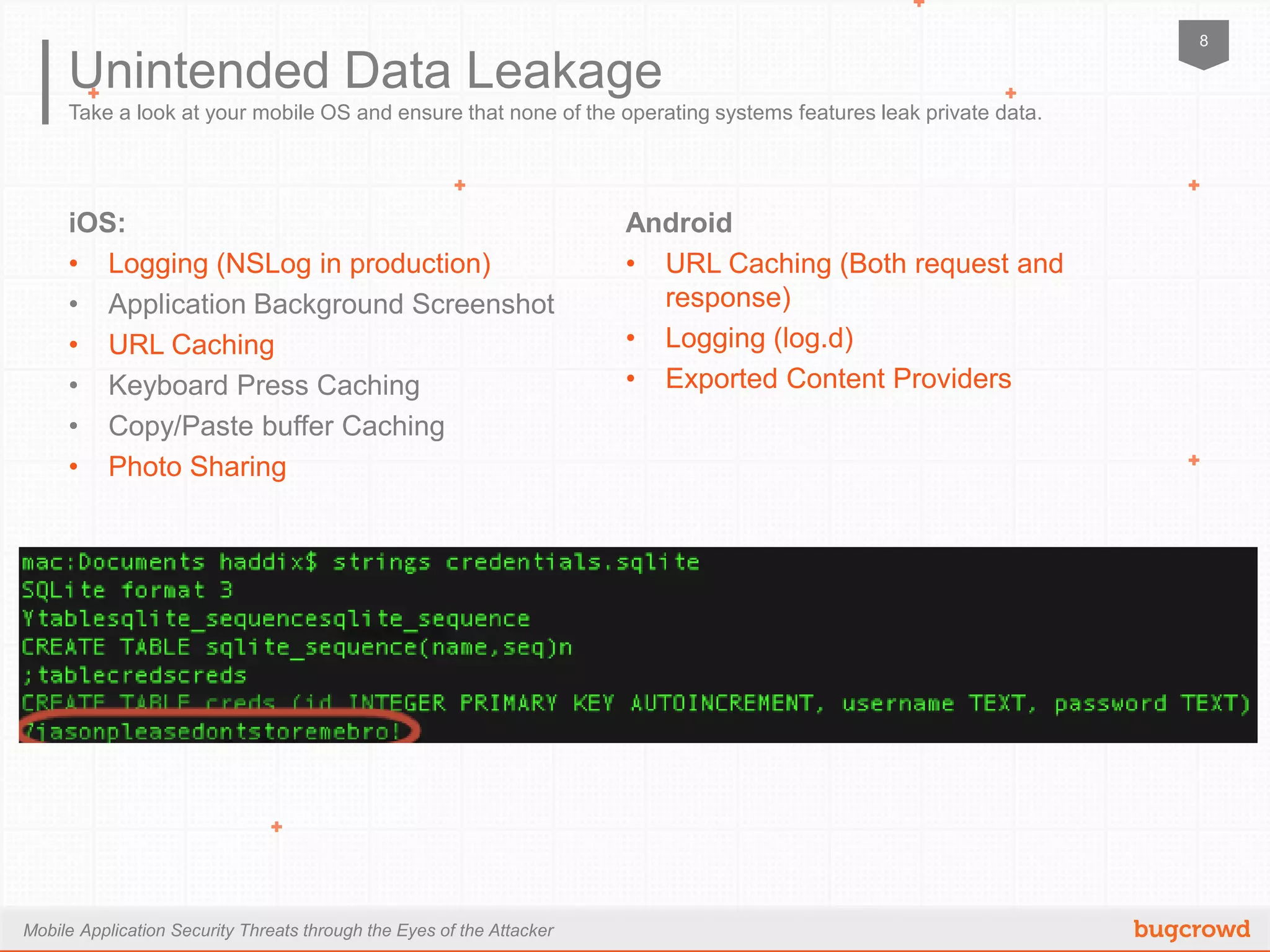
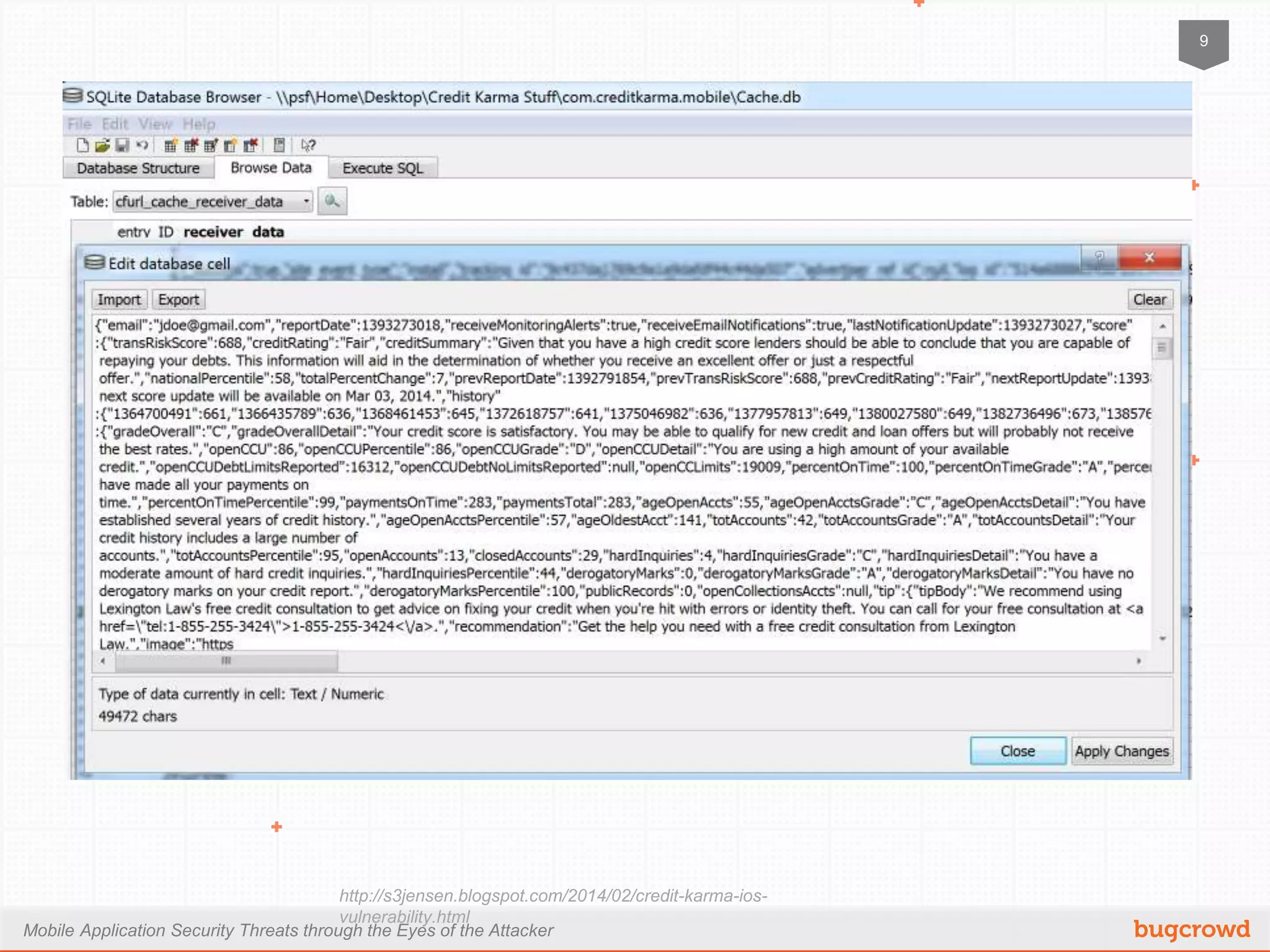
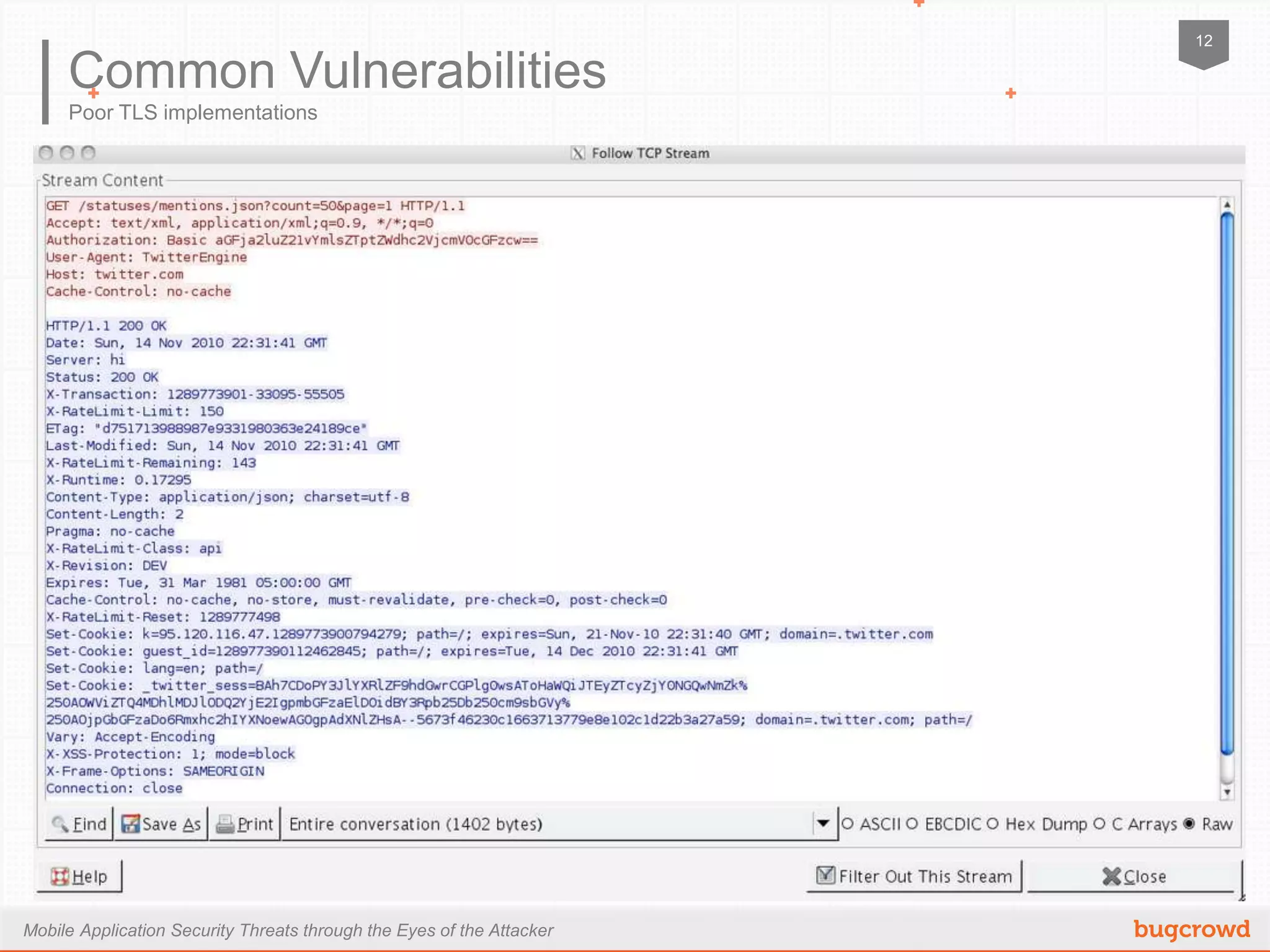
The document discusses mobile application security threats from an attacker's perspective, focusing on the growing adoption of mobile devices and the associated risks. Key points include the OWASP mobile top ten risks, secure data storage practices, traffic encryption, and server-side protections. It emphasizes the importance of thorough testing and utilizing available resources to enhance security in mobile applications.