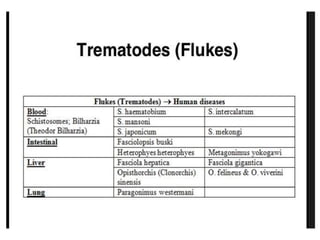
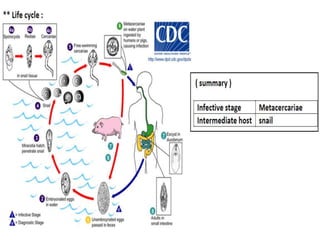
Schistosomes are trematode parasites that infect humans and animals. They have separate sexes unlike other trematodes. The eggs of different Schistosome species vary in shape and features. Schistosome infection occurs through skin penetration by the cercarial stage released from infected snails. Adult worms reside in the mesenteric or bladder veins depending on the species. The pathology results primarily from the host immune response to eggs that are deposited in tissues.