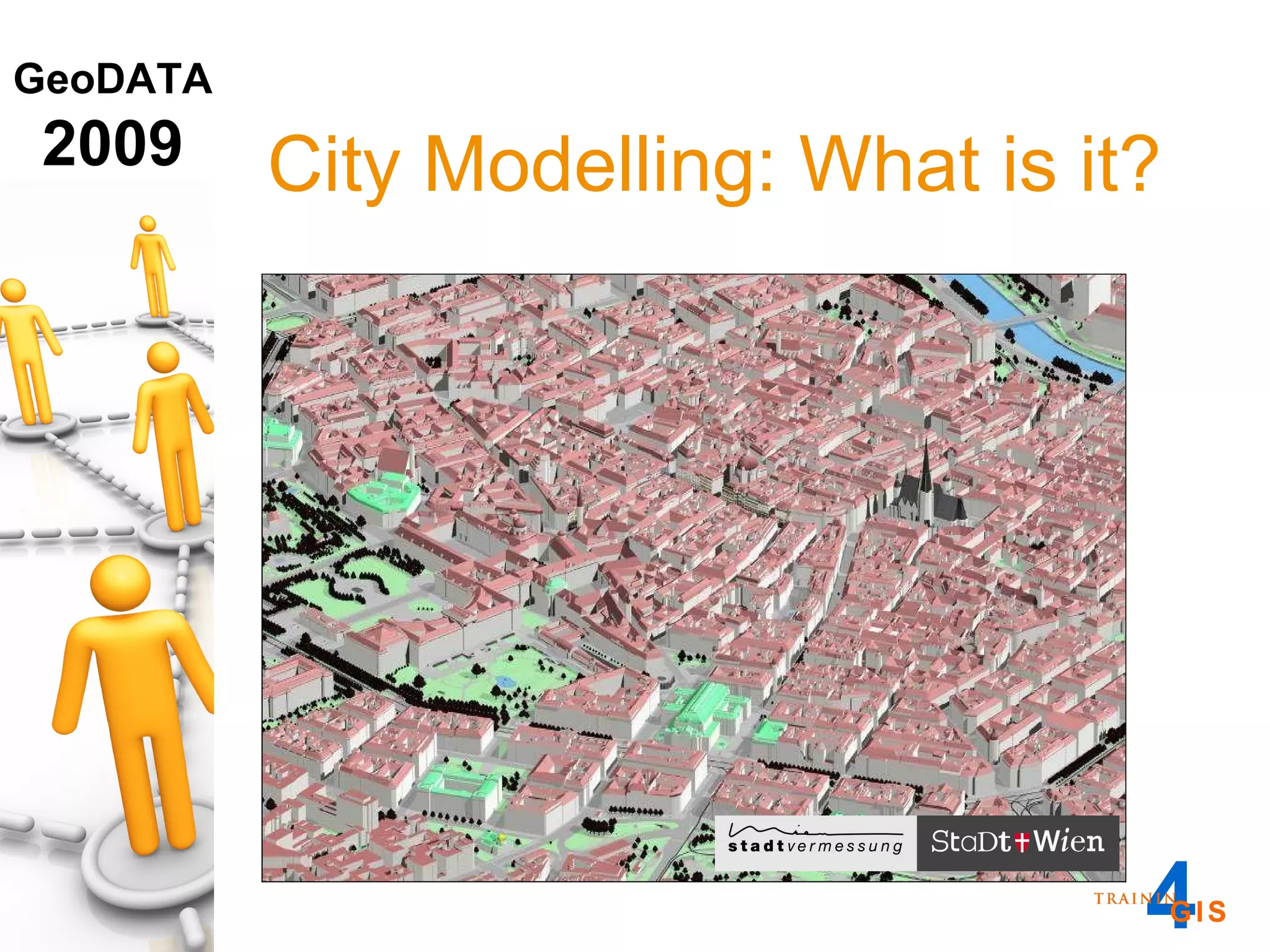
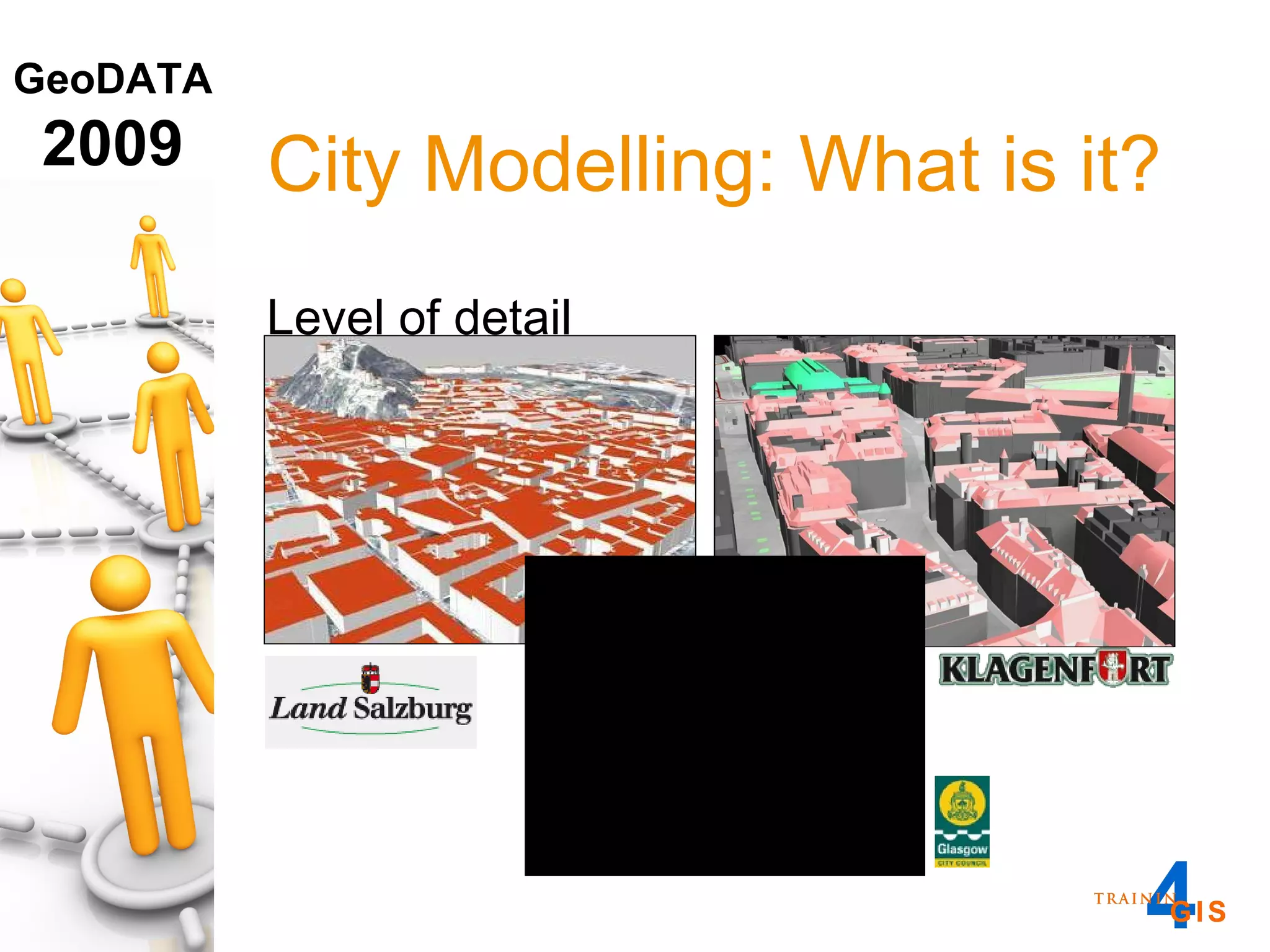
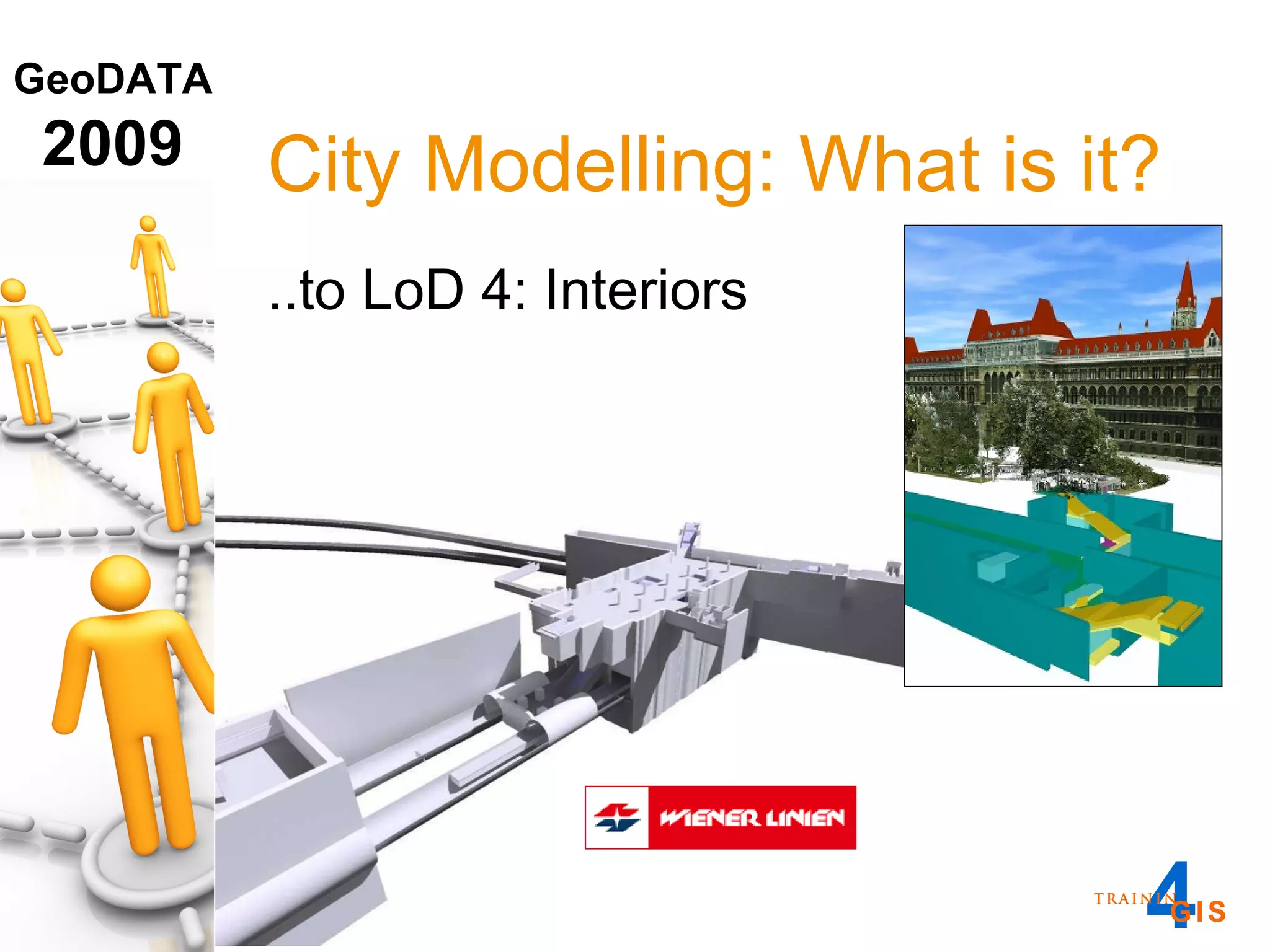
