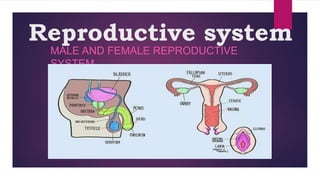
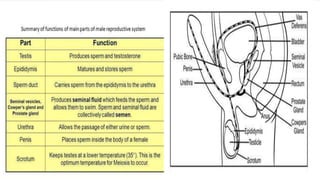
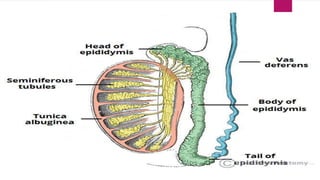
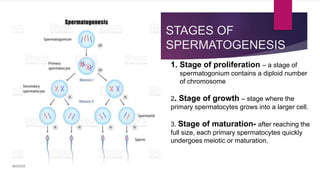
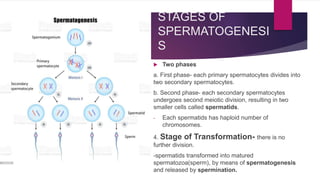
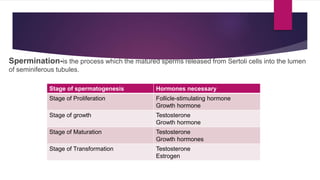
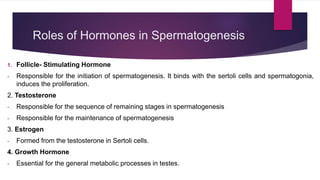
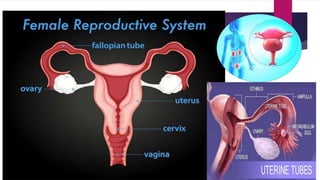
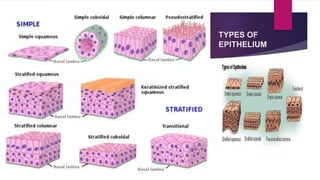
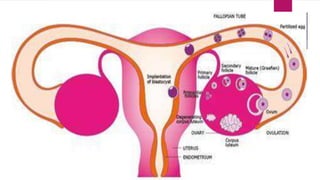
The male and female reproductive systems ensure the continuation of species through the production of gametes. The testes produce sperm in males through spermatogenesis, while the ovaries produce eggs in females. Spermatogenesis occurs in the seminiferous tubules and involves the transformation of spermatogonia into mature sperm through meiosis. Hormones such as FSH, testosterone, and estrogen regulate spermatogenesis. In females, the ovaries and accessory organs such as the uterus and vagina comprise the reproductive system, which undergoes cyclical changes regulated by hormones to facilitate fertilization and pregnancy.