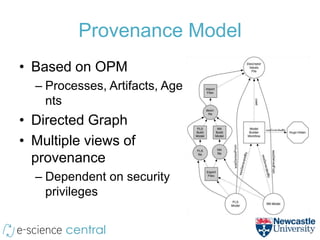
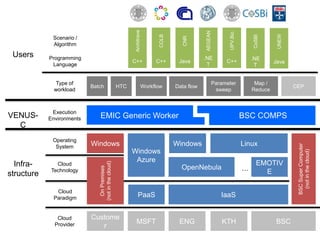
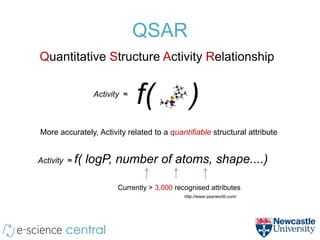
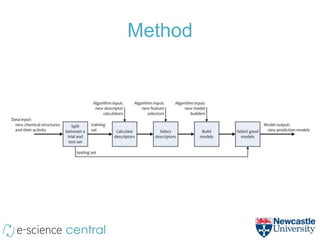
This document summarizes a method for using cloud computing resources to efficiently explore large model spaces for quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) modeling. Key points:
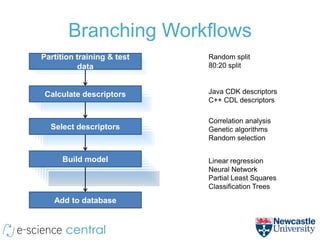
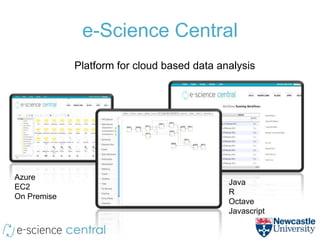
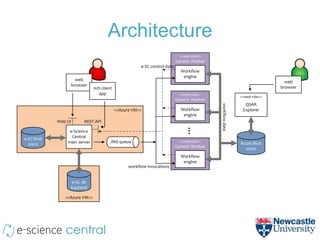
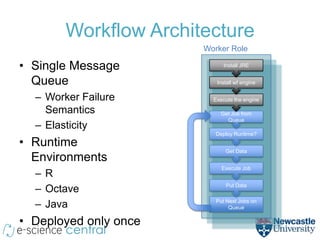
- The method uses e-Science Central and Windows Azure to run QSAR modeling workflows in parallel across many nodes, allowing exploration of large model spaces.
- Over 250,000 models were generated exploring different modeling methods (e.g. linear regression, neural networks) across 460,000 workflow executions and 4.4 million service calls.
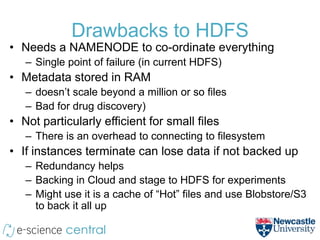
- Scaling to 200 nodes reduced modeling time from over 11 days to under 2 hours, demonstrating near-linear speedups from additional nodes.



![Scalability: Large Scale QSAR
16:48
480 datasets sequential time: 11 days
GW
100 Nodes 200 Nodes
14:24 Azur
e
Response Time 3hr 19mins 1hr 50mins
Speedup 94x 156x 12:00
Execution time [hh:mm]
Efficiency 94% 78%
09:36
Cost $55.68 $51.84
250.0
07:12
200.0
Relative processing speed-up
04:48
150.0
100.0 02:24
50.0 Azure
ideal 00:00
GW 0 50 100 150 200 250
0.0
Number of processors
0 50 100 150 200 250
Number of processors](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sjwslcsc2012talk-121128030441-phpapp01/85/Microsoft-HPC-User-Group-14-320.jpg)