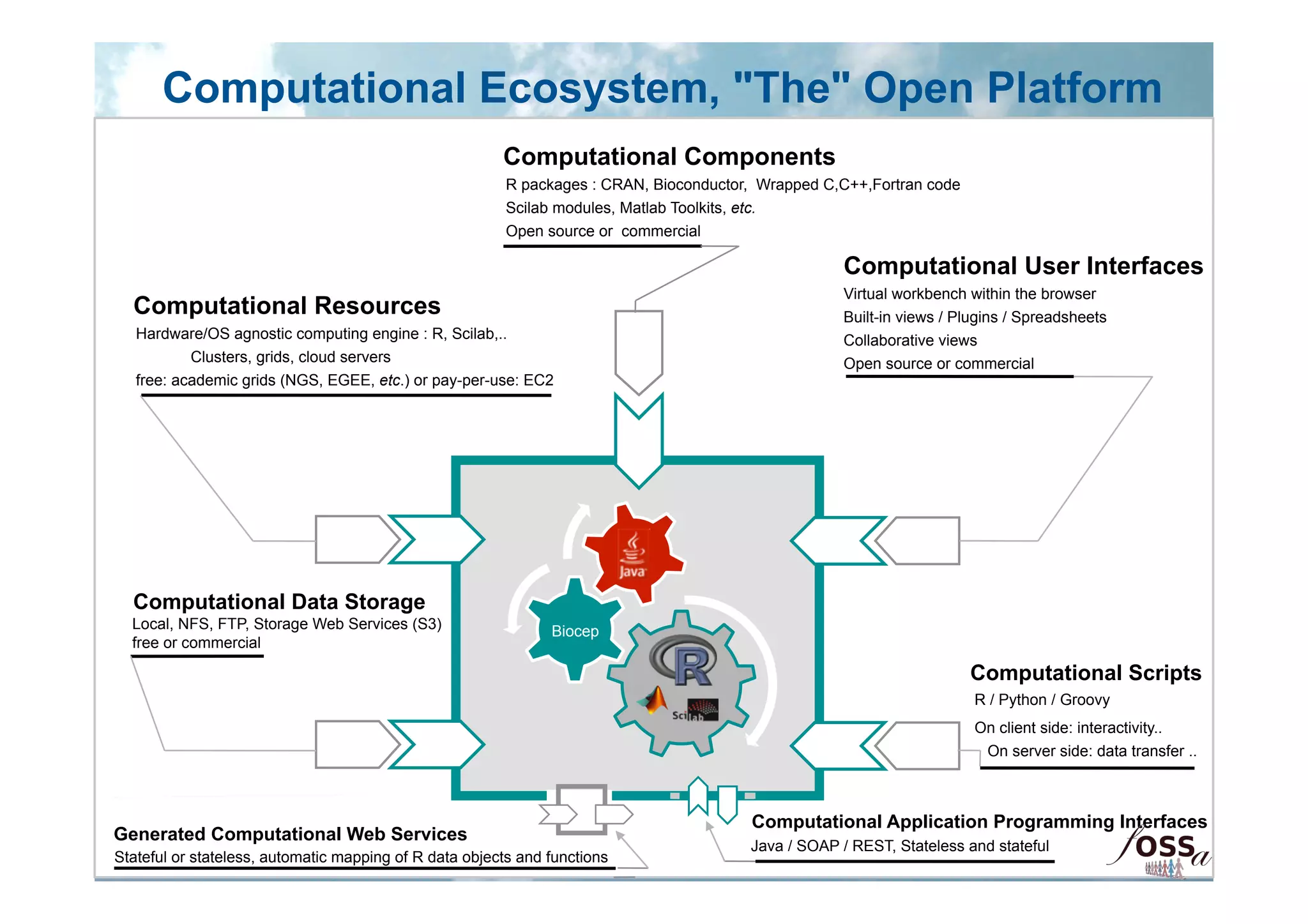
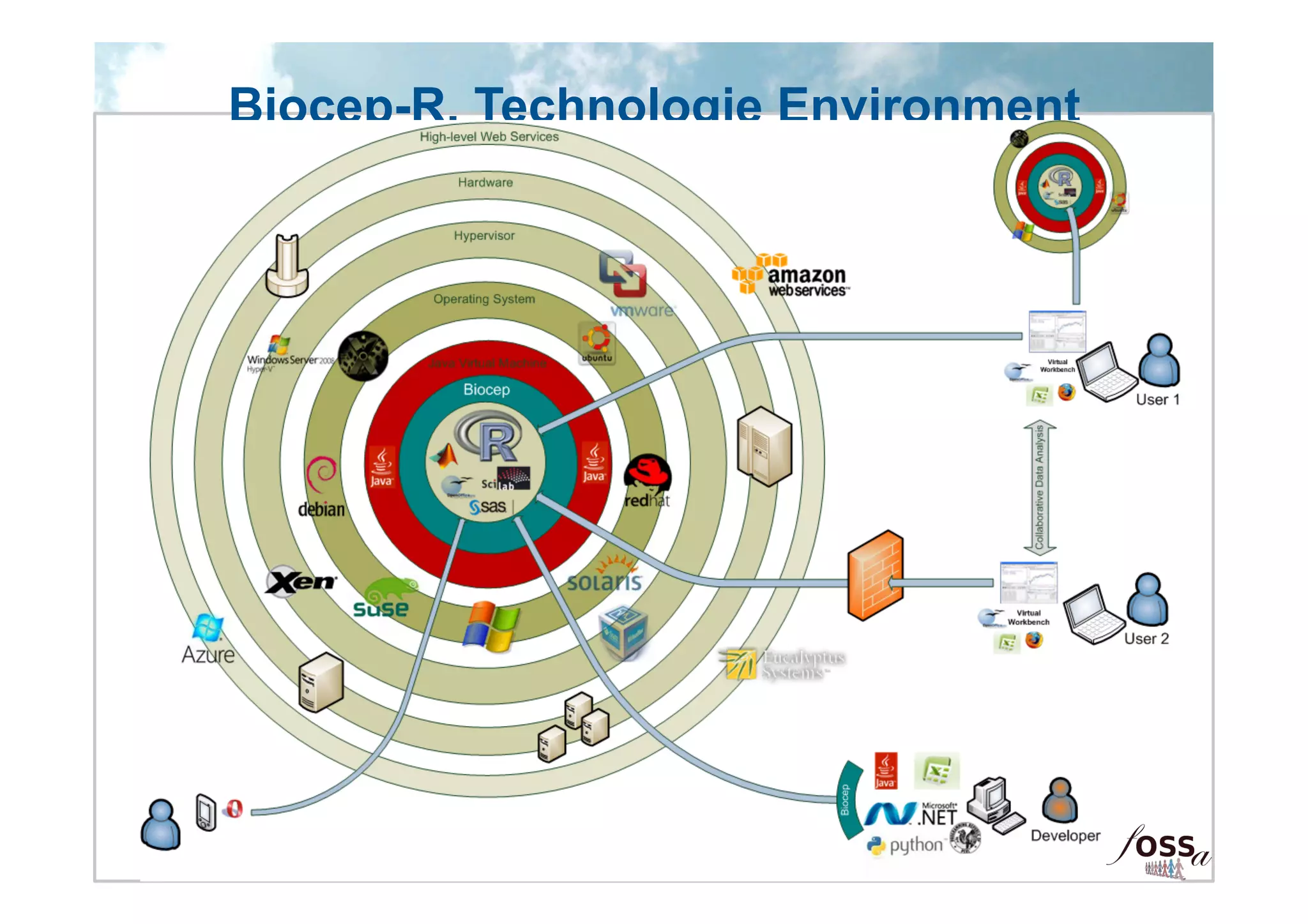
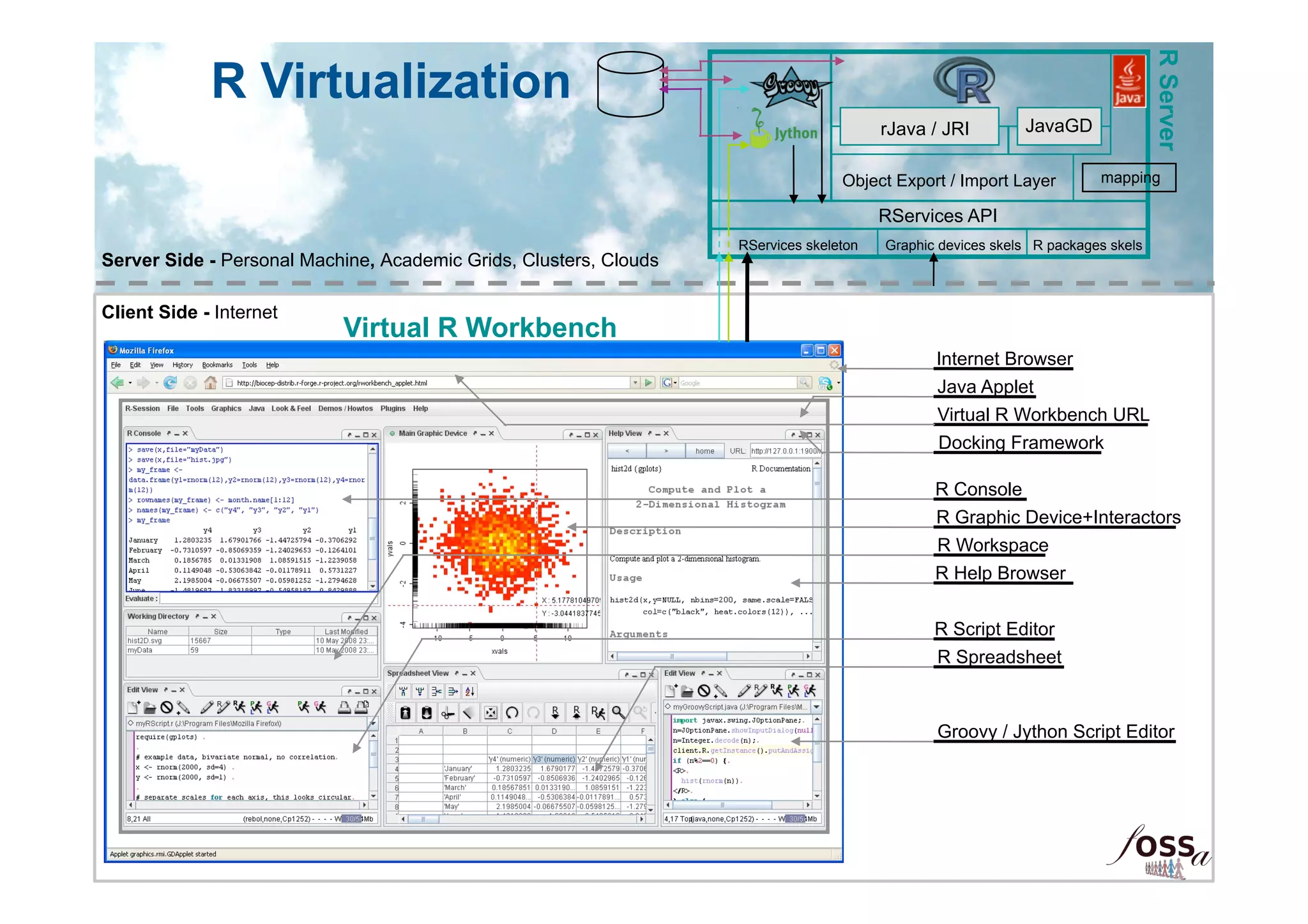