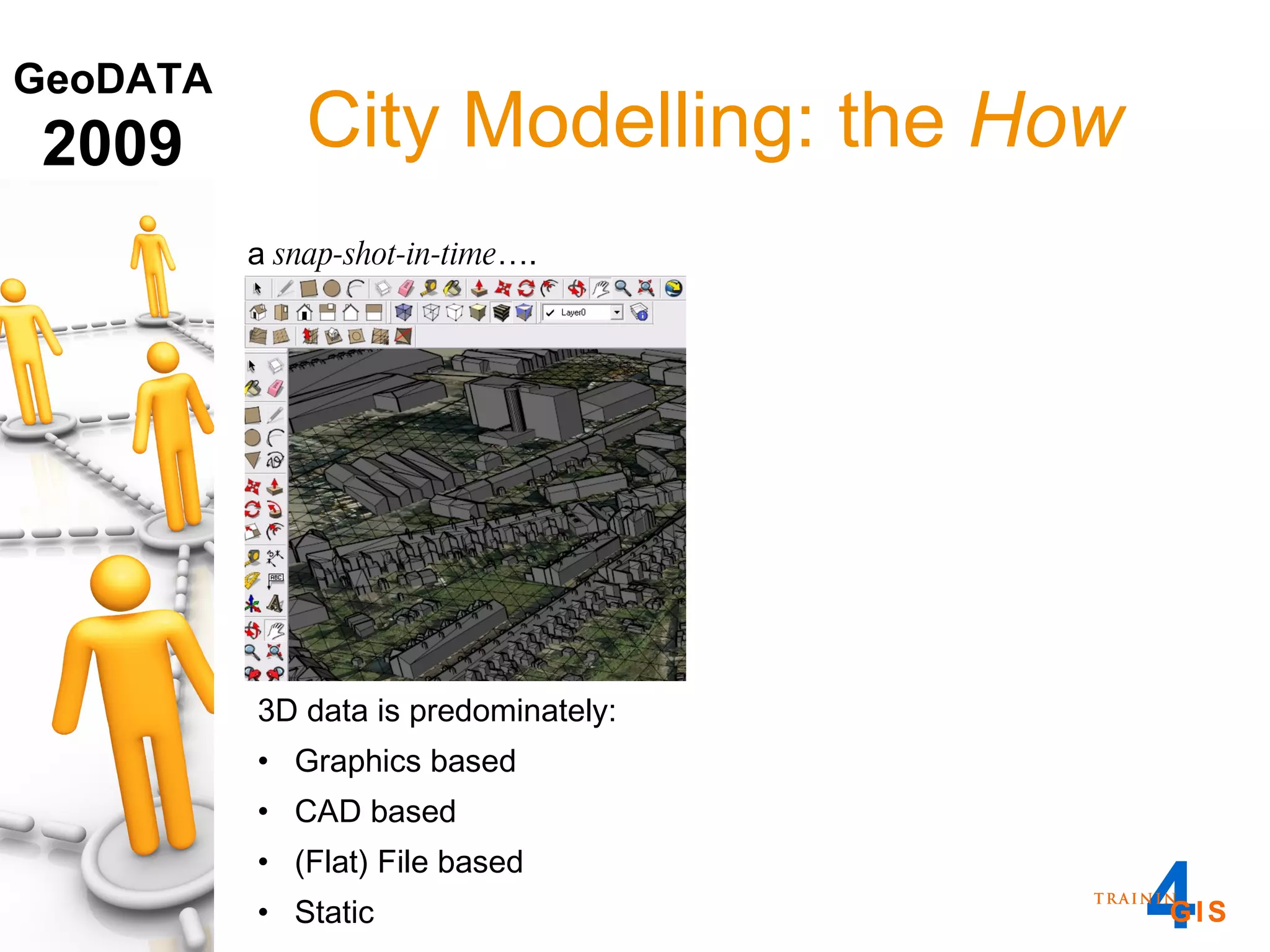
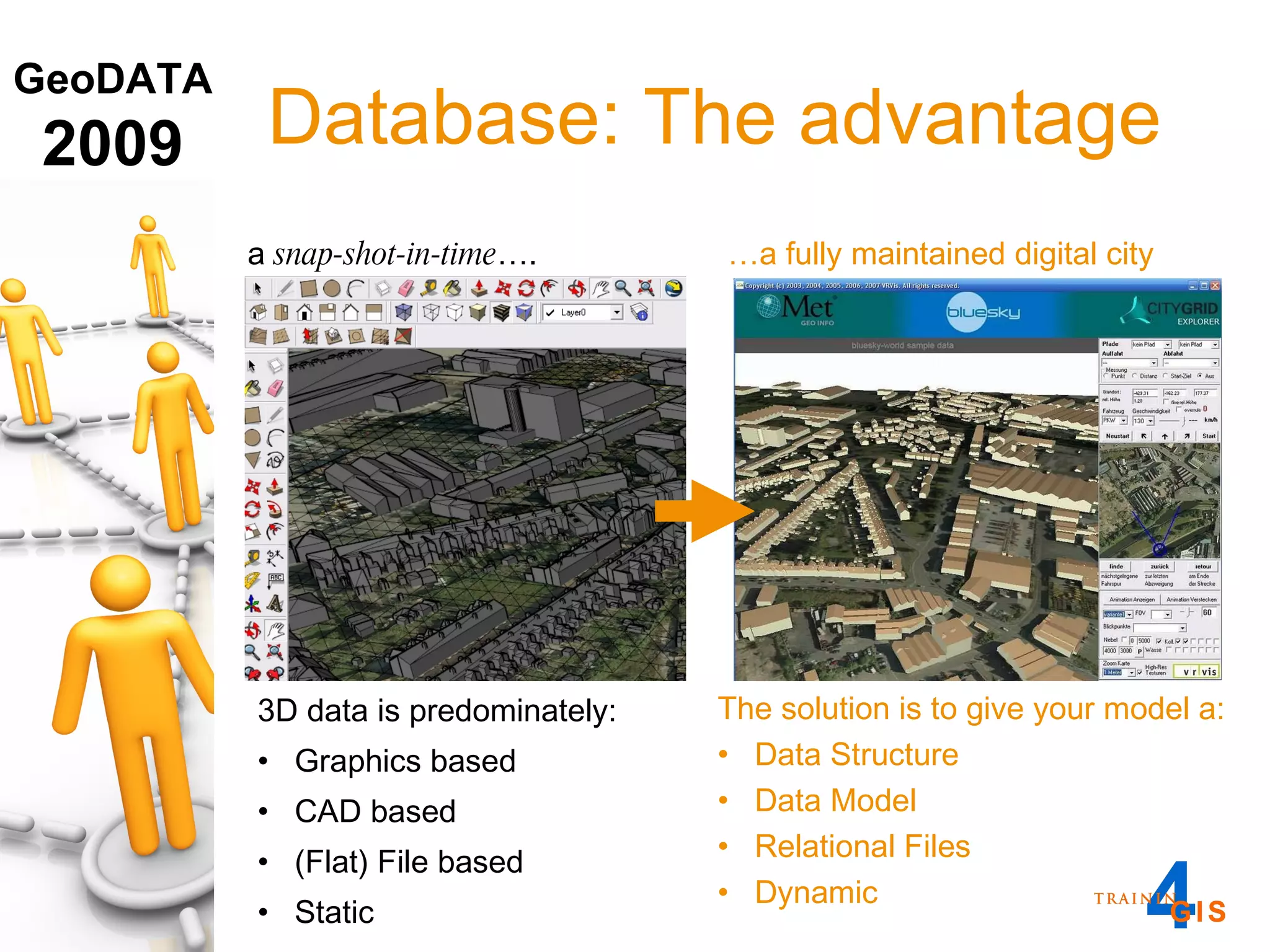
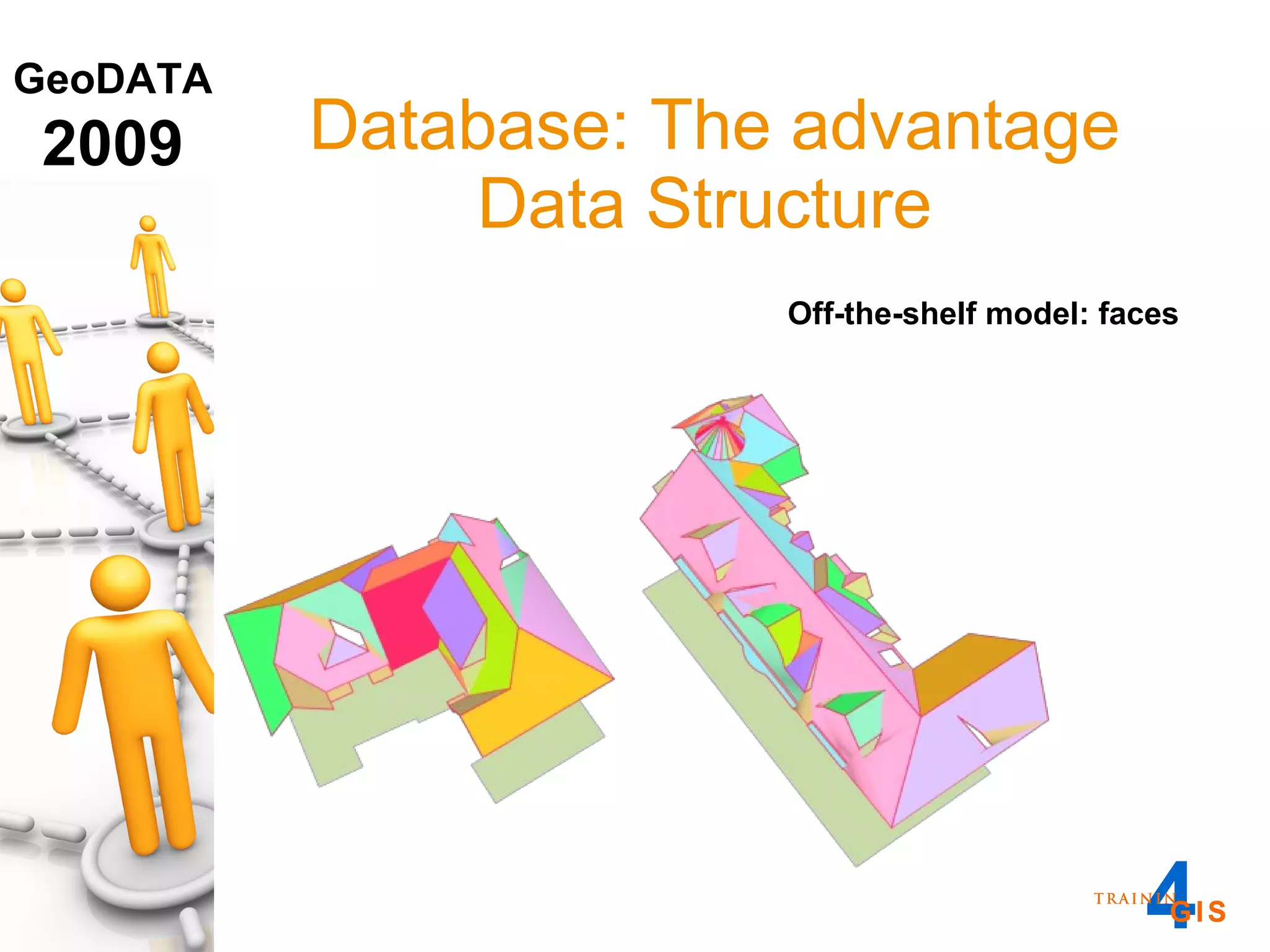
