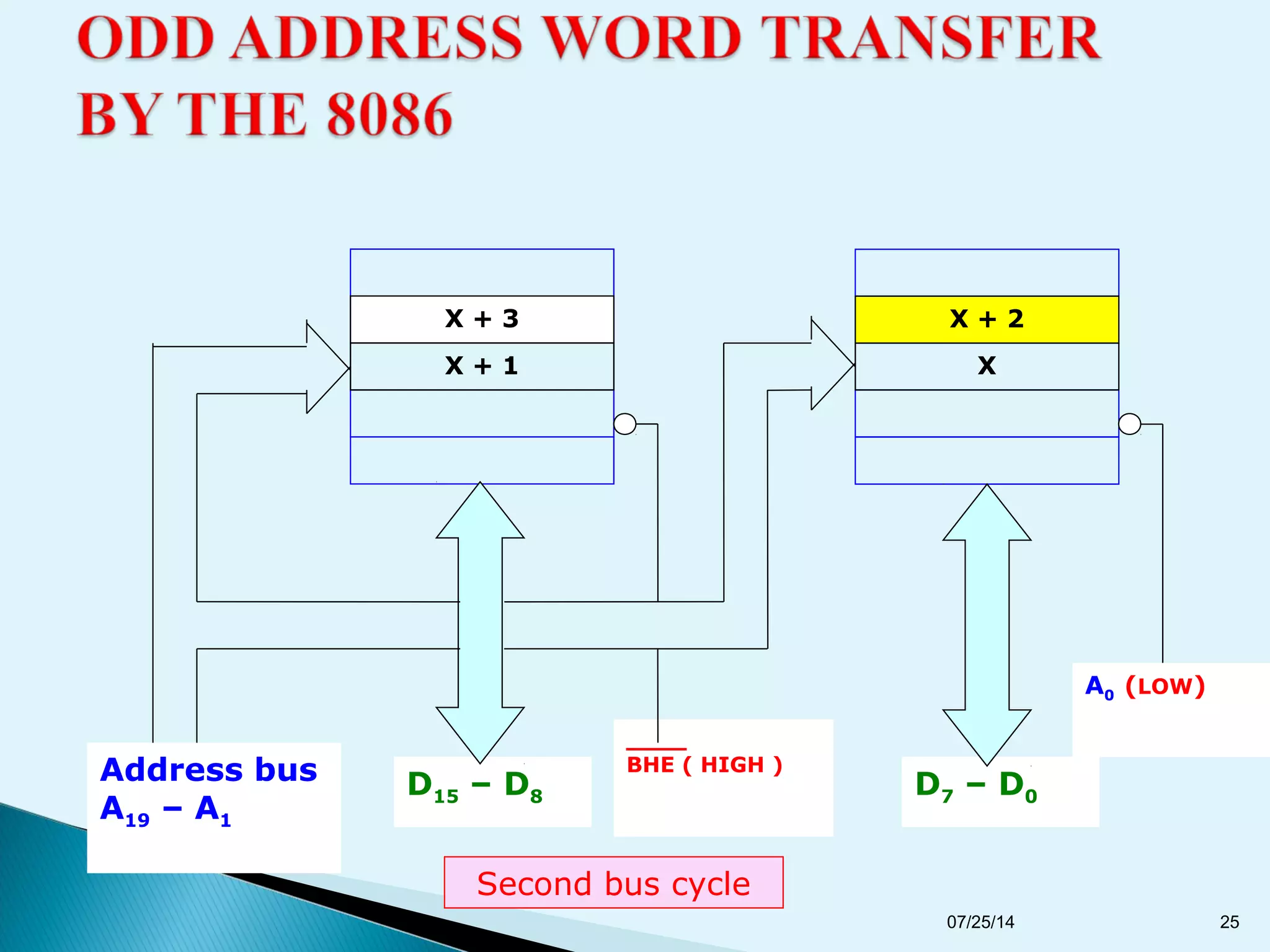
This document discusses the 8086 microprocessor. It provides details on the features of the 8086 including its pin diagram and operating modes. It describes the minimum and maximum mode systems, hardware organization, and applications such as in home appliances, agricultural automation, and networking. The document is presented by five students and guided by their assistant professor.