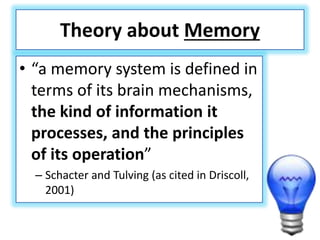
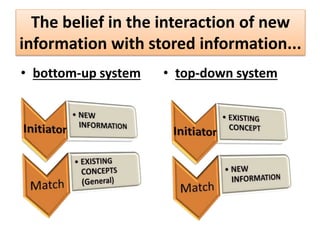
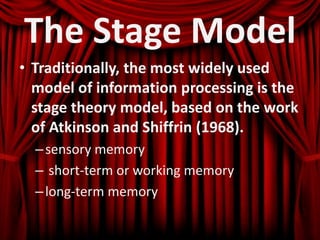
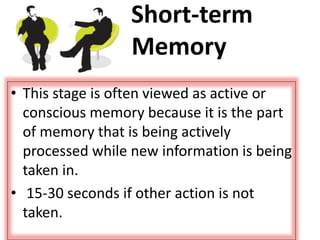
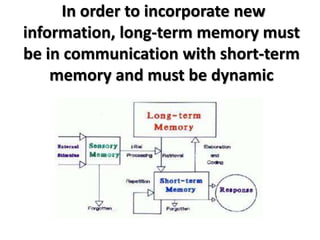
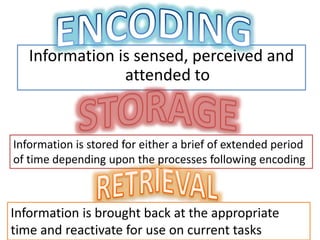
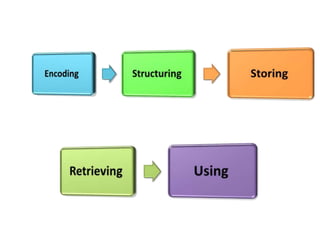
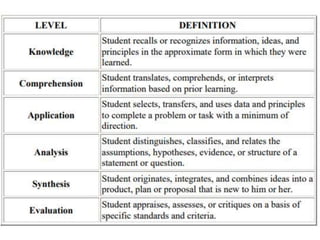
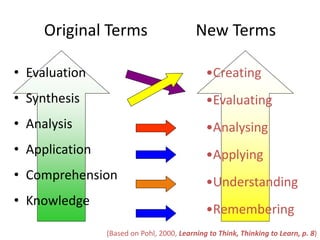
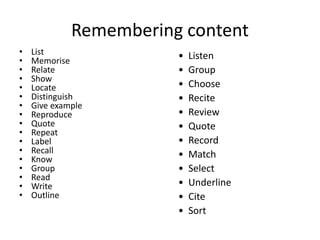
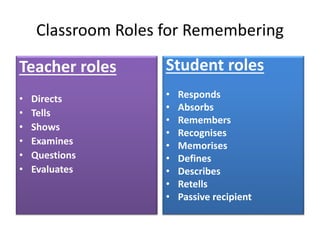
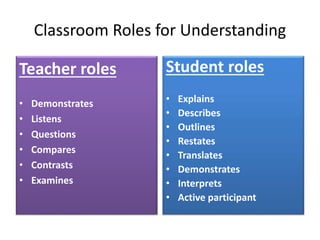
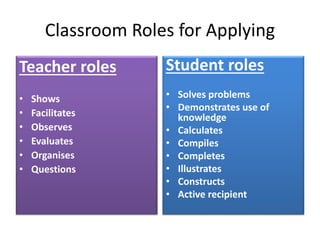
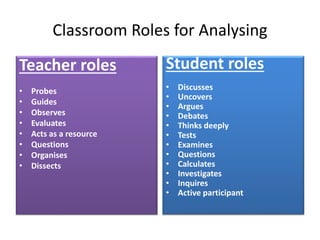
Here is an example of developing performance standards for a topic in language and communication development based on Bloom's New Taxonomy:
Topic: Listening comprehension
Remembering: The student can recall specific facts and details from an oral text.
Understanding: The student can summarize key ideas and events from an oral text in their own words.
Applying: The student can follow multi-step oral instructions to complete a task.
Analyzing: The student can identify the main idea and supporting details of an oral text and explain how they are related.
Evaluating: The student can critique an oral argument by identifying strong and weak points.
Creating: The student can synthesize information from multiple oral sources