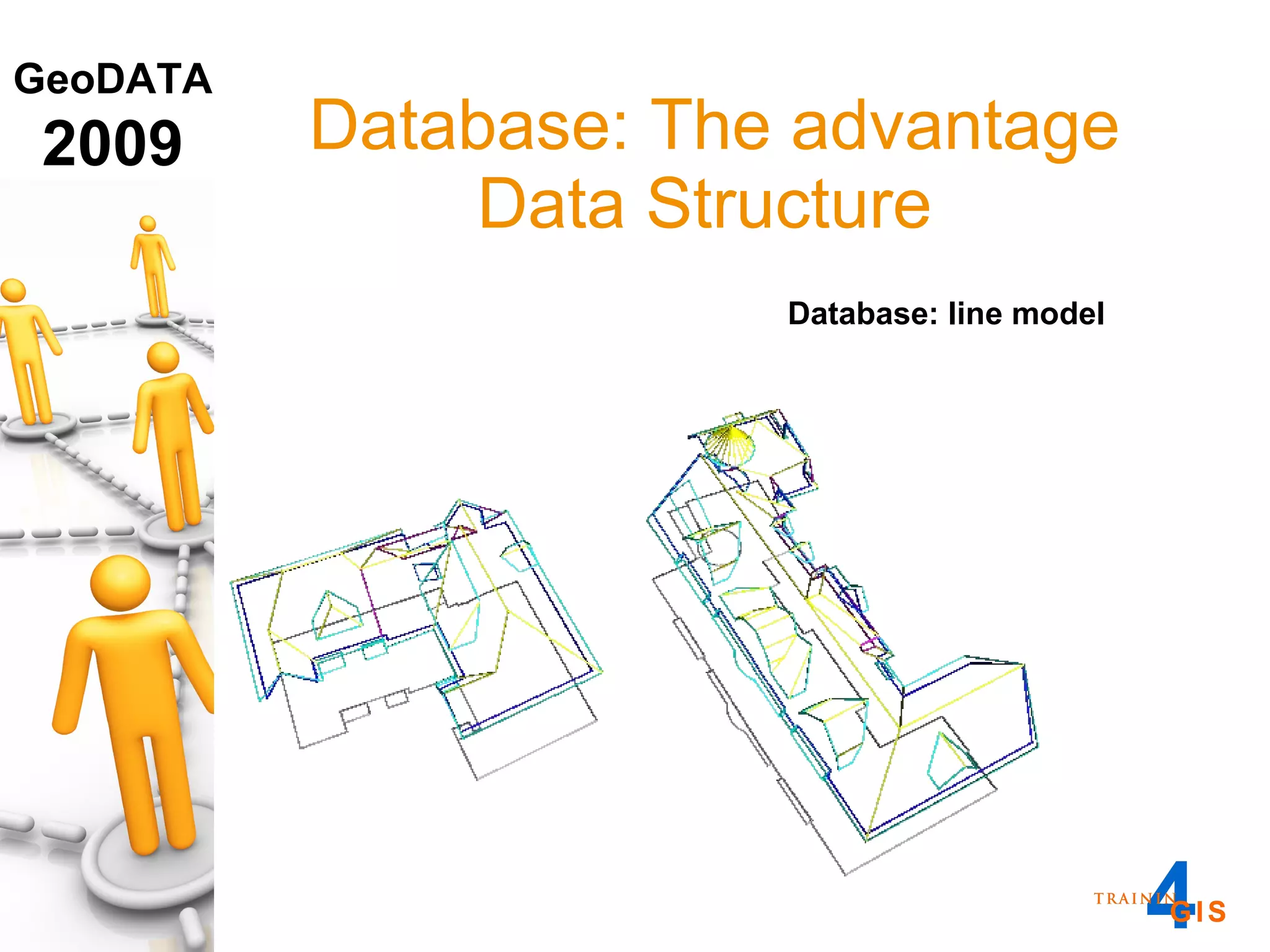
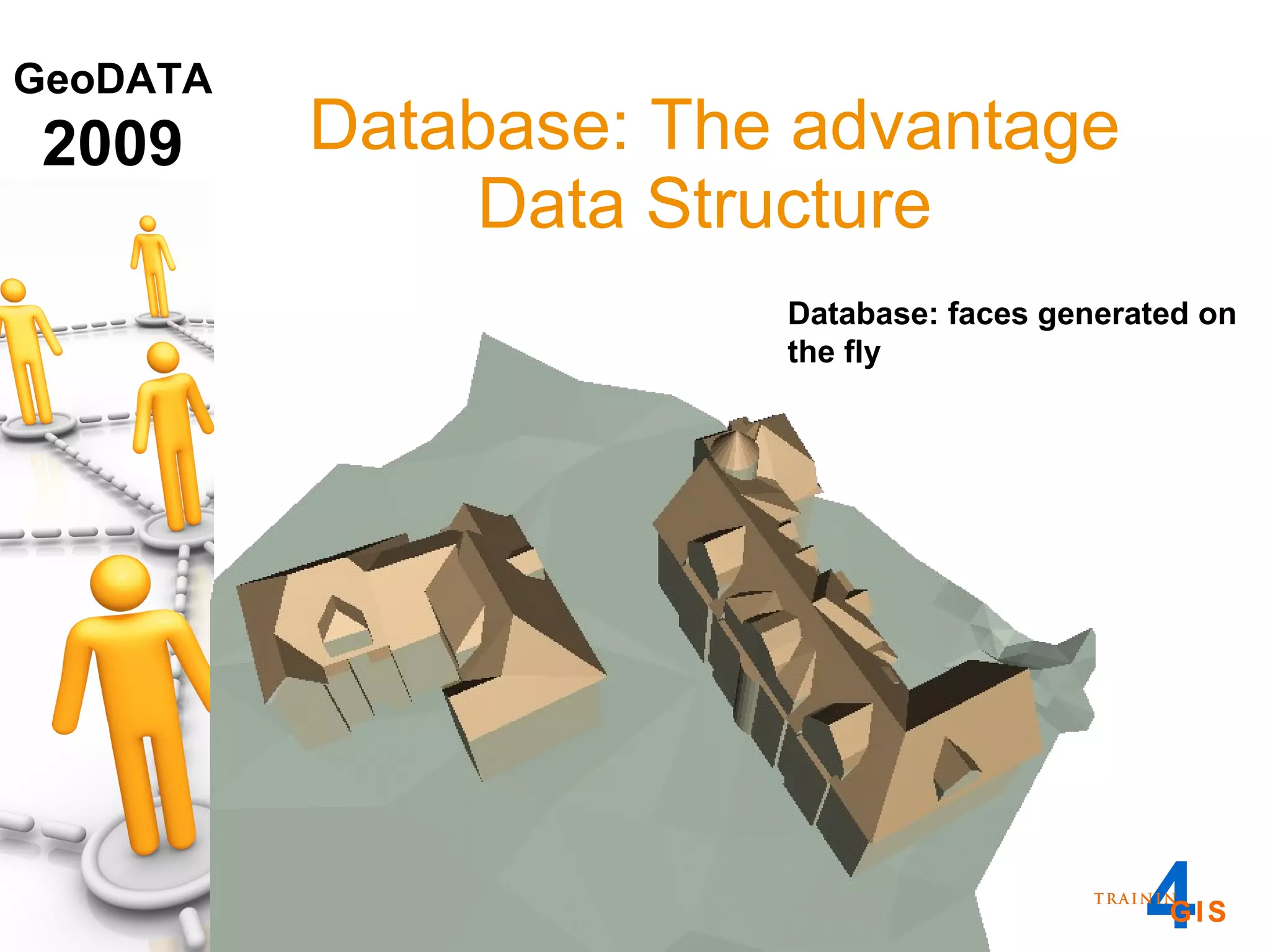
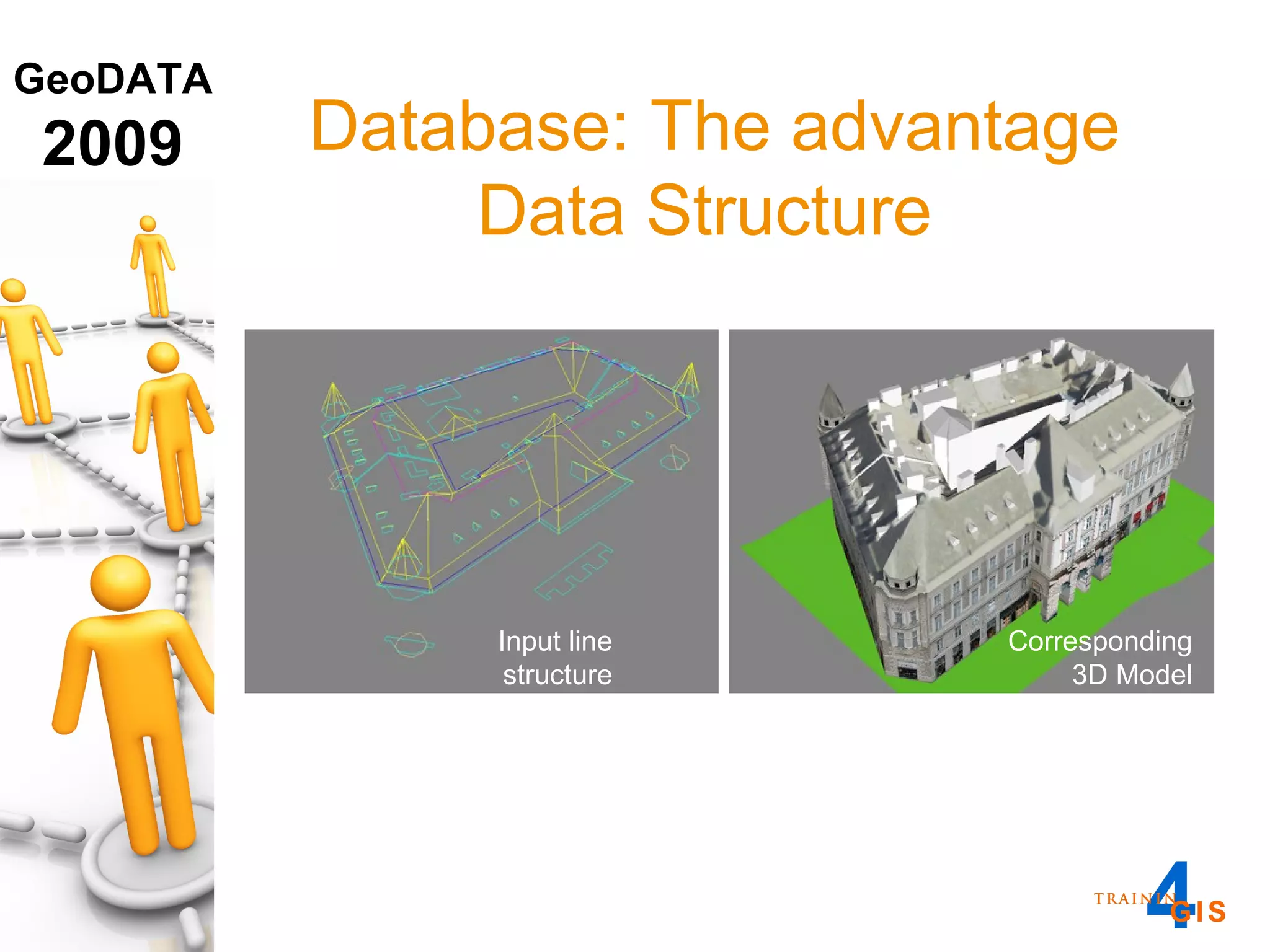
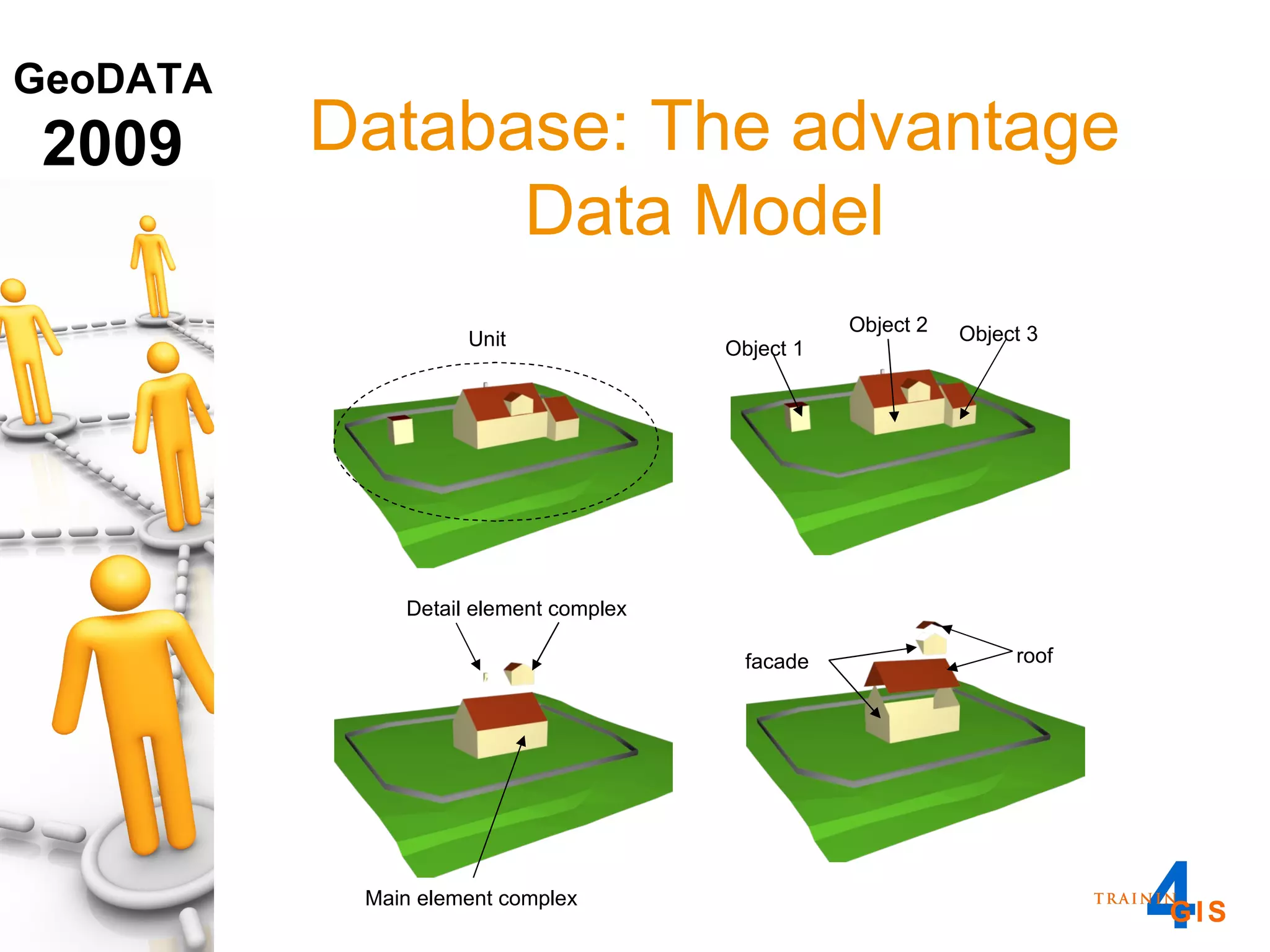
