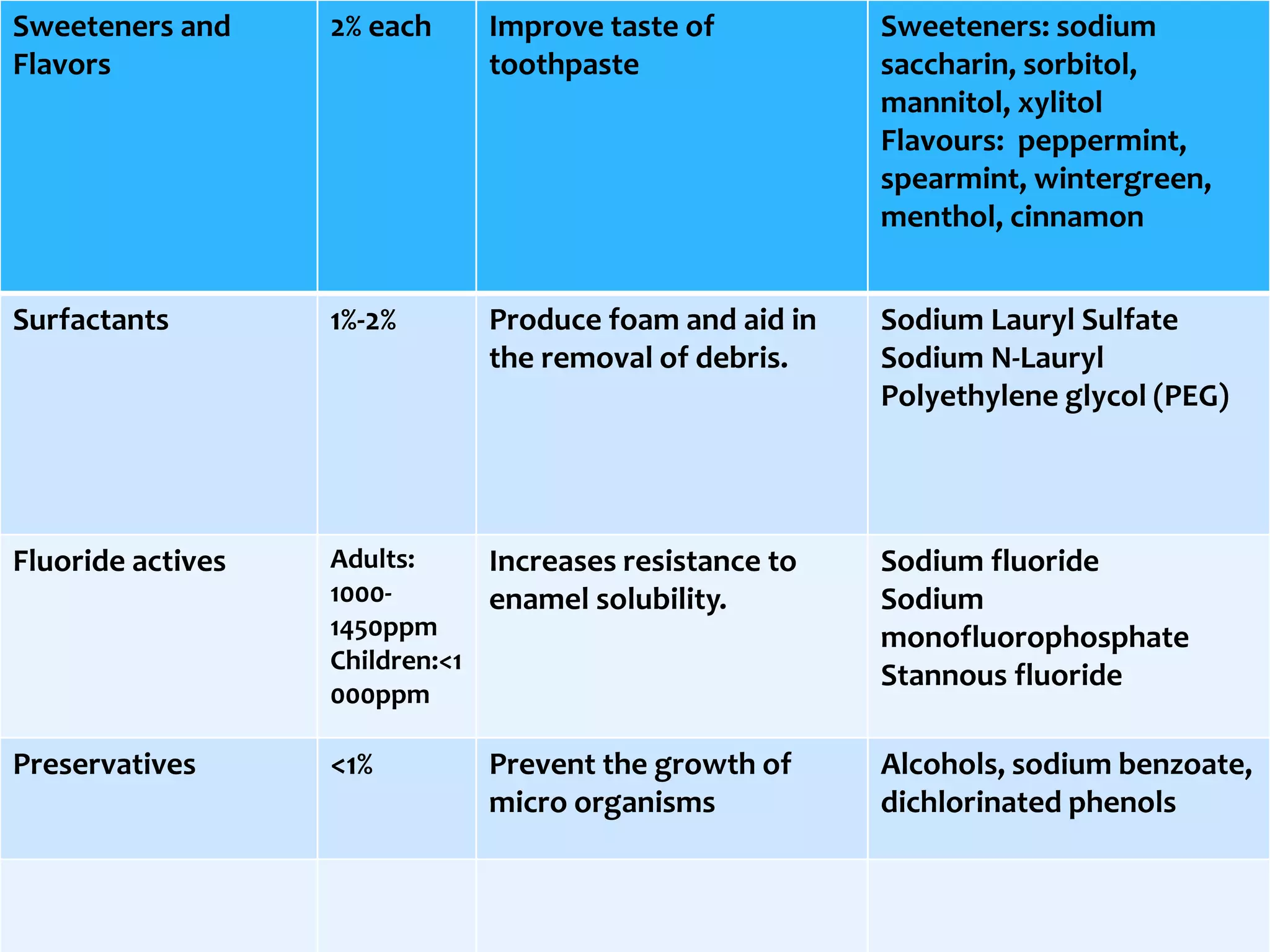
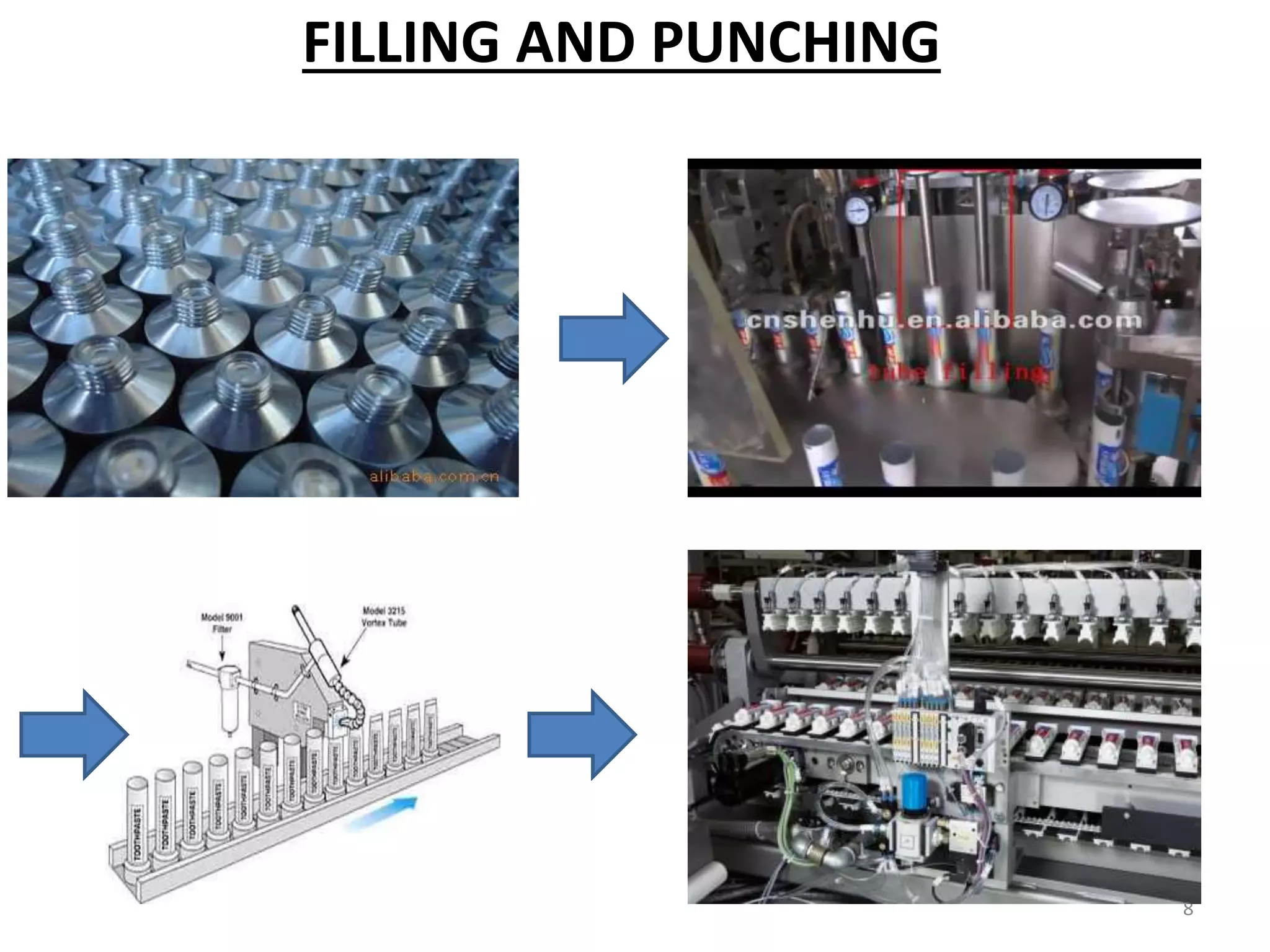
The production process of toothpaste involves mixing various ingredients like abrasives, binders, humectants, sweeteners, flavors, surfactants, and fluoride actives in precise quantities. The ingredients are mixed together and then the mixture is used to fill tubes through an automated filling and punching process. Once filled, the tubes are moved to a warehouse for storage before distribution. Mass production is employed to efficiently create large volumes of standardized toothpaste products on an assembly line.