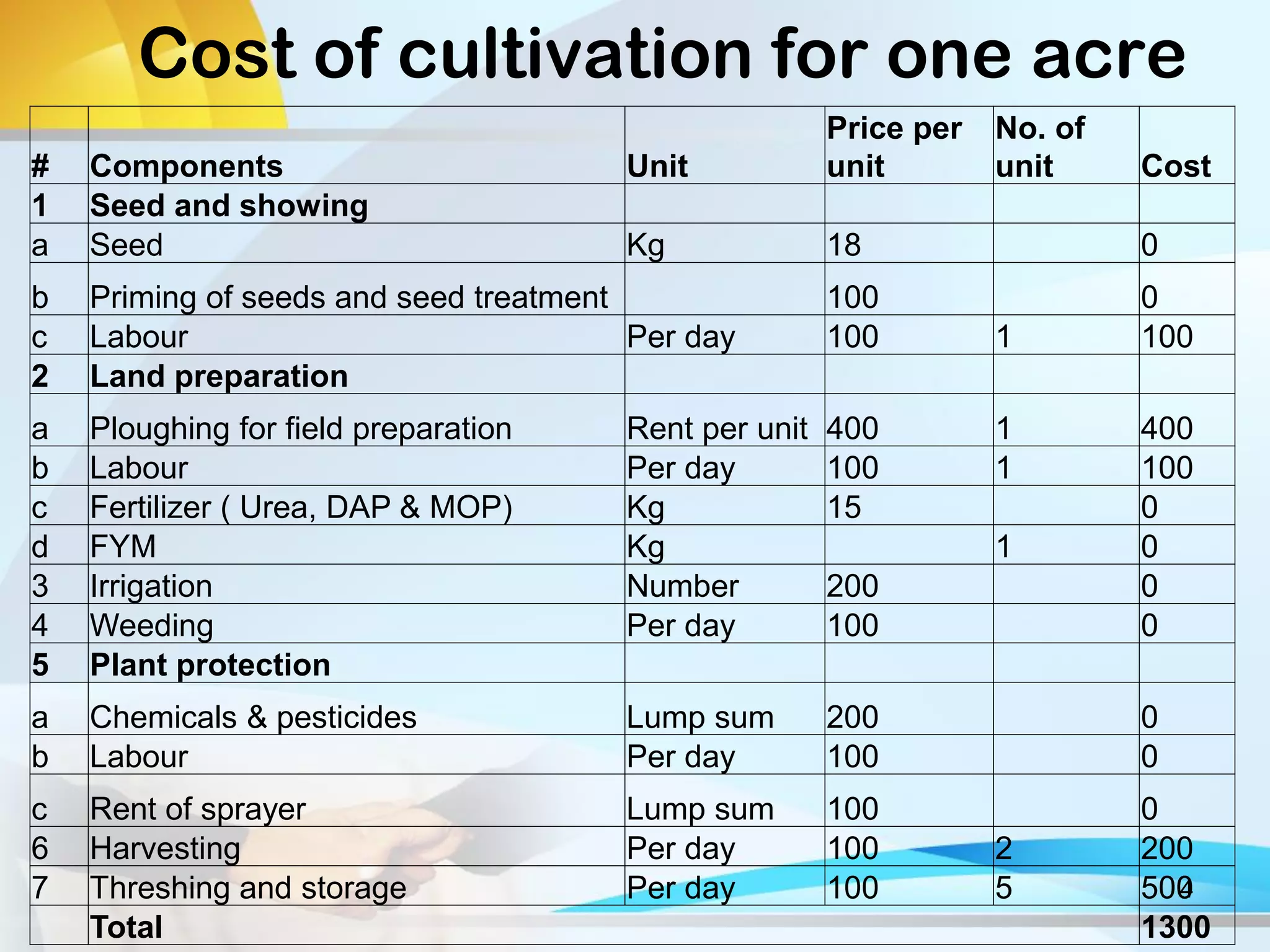
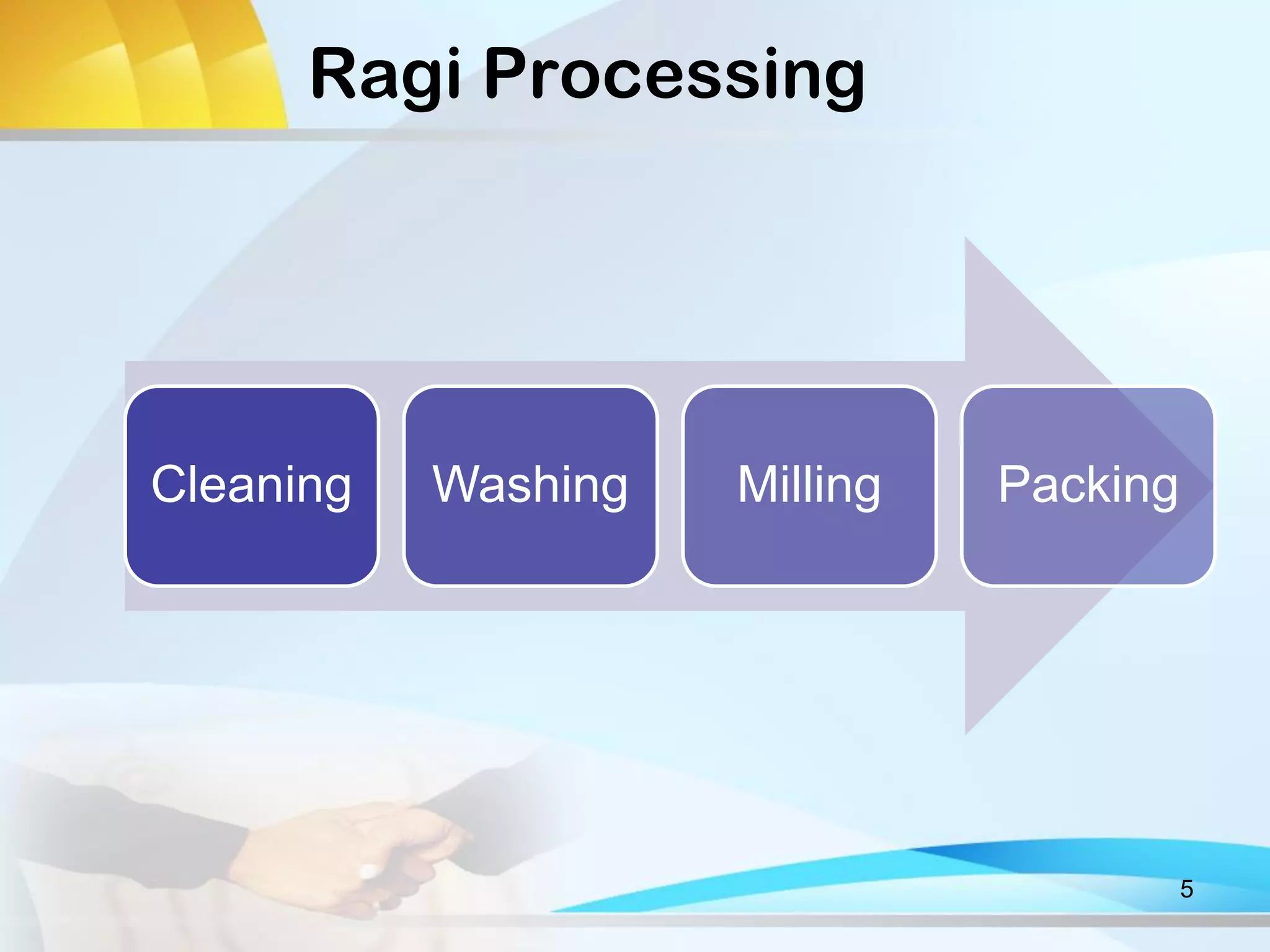
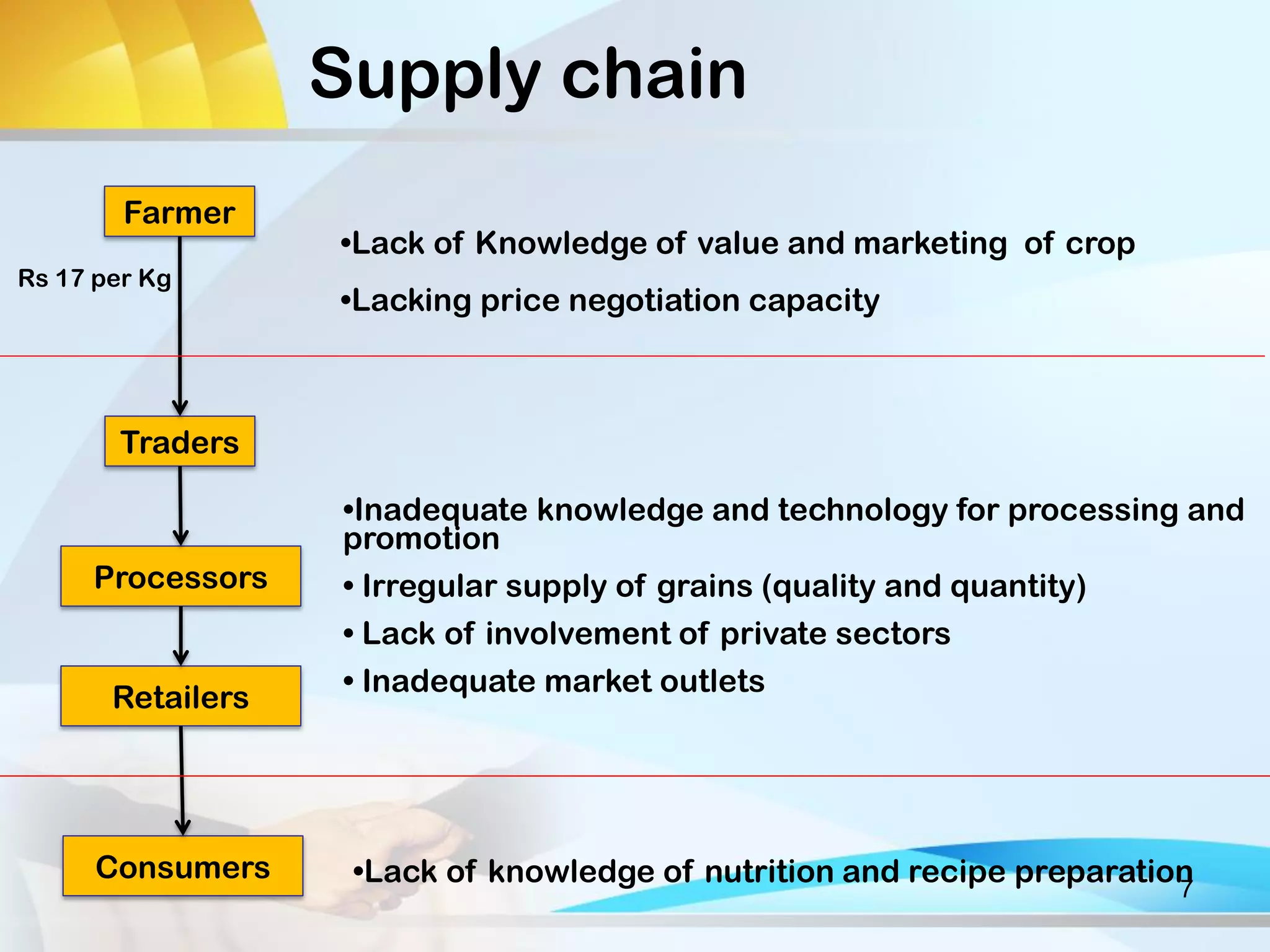
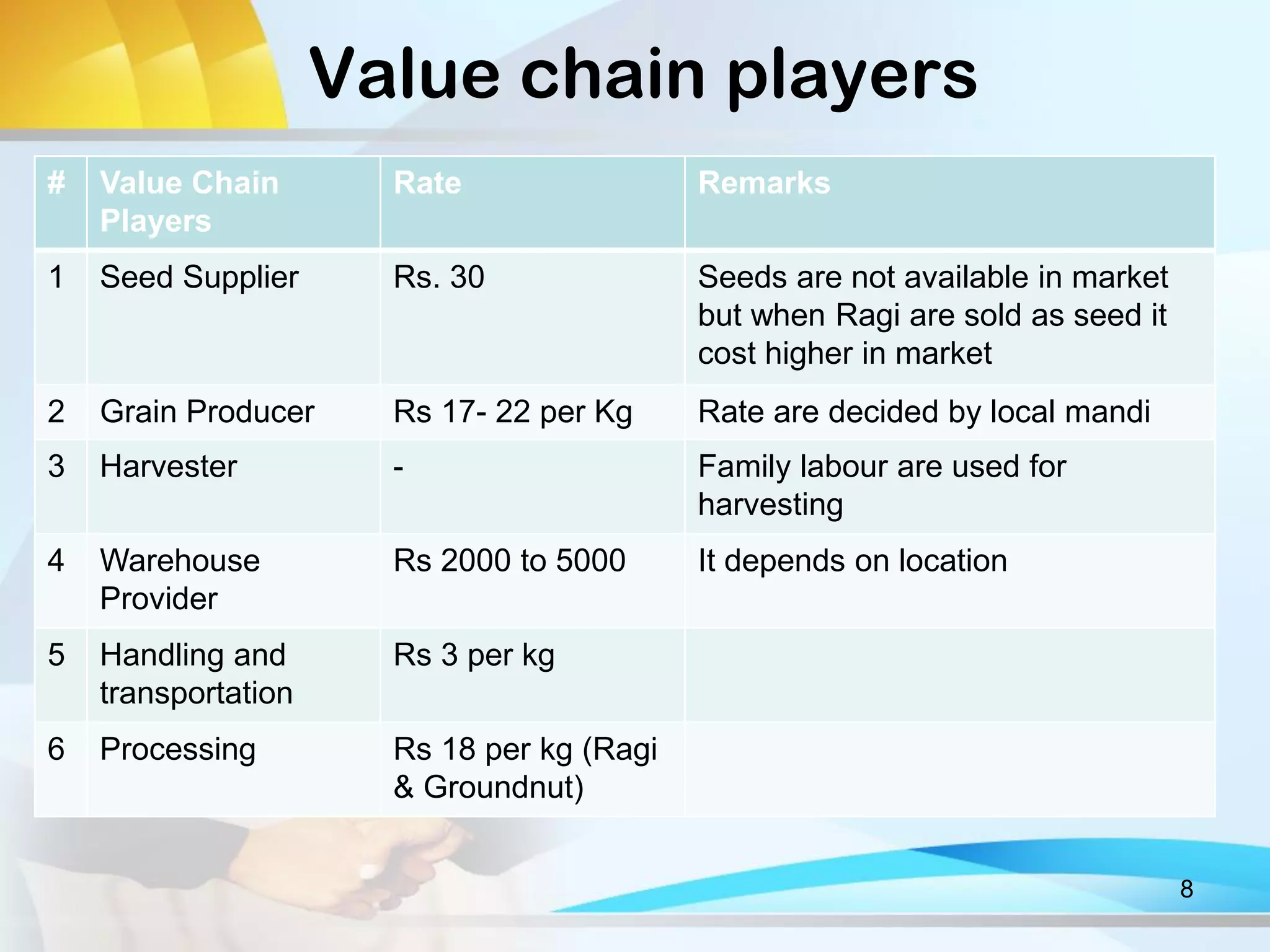
This document discusses Ragi (finger millet) cultivation in India. It provides information on the potential and cost of Ragi production, processing methods, value and supply chains, constraints to cultivation, and a SWOT analysis. Specifically, it notes that the per acre yield of Ragi is 10-12 quintals, the total cost of cultivation for one acre is Rs. 1300, and that processing involves cleaning, washing, and milling the grains. It also outlines the different players in the Ragi value chain and discusses gender roles and challenges in Ragi cultivation. Key constraints mentioned are the traditional methods used, lack of improved varieties, and absence of mechanical processing. The SWOT analysis highlights Ragi's nutritional value but also