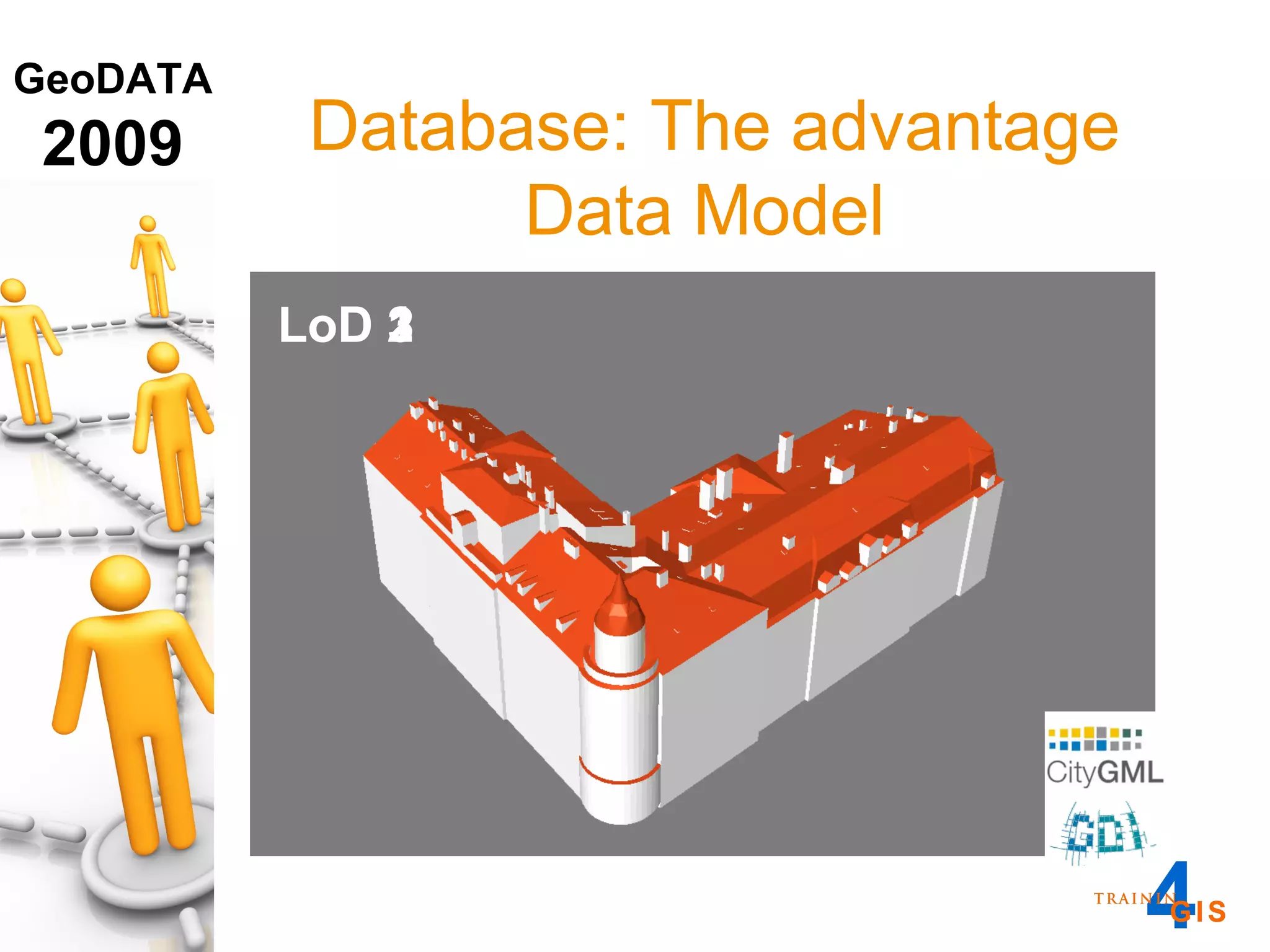
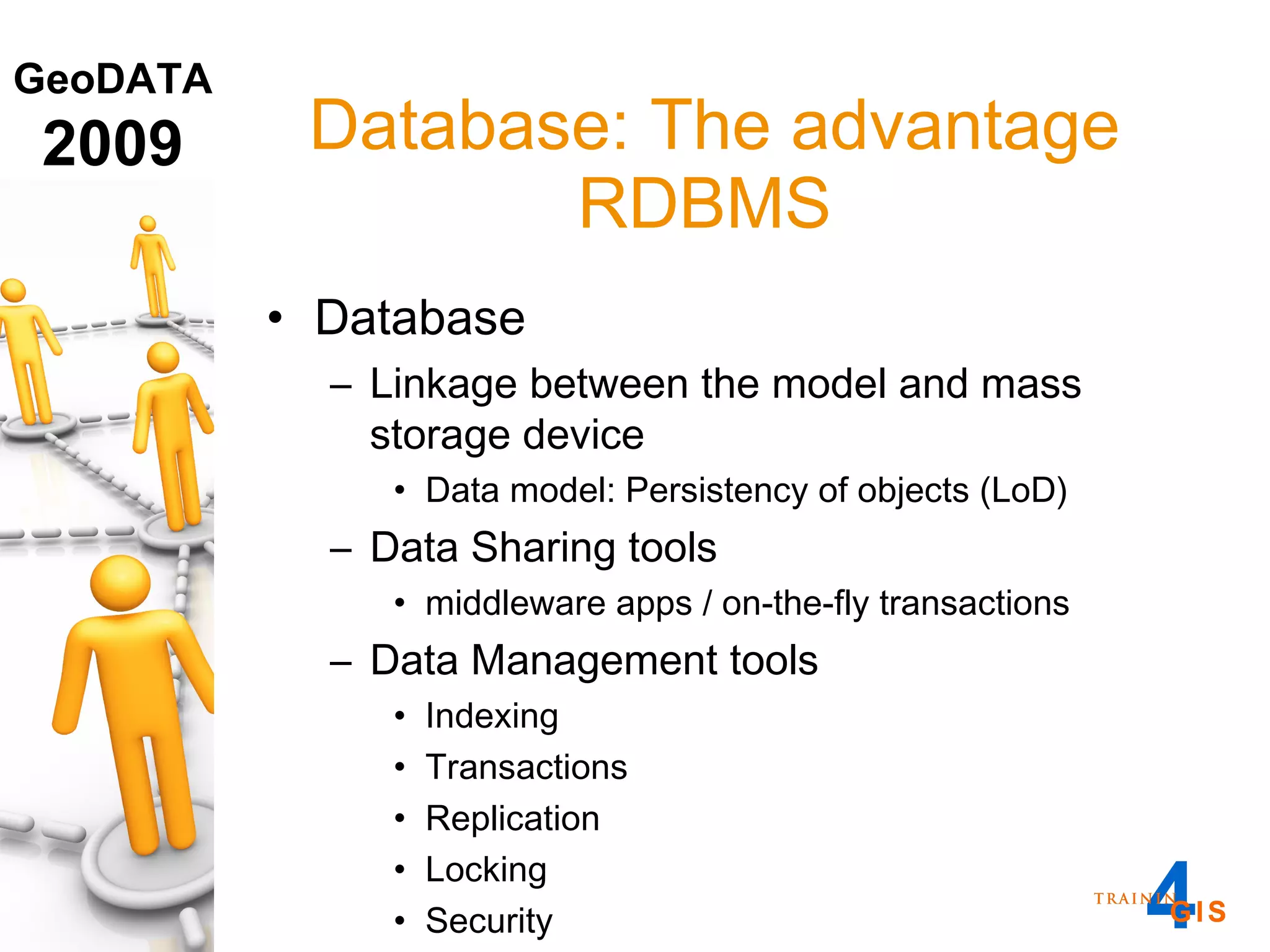
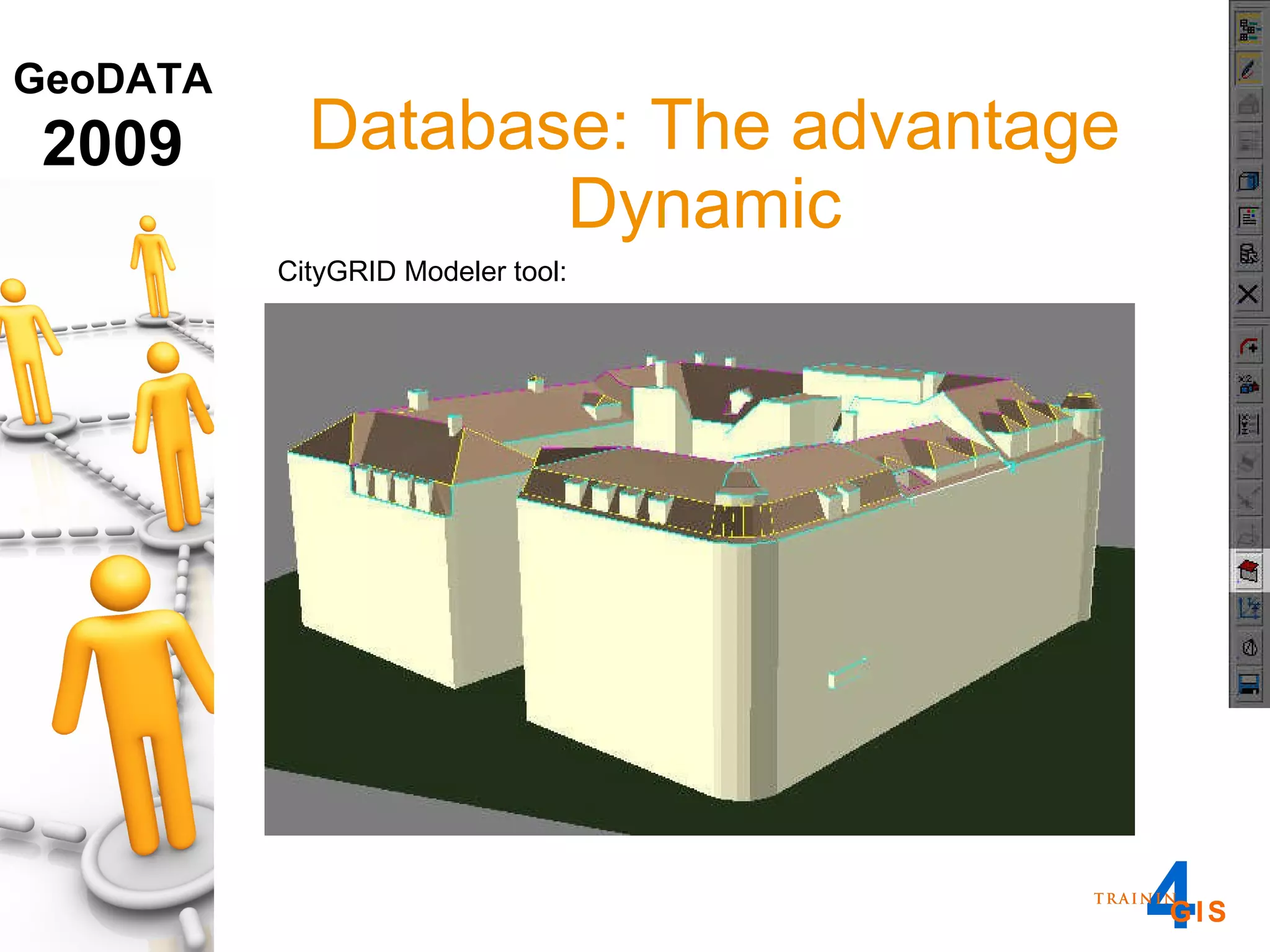