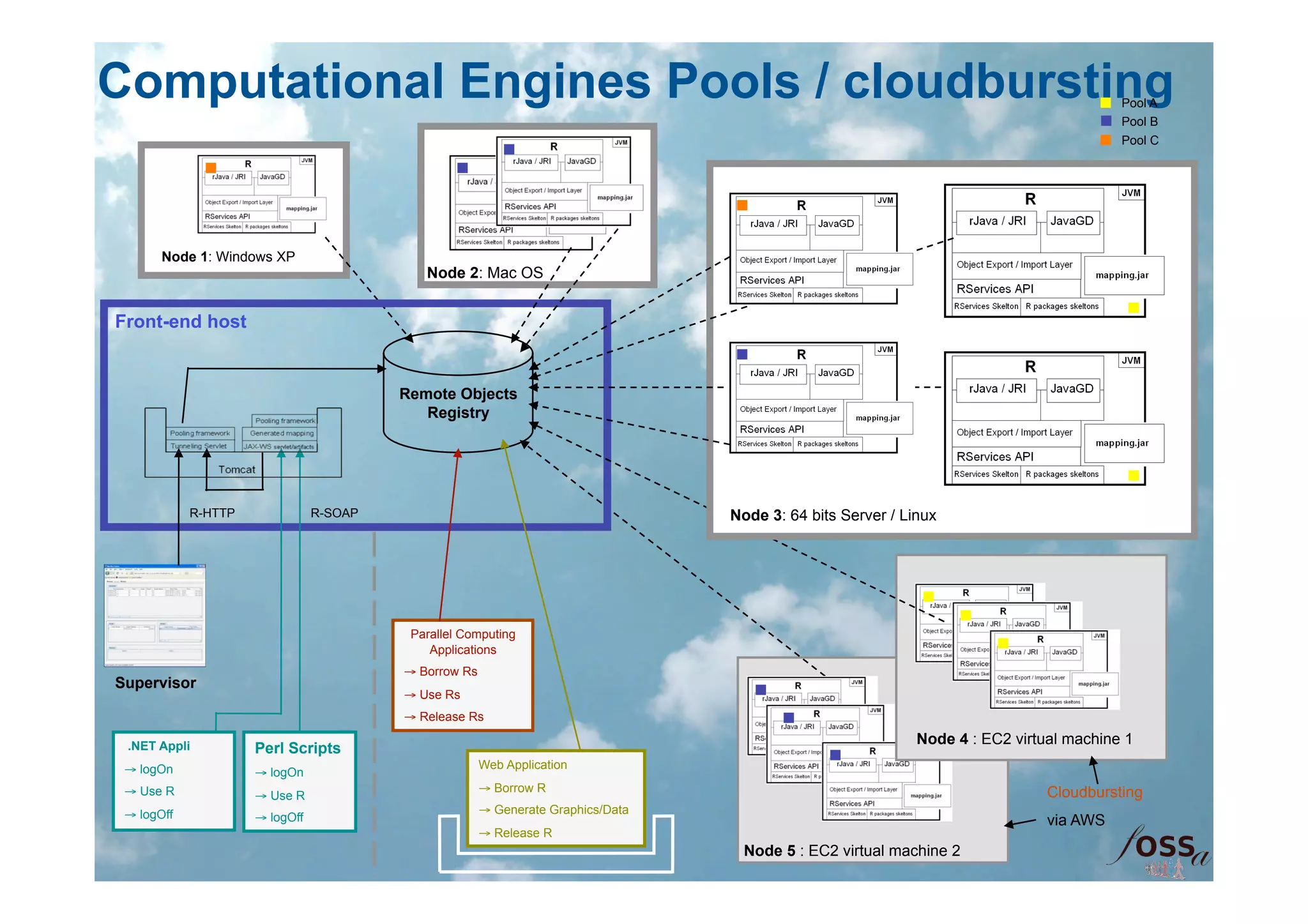
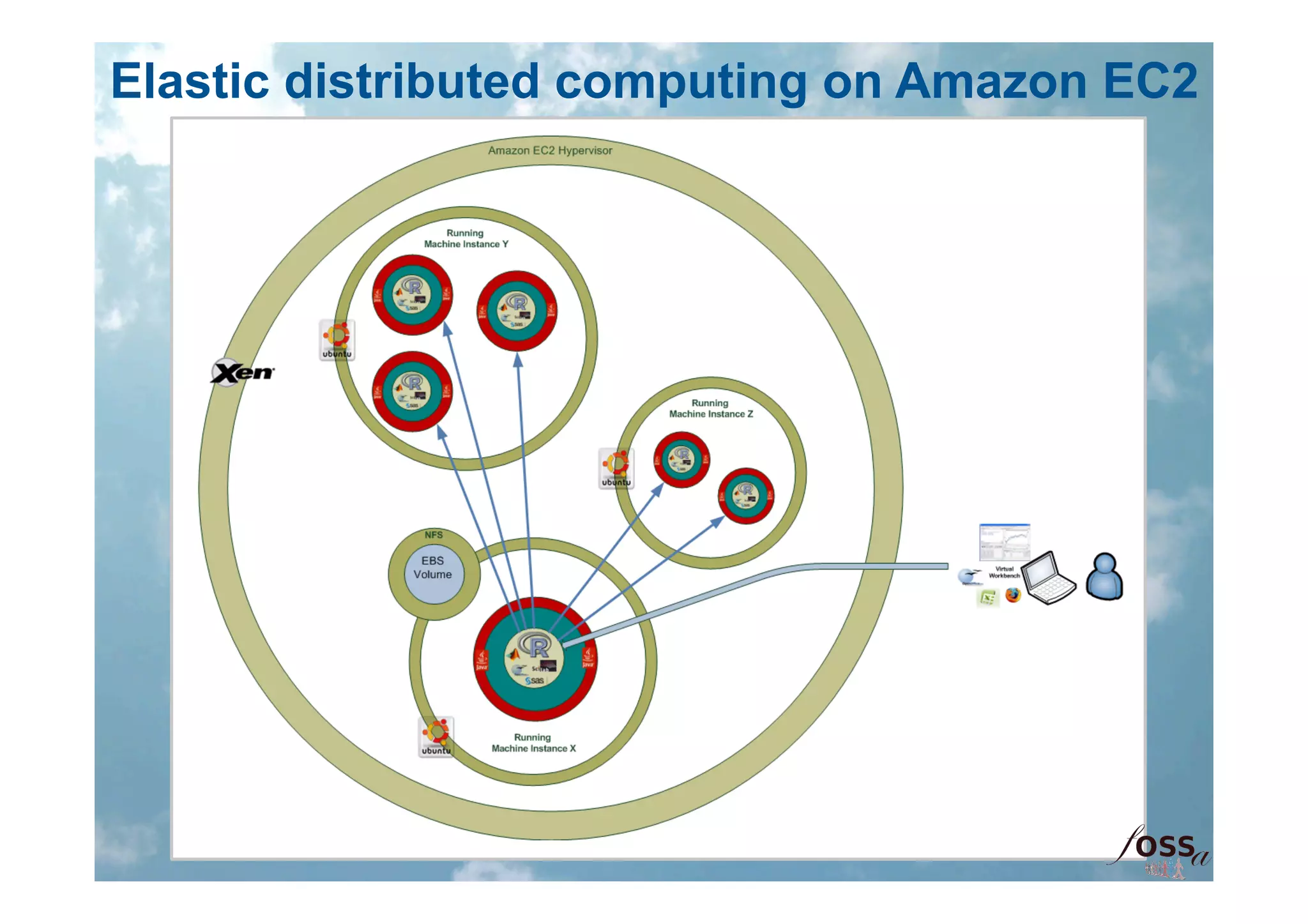
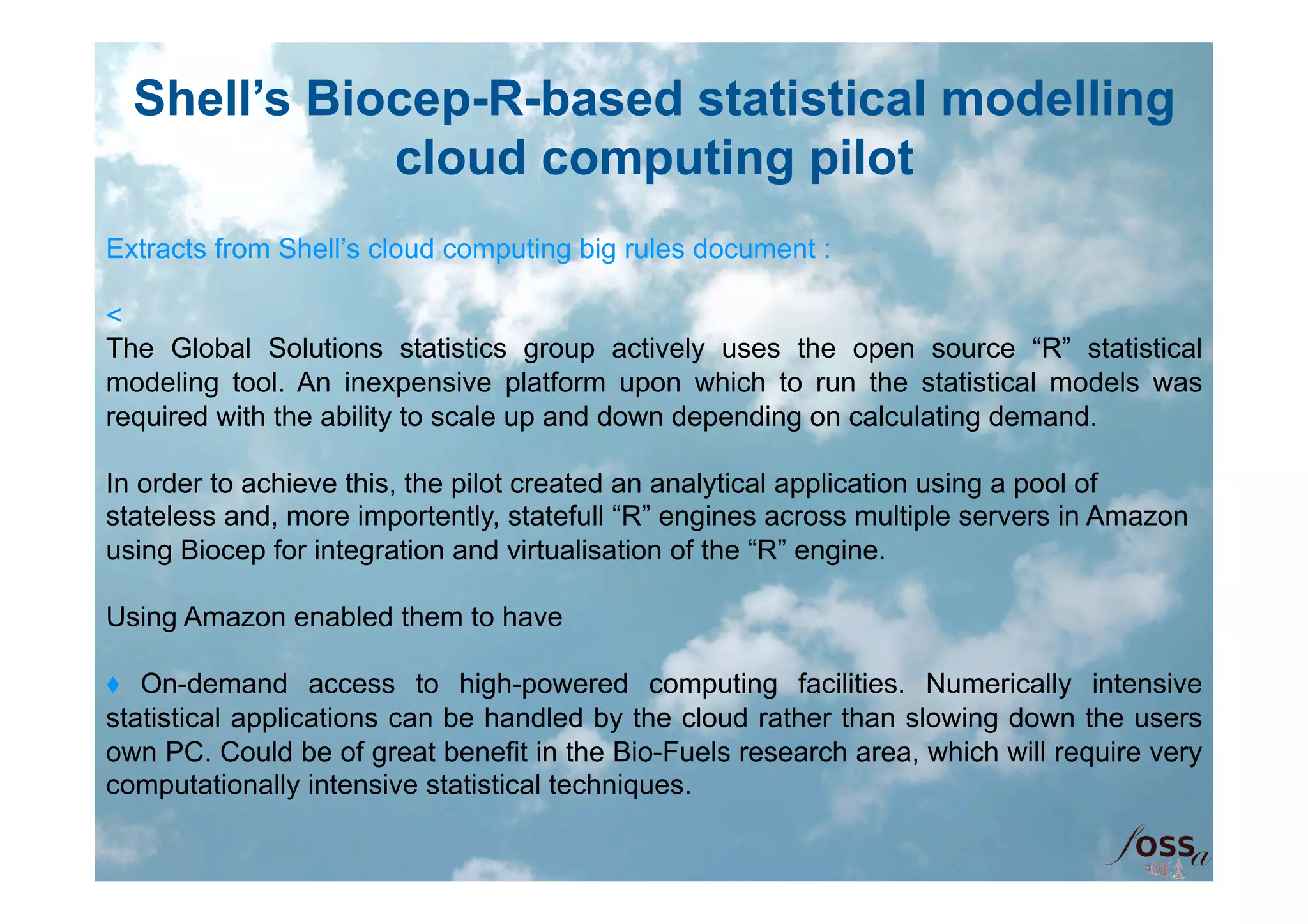
The document discusses the integration of open science and cloud computing, emphasizing the importance of cloud-based platforms for mathematical and statistical computing. It highlights tools like R and Scilab for data analysis, their applications in collaborative environments, and the advantages of using cloud infrastructure for scalable computing. The document also mentions the benefits of cloud computing in disaster recovery, real-time collaboration, and improved accessibility to statistical applications.