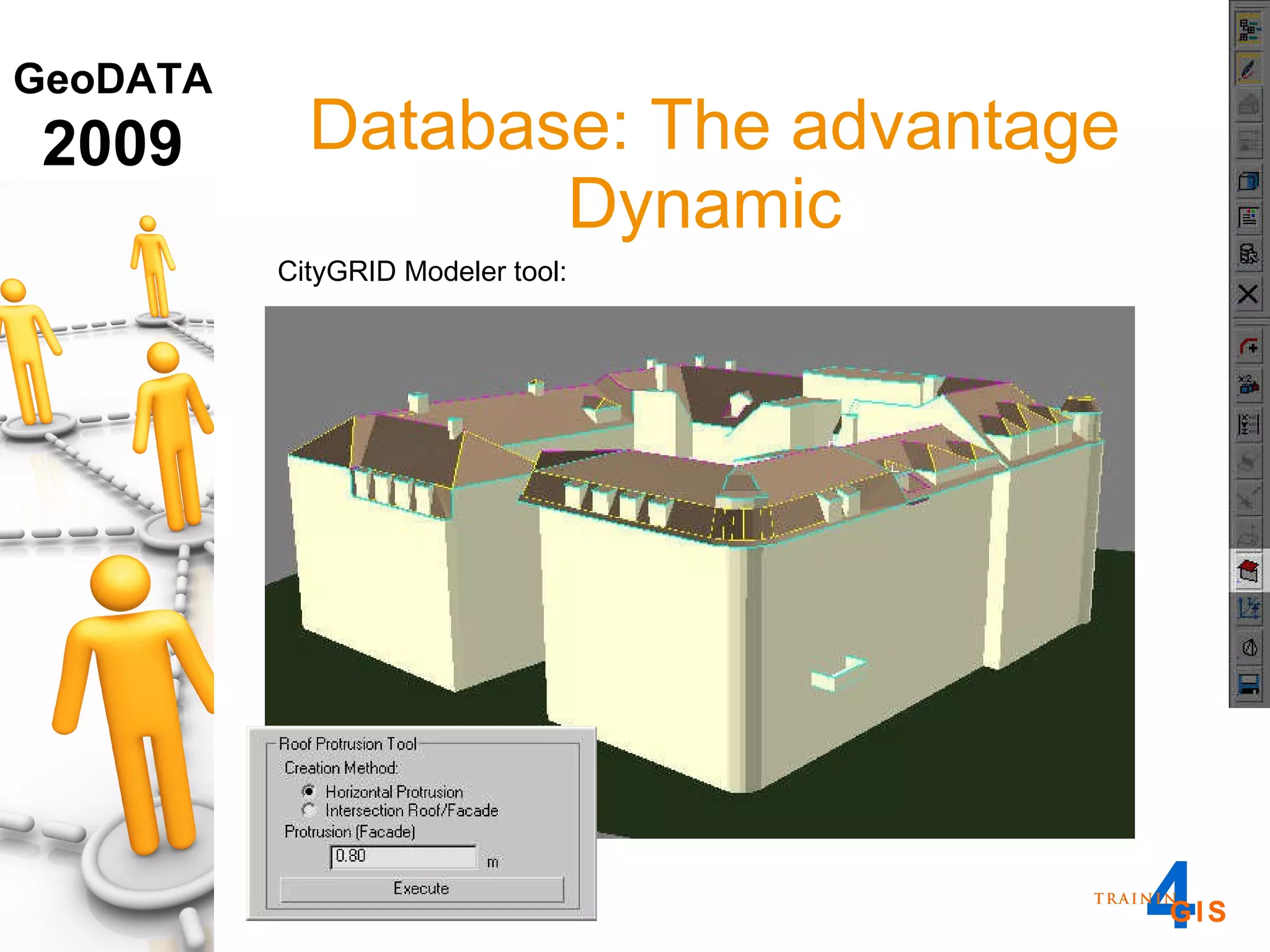
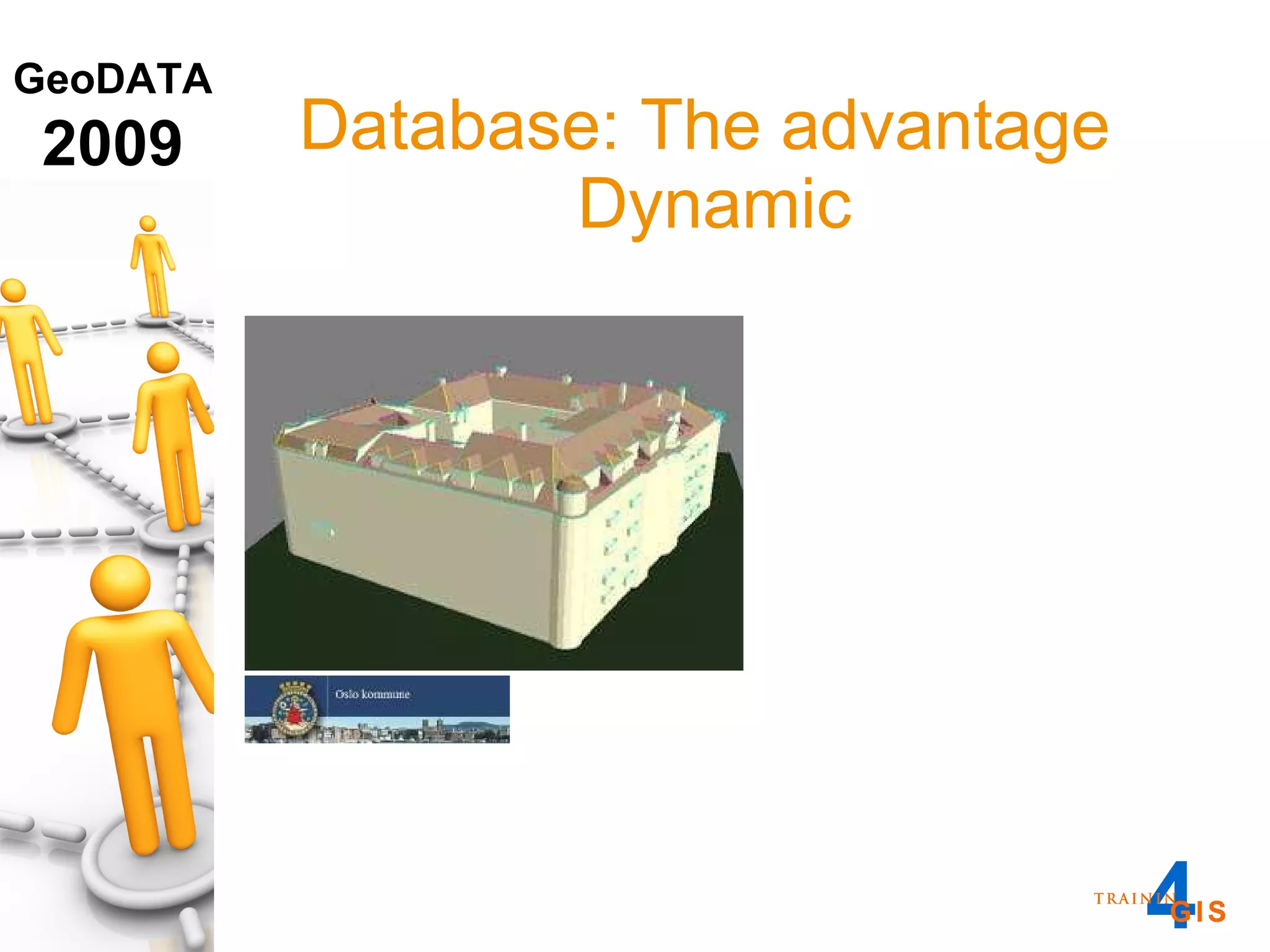
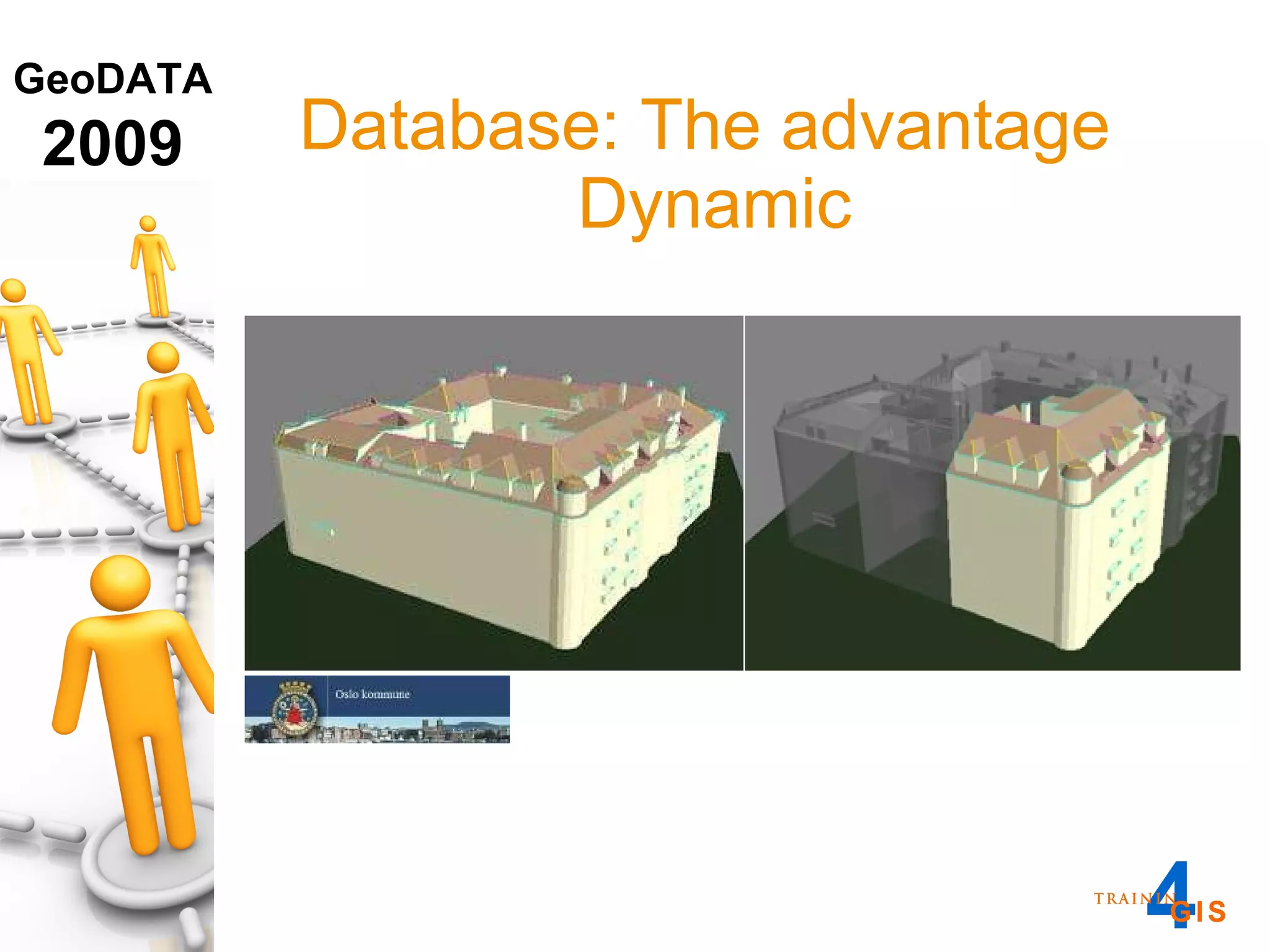
This document discusses the advantages of using a database model over file-based models for 3D city modeling. A database model provides a data structure, data model, and relational links that allow the city model to be dynamic, securely accessed and updated over time. This protects the investment in collecting the 3D data and saves money by facilitating ongoing use and management of the digital